Need to communicate at AMA: Vitality 2025 or AMA: Automotive & Mobility 2025? Submit your utility now!
Researchers from J. Stefan Institute and the College of Ljubljana in Slovenia have achieved a scientific first by 3D printing tiny useful constructions straight inside dwelling cells.
Utilizing a high-precision laser approach referred to as two-photon polymerization (2PP), they created customized polymer microstructures together with microlasers, monitoring barcodes, and even a ten µm mannequin of an elephant, all throughout the cytoplasm of dwelling HeLa cells.
Revealed in arXiv, the method permits these constructions to type in place with out harming the cell’s inside atmosphere, providing a brand new technique to engineer cells from the within out. The examine was led by Matjaž Humar, Physicist at J. Stefan Institute and College of Ljubljana, who conceived and supervised the undertaking.

Direct fabrication inside dwelling cells
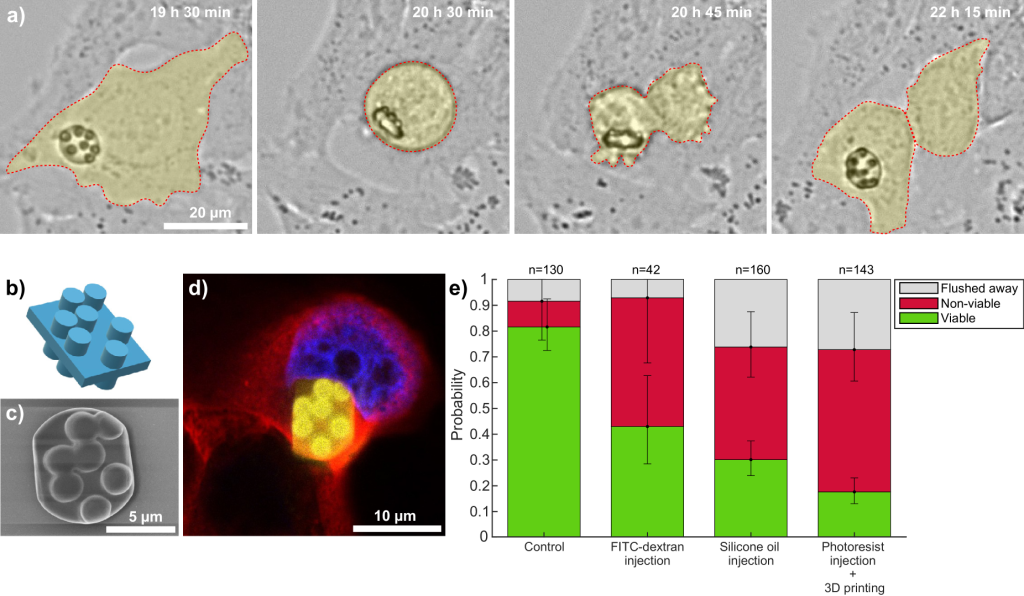
The method begins with the injection of a photoresist droplet into the cell, adopted by laser scanning to set off polymerization solely on the level of focus. Because the laser strikes via the droplet in a programmed sample, it creates a stable 3D construction whereas the remaining materials dissolves naturally. This methodology permits exact, in-situ fabrication of microdevices with out introducing exterior particles.
The researchers used the Photonic Skilled GT2 system from Nanoscribe for printing, which employs a femtosecond 780 nm laser fitted to submicron decision. For supplies, they examined a number of photoresists from the identical producer and chosen IP-S for its low toxicity and water solubility. A ten µm droplet sometimes dissolves inside a number of hours, giving a two-hour window to finish printing. Its compatibility in each liquid and stable varieties was crucial to sustaining mobile viability all through the method.
To know how the process affected cell well being, the group ran a 24-hour viability examine. Of the cells with printed constructions, 55 % remained alive. Cells injected with inert silicone oil confirmed 44 % viability, and people receiving solely buffer reached 50 %. Even untouched controls noticed 10 % cell loss of life, probably on account of prolonged dealing with. These figures recommend membrane penetration throughout injection was the principle supply of stress, not the constructions themselves.
