Suppose you need to find a specific piece of data in a library that’s the measurement of a metropolis. It is a predicament that companies should take care of each day concerning their digital information. They comprise large portions of logs, paperwork, and consumer actions. Finding what’s essential is like looking for a needle in a digital haystack. That’s the place Elasticsearch matches in. Consider it as a potent magnet that may discover the required data in a mountain of information in a second.
Elasticsearch is a search and analytics engine that’s quick and scalable. It’s constructed to course of up to date information necessities at an exceptional tempo. We’re going to focus on its potent capabilities on this information. We are going to start with its typical energy in full-text search, which searches information utilizing exact key phrases. Then we’ll enter the realm of AI and its subtle vector search, which is aware of the which means of your queries.
To make these concepts a actuality, we’re going to undergo the development of a contemporary RAG app to develop smarter AI assistants. We may even construct a full ETL pipeline to know how uncooked information turns into helpful data. By the tip, you’ll perceive how Elasticsearch works and why builders and information analysts depend on it at present.
So, allow us to begin with the very fundamentals.
What’s Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch works like a extremely organized digital library. As an alternative of books, it shops information as versatile JSON paperwork. It’s based mostly on a sturdy open supply platform named Apache Lucene. This serves because the sooner engine, making each search extraordinarily quick. This design permits it to handle easy log information along with difficult and structured data with ease.
It’s utilized in quite a few methods by individuals. It could actually drive the search field in a web based retailer, real-time server logs to know what’s unsuitable with it, or it might probably develop interactive dashboards that characterize enterprise efficiency.
Elasticsearch Key Options
Let’s have a look at its key options.
- Full-text search: It’s the usual key phrase search, however made very clever. Elasticsearch divides the textual content into single phrases or tokens and indexes them on a particular map. That is just like the index put behind a e book that permits it to find paperwork together with your key phrases in close to real-time. It additionally permits such superior options as relevance rating to current the perfect outcomes first.
- Actual-time analytics: Elasticsearch shouldn’t be solely good at trying to find data. It could actually make you recognize of it because it arrives. Elasticsearch enables you to run complicated calculations like sums, averages, and histograms instantly inside search queries. This makes it perfect for constructing stay dashboards that observe web site site visitors or monitor software efficiency in actual time.
- Distributed and scalable: It’s constructed to scale. Elasticsearch doesn’t use a single, large server however distributes information and workloads amongst a bunch of servers. Think about it to be a puzzle the place each individual works on part of the puzzle. This allows it to scale to petabytes of information with milliseconds response occasions.
- Vector search: The function introduces the ability of AI to your information. Elasticsearch performs semantic and contextual searches by understanding the which means of search phrases, slightly than relying solely on key phrase matching. It’s the know-how of the up to date trendy semantic search and suggestion engines, and it’s a key to making a profitable RAG software.
All these traits mix to make sure that Elasticsearch is a single answer to nearly any information downside. It’s one trusted system to retailer, search, and analyze all of your data.
Full-Textual content vs. Vector Search
To get an actual really feel of Elasticsearch, it is very important have data of the 2 main search options of the product. They each have their objective, and the chance to intertwine them is the important thing to the ability of the platform.
Full-Textual content Search: The Energy of Key phrases
Consider a database of recipes that you’re looking via. Within the instance of typing within the search question of a garlic bread recipe, full-text search will scan the index of paperwork that comprise those self same phrases. It’s precise, word-for-word, and it’s exceptionally efficient in finding explicit data. It’s good when you’ve gotten the phrases that you’re trying to find.
Right here is an easy instance. First, you add a doc to Elasticsearch:
{
"title": "Straightforward Garlic Bread",
"elements": "Bread, garlic, butter, parsley"
}
Then, you run a full-text search question:
{
"question": {
"match": { "elements": "garlic butter" }
}
}This question is quickly despatched by the recipe being the phrases “garlic” and Butter are there within the elements discipline. That is the perfect search approach in logs, authorized paperwork, or another textual content through which key phrases are important.
Vector Search: The Artwork of That means
Now, suppose that you simply search for the identical recipe database however put in savory facet for pasta. A key phrase search may fail. That is the place the ability of vector search is seen. It is aware of what you imply by your question. It understands that garlic bread is a savory facet dish, often served with pasta.
The idea of vector search is that textual content is remodeled right into a numerical type generally known as an embedding. That is the semantic which means of the textual content, which is captured by this vector. Your question can be remodeled right into a vector. Elasticsearch then identifies the paperwork with vectors nearest to that of your question.
You start with a mapping that accommodates these vectors:
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"description": { "sort": "textual content" },
"description_vector": { "sort": "dense_vector", "dims": 384 }
}
}
}
Then, you may carry out a k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) search to search out probably the most related outcomes by which means:
{
"knn": {
"discipline": "description_vector",
"query_vector": [0.12, -0.45, 0.89, ...],
"okay": 5
}
}The true energy of Elasticsearch is that it might probably do hybrid searches, balancing the search accuracy of full-text search with the context-awareness of vector search.
