Discover ways to make rounded corners for UIImageView gadgets wrapped inside assortment view cells, with rotation help.
Round cells inside a group view
Attaining the aim is comparatively simple, however if you happen to don’t know what’s occurring within the background it’s going to be tougher than you’ll assume first. So let’s create a brand new undertaking add a storyboard with a UICollectionViewController, drag a UIImageView contained in the cell, resize it, add some constraints, set the cell identifier.
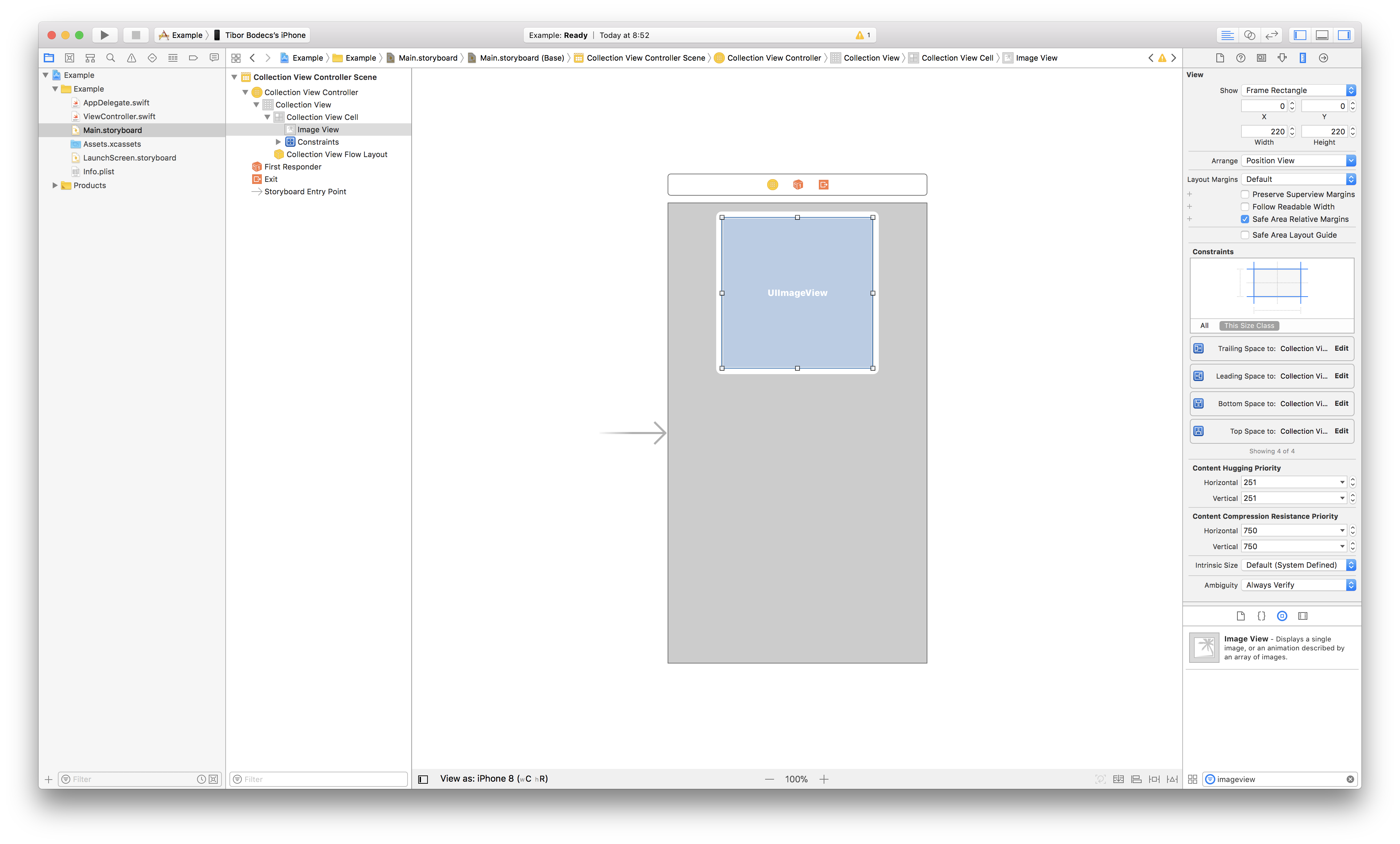
It ought to look one thing just like the picture above. Nothing particular only a easy UI for our instance utility. Now seek for some random picture, add it to the undertaking and let’s do some actual coding. First I’ll present you the little trick inside the cell subclass.