In some circumstances, cells continued regular exercise, together with one which efficiently divided and handed the printed construction to a daughter cell. Confocal imaging confirmed that inside elements, together with the nucleus, tailored across the construction with out compromising integrity, demonstrating that cells may accommodate these overseas components with out instant disruption.
To evaluate potential distortion attributable to the curved droplet, the group used simulations and microscopy. Laser focus shift was restricted to 0.5 µm, and over 90 % of the droplet quantity maintained decision finer than 400 nm. Scanning electron microscopy confirmed structural constancy, with printed options as small as 260 nm, approaching the decision of bulk printing.
The researchers demonstrated how these prints might be utilized in real-world functions by creating 3D barcodes composed of stacked 4 × 4 grids, enabling 61 bits of information per construction, greater than sufficient to uniquely tag each cell within the human physique. These predesigned codes enable constant labeling and long-term monitoring in advanced organic research.
In addition they printed diffraction gratings inside cells, which produced distinct light-scattering patterns when illuminated. As a result of the diffraction profile is dependent upon construction geometry and orientation, these prints allowed distant optical readout of cell place or rotation. The group then produced microlasers by printing high-refractive-index, dye-doped photoresist droplets. These 9 µm resonators emitted laser mild when excited however have been considerably extra poisonous, with 80 % of cells dying or visibly burdened inside 22 hours.
Although present limitations embrace materials toxicity and cell loss from injection, the method opens promising instructions. Constructions might be designed to work together mechanically with organelles, alter cell form, or isolate particular areas of the cytoplasm. Researchers may probe biochemical pathways, simulate illness circumstances, or introduce instruments for sensing and sign processing fully from throughout the cell.
This method avoids the restrictions of particle ingestion, which solely works for sure cell varieties and sometimes traps materials inside vesicles. By constructing straight within the cytoplasm, scientists achieve entry to a broader vary of cells and larger management over the place and the way artificial constructions work together with native biology.

2PP’s rising position in biomedicine
Two-photon polymerization is more and more turning into a go-to methodology for fabricating high-resolution microstructures within the medical subject.
Excessive-resolution micro-scale 3D printing firm UpNano GmbH developed UpFlow, a photopolymer designed for 2PP, enabling quick and exact fabrication of micro-environments for embryo tradition.
Working with Australian IVF specialist Fertilis, the fabric was used with the NanoOne 3D printer to supply a 3D printed system that includes 0.05 mm constructions that mixed fertilization, embryo tradition, and cryopreservation in a single unit. This streamlined method lowered the necessity for handbook embryo dealing with and lower manufacturing time from two weeks to only 4 hours. The system additionally lowered implantation cycles by 30-40 %, whereas making certain optical readability and environment friendly post-processing of effective microchannels.
Elsewhere, Aston College built-in the Quantum X bio 3D printer to advance its biomedical analysis capabilities via 2PP. Designed for high-precision fabrication, the system allowed researchers to duplicate advanced cell orientations present in organs just like the mind and liver.
It supported research on astrocyte habits, the blood-brain barrier, comfortable liver tissue fashions, and drug supply mechanisms. Housed in a specifically managed atmosphere, the printer marked the primary UK set up of its form and shaped a part of broader efforts in tissue engineering and drug discovery throughout a number of analysis departments.
What 3D printing developments must you be careful for in 2025?
How is the way forward for 3D printing shaping up?
To remain updated with the most recent 3D printing information, don’t overlook to subscribe to the 3D Printing Business e-newsletter or observe us on Twitter, or like our web page on Fb.
Whilst you’re right here, why not subscribe to our Youtube channel? That includes dialogue, debriefs, video shorts, and webinar replays.
Featured picture exhibits a confocal picture of a ten µm elephant printed inside a stay HeLa cell. Picture through J. Stefan Institute.