Constructing a Easy RAG Utility utilizing Elasticsearch
Massive language fashions (LLMs) are highly effective, however they’ve a transparent limitation: they solely know what they had been educated on and might generally hallucinate. Retrieval-Augmented Technology (RAG) addresses this downside by grounding responses in exterior, up-to-date information. A RAG software will provide the LLM with up-to-date and related data from a reputable supply previous to the creation of a solution. It’s as if the AI will get an open-book take a look at.
The most effective e book on the topic to cross this examination is Elasticsearch because of its fast and exact search. A RAG software operates within the following approach:
- Person Question: A consumer asks a query, like “How do I reset my password?”
- Retrieve Context: Elasticsearch searches its doc index for data associated to password resets. This can be a full-text search of key phrases or an try to look utilizing semantic which means as a vector.
- Increase Immediate: Elasticsearch finds probably the most related paperwork and combines them with the preliminary question right into a immediate with extra particulars for the LLM.
- Generate Reply: The consumer is offered with the immediate and requested: “Reply the query posed by the consumer with the assistance of the given paperwork solely. This bases the mannequin on factual information in responding.
This workflow ensures the solutions are correct, present, and reliable.
Elasticsearch in RAG Utility
Now, allow us to discover a simplified Python instance exhibiting the retrieval step of a RAG software.
1. First, create a free Elastic Cloud deployment.
Go to https://cloud.elastic.co
Begin a free trial.
Now copy the ENDPOINT and API KEY from the highest proper nook.
2. Now, let’s begin with putting in the Elastic Search library
!pip set up elasticsearch3. Connect with Elasticsearch
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch, helpers
shopper = Elasticsearch(
“https://my-elasticsearch-project-da953b.es.us-central1.gcp.elastic.cloud:443”,
api_key=”YOUR_API_KEY”
)
This connects the pocket book to an Elastic Serverless challenge. The URL factors to your cloud deployment. The API key permits approved entry.
4. Now, create an Index
# -----------------------------
# Outline the index title and create index (if it would not exist)
# -----------------------------
index_name = "national-parks"
if not shopper.indices.exists(index=index_name):
create_response = shopper.indices.create(index=index_name)
print("Index created:", create_response)
else:
print(f"Index '{index_name}' already exists.")Output:

An index is sort of a database desk. This block checks whether or not the index already exists. If not, it creates one. This offers you a spot to retailer paperwork.
5. Now add a semantic_text discipline
# -----------------------------
# Add or replace mappings for the index
# -----------------------------
mappings = {
"properties": {
"textual content": {
"sort": "semantic_text"
}
}
}
mapping_response = shopper.indices.put_mapping(
index=index_name,
physique=mappings
)
print("Mappings up to date:", mapping_response) Output:

The mapping tells Elasticsearch how you can analyze every discipline. The semantic_text sort prompts Elasticsearch’s built-in machine studying mannequin. While you later insert textual content into this discipline, Elasticsearch produces vector embeddings robotically and shops them for semantic search. You do not want to make use of your personal embedding mannequin.
6. Let’s add paperwork to the database
# -----------------------------
# Pattern paperwork to ingest
# -----------------------------
docs = [
{
"text": "Yellowstone National Park is one of the largest national parks in the United States. It ranges from the Wyoming to Montana and Idaho, and contains an area of 2,219,791 acres across three different states. Its most famous for hosting the geyser Old Faithful and is centered on the Yellowstone Caldera, the largest super volcano on the American continent. Yellowstone is host to hundreds of species of animal, many of which are endangered or threatened. Most notably, it contains free-ranging herds of bison and elk, alongside bears, cougars and wolves. The national park receives over 4.5 million visitors annually and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site."
},
{
"text": "Yosemite National Park is a United States National Park, covering over 750,000 acres of land in California. A UNESCO World Heritage Site, the park is best known for its granite cliffs, waterfalls and giant sequoia trees. Yosemite hosts over four million visitors in most years, with a peak of five million visitors in 2016. The park is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including mule deer, black bears, and the endangered Sierra Nevada bighorn sheep. The park has 1,200 square miles of wilderness, and is a popular destination for rock climbers, with over 3,000 feet of vertical granite to climb. Its most famous and cliff is the El Capitan, a 3,000 feet monolith along its tallest face."
},
{
"text": "Rocky Mountain National Park is one of the most popular national parks in the United States. It receives over 4.5 million visitors annually, and is known for its mountainous terrain, including Longs Peak, which is the highest peak in the park. The park is home to a variety of wildlife, including elk, mule deer, moose, and bighorn sheep. The park is also home to a variety of ecosystems, including montane, subalpine, and alpine tundra. The park is a popular destination for hiking, camping, and wildlife viewing, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site."