class Cell: UICollectionViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var imageView: UIImageView!
override var bounds: CGRect {
didSet {
layoutIfNeeded()
}
}
override func awakeFromNib() {
tremendous.awakeFromNib()
imageView.layer.masksToBounds = true
}
override func layoutSubviews() {
tremendous.layoutSubviews()
setCircularImageView()
}
func setCircularImageView() {
imageView.layer.cornerRadius = CGFloat(
roundf(Float(imageView.body.dimension.width / 2.0))
)
}
}
Are you able to see it? Sure, it’s best to override the bounds property. As the following step now we have to jot down the controller class with some fundamental information supply for the gathering view and with the correct help for the rotation strategies. 🤓
class ViewController: UICollectionViewController {
override func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
numberOfItemsInSection part: Int
) -> Int {
30
}
override func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath
) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(
withReuseIdentifier: "Cell",
for: indexPath
) as! Cell
cell.imageView.picture = UIImage(named: "Instance.jpg")
cell.imageView.backgroundColor = .lightGray
return cell
}
override func traitCollectionDidChange(
_ previousTraitCollection: UITraitCollection?
) {
tremendous.traitCollectionDidChange(previousTraitCollection)
guard
let previousTraitCollection = previousTraitCollection,
traitCollection.verticalSizeClass != previousTraitCollection.verticalSizeClass ||
traitCollection.horizontalSizeClass != previousTraitCollection.horizontalSizeClass
else {
return
}
collectionView?.collectionViewLayout.invalidateLayout()
collectionView?.reloadData()
}
override func viewWillTransition(
to dimension: CGSize,
with coordinator: UIViewControllerTransitionCoordinator
) {
tremendous.viewWillTransition(to: dimension, with: coordinator)
collectionView?.collectionViewLayout.invalidateLayout()
coordinator.animate(alongsideTransition: { context in
}, completion: { context in
collectionView?.collectionViewLayout.invalidateLayout()
collectionView?.visibleCells.forEach { cell in
guard let cell = cell as? Cell else {
return
}
cell.setCircularImageView()
}
})
}
}
extension ViewController: UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout {
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
structure collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout,
sizeForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath
) -> CGSize {
.init(
width: collectionView.body.dimension.width/3.0 - 8,
top: collectionView.body.dimension.width/3.0 - 8
)
}
}
In case you are accustomed to assortment views, you would possibly ask why am I doing this tutorial? It’s so easy. It simply works, proper? No, truly with out the overridden bounds property the instance would look one thing like this on the left facet. 😢