}
]These paperwork are plain textual content. Every doc describes a nationwide park. Elasticsearch will convert every textual content entry right into a semantic embedding internally.
7. Now bulk ingest the created docs
# -----------------------------
# Bulk ingest paperwork
# -----------------------------
ingestion_timeout=300 # Permit time for semantic ML mannequin to load
bulk_response = helpers.bulk(
shopper.choices(request_timeout=ingestion_timeout),
docs,
index=index_name,
refresh="wait_for" # Wait till listed paperwork are seen for search earlier than returning the response
)
print(bulk_response)Output:
Bulk indexing is quicker than sending paperwork one by one. The timeout is elevated to offer Elasticsearch time to load the built-in mannequin on first use. The refresh possibility makes certain the paperwork are searchable earlier than the operate returns.
8. Now, let’s run a semantic search and take a look at it
# -----------------------------
# Outline semantic search question
# -----------------------------
retriever_object = {
"normal": {
"question": {
"semantic": {
"discipline": "textual content",
"question": "Sierra Nevada"
}
}
}
}
search_response = shopper.search(
index=index_name,
retriever=retriever_object,
)
show(search_response['hits']['hits'])Output:
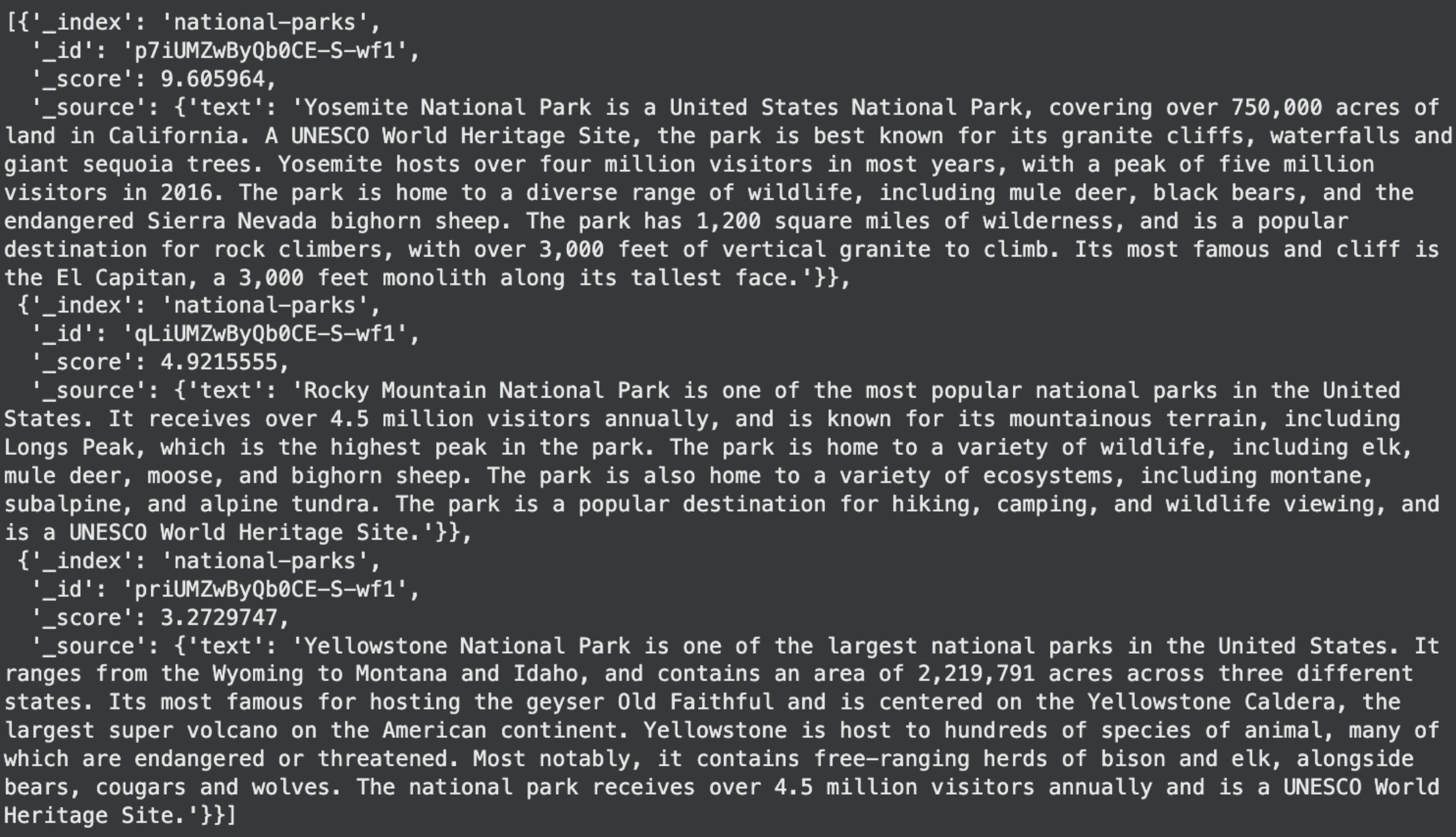
That is the retrieval step in a RAG pipeline. The question “Sierra Nevada” shouldn’t be a key phrase search. Elasticsearch creates an embedding for the question and compares it to the saved doc embeddings. It then returns the doc that’s semantically closest. On this case, the Yosemite doc mentions the Sierra Nevada area, so it turns into the highest match.
From right here, the retrieved textual content turns into the context on your language mannequin. The mannequin reads the retrieved doc together with the consumer’s query and produces a grounded, factual reply.
Elasticsearch vs. Devoted Vector Databases
There are quite a few specialised vector databases which were developed with the event of AI. The query that comes up then is when to think about using Elasticsearch or a devoted vector database? Think about the dilemma of a multi-purpose software versus an influence noticed of a really particular nature.
- Elasticsearch is a multi-purpose multi-tool. It’s the perfect choice within the occasion that your software requires greater than merely looking by vectors. In case you want strong key phrase filtering, log evaluation, safety, and interactive dashboards, Elasticsearch offers all the built-in bundle. When coping with a single system, it’s generally simpler and cheaper to handle than making an attempt to make use of many specialised instruments.
- The specialised energy noticed is named a vector database. These instruments are designed with a single goal, which is conducting the seek for similarity of vectors at excessive velocities and huge scales. A specialised vector database might present the bottom doable latency in case your core software is a real-time suggestion engine to thousands and thousands of customers.
One business comparability states that Elasticsearch is optimized towards textual content search and analytics, whereas vector databases are scaled in the direction of ultrafast search by vector similarity. Elasticsearch is the extra smart and extra highly effective alternative in most tasks that require a mix of the search sorts.
ETL Pipeline with the Elastic Stack
Uncooked information is often sloppy and disordered. It needs to be cleaned, processed, and loaded right into a system akin to Elasticsearch earlier than it may be analyzed. That is known as an ETL (Extract, Rework, Load). The Elastic Stack is an easy-to-build one.
The important thing gamers on this ETL pipeline are:
- Logstash (The Manufacturing facility Employee): It extracts information from numerous sources like information, databases, or message queues. It then transforms the info by parsing it into structured fields, enriching it with further data, and cleansing it up.
- Elasticsearch (The Warehouse): That is the place the remodeled, structured information is loaded and listed. As soon as inside, it’s prepared for high-speed search and evaluation.
- Kibana (The Showroom): That is the visualization layer. Kibana connects to Elasticsearch and permits you to discover your information, create charts and graphs, and construct interactive dashboards with only a few clicks.
Conclusion
We began our journey with an enormous, digital haystack to hunt what we wish, and got here throughout a powerful magnet. Elasticsearch is that magnet. It has been far more than only a mere search field. It’s an end-to-end platform that artfully combines the old school approach of looking with key phrases and the sensible and context-aware world of AI.
We might observe its two strengths: the power to look via the textual content and extract particular data, in addition to the power to look by which means and the ability of a vector search. We understood how all these options are mixed with a view to create the clever and trusted RAG software, which assures the factual and helpful solutions given by AI assistants. One other software that we have now constructed is a secure ETL pipeline, which permits us to transform uncooked information into clear and actionable information utilizing the Elastic Stack.
So, it’s straightforward to see how Elasticsearch is a scalable, common, and demanding information answer to up to date issues. It’s the foundation of making your first search with or with no complicated AI system as a result of it offers you the muse to rework information into discovery.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
Elasticsearch is primarily utilized in fast looking and knowledge analytics. It drives web site search engines like google and yahoo, software monitoring and enterprise intelligence dashboard.
Sure, the core Elasticsearch software program is open-source and free. Elastic, the corporate behind it, provides paid subscriptions for superior options and official help.
Elasticsearch is geared in the direction of search and evaluation of text-based information that’s massive in scale. The standard databases are often constructed to retailer and management structured, transactional information.
The builders can talk with it via an API, whereas applications akin to Kibana are a graphical interface. This allows an individual to look, discover information, and analyze information with out coding.
ELK Stack (or Elastic Stack) is comprised of Elastic, Logstash, and Kibana. They collaborate and give you a holistic answer to information ingestion, storage, evaluation, and visualization.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.

![What’s Elasticsearch? [A Beginner’s Guide 2026] What’s Elasticsearch? [A Beginner’s Guide 2026]](https://i1.wp.com/cdn.analyticsvidhya.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Introduction-to-Elasticsearch-A-Beginners-Guide-1.png?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)