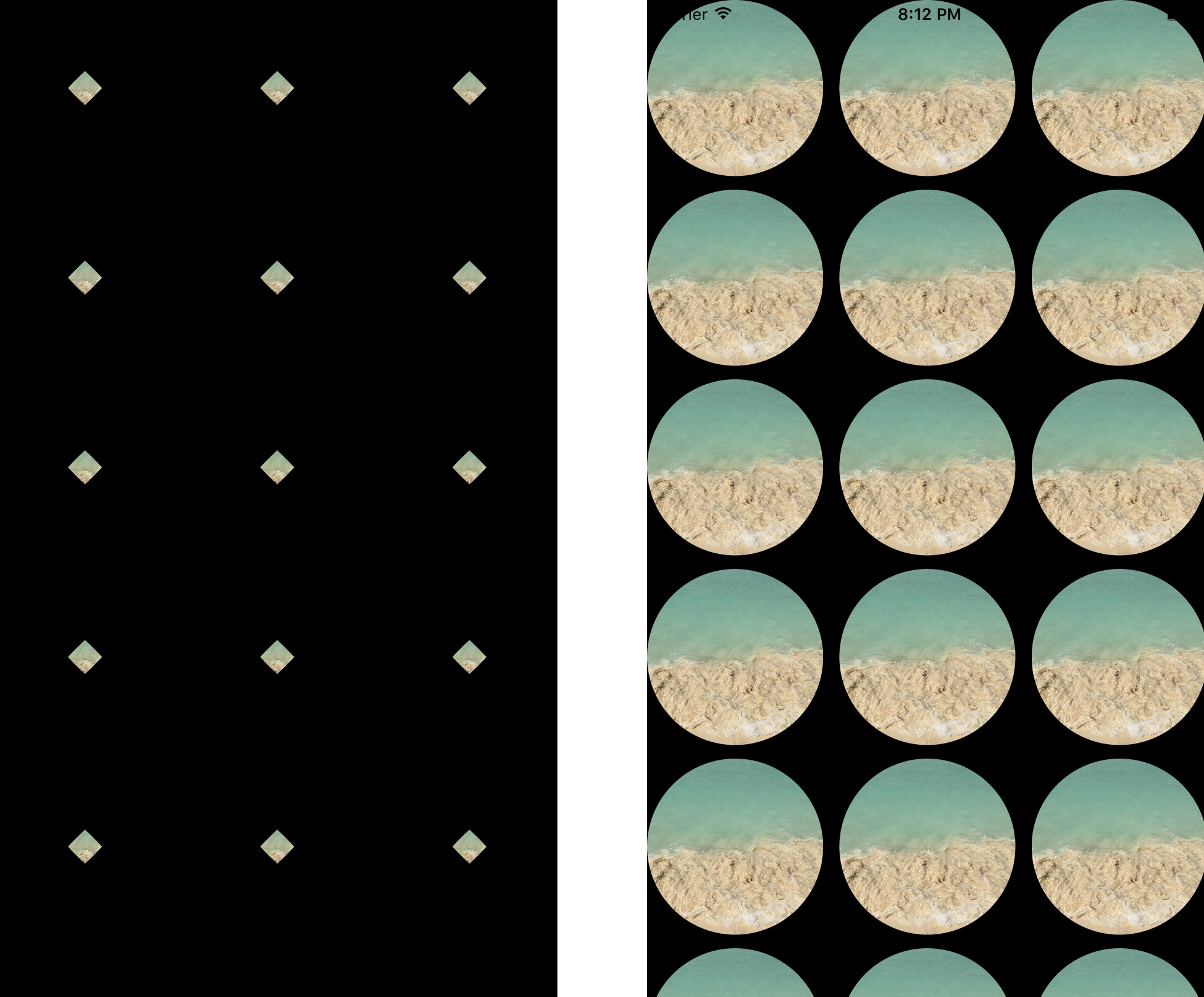
Humorous, huh? The picture on the best facet is the precise outcome with the overridden bounds, that’s the anticipated habits. Scrolling and rotation goes to be actually unusual if you happen to don’t override bounds and also you don’t reset the cornerRadius property for the seen views. You would possibly ask: however why? 🤔
Layers, springs & struts and a few rationalization
Apple nonetheless has “Springs & Struts” based mostly code inside UIKit. Because of this body and certain calculations are occurring within the underlying system and the constraint system is attempting to work exhausting as nicely to determine the correct measures.
“Springs & Struts” must die!
Whereas there may be an init(body:) methodology, or a required init(coder:) these structure issues will suck as hell. I actually like Interface Builder, however till we cannot get a positive device to create nice person interfaces IB goes to be simply one other layer of doable bugs.
This challenge gained’t even be there if you happen to create the cell from code solely utilizing auto structure constraints or structure anchors! It’s as a result of IB creates the cell based mostly on the body you gave in whilst you designed your prototype. However if you happen to neglect init(body:) and also you simply create a brand new UIImageView occasion and let auto structure do the exhausting work, the structure system will remedy every little thing else. Verify this.
class Cell: UICollectionViewCell {
weak var imageView: UIImageView!
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been carried out")
}
override init(body: CGRect) {
tremendous.init(body: body)
translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
let imageView = UIImageView()
imageView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
addSubview(imageView)
imageView = imageView
imageView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: topAnchor)
imageView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: bottomAnchor)
imageView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: leadingAnchor)
imageView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: trailingAnchor)
}
override func layoutSubviews() {
tremendous.layoutSubviews()
imageView.layer.masksToBounds = true
imageView.layer.cornerRadius = CGFloat(
roundf(Float(imageView.body.dimension.width/2.0))
)
}
}
Clearly you need to write extra code, register your cell class manually contained in the controller class and also you additionally need to override the layoutSubviews methodology contained in the cell, nevertheless it’ll work as it’s anticipated. 🙄
collectionView?.register(Cell.self, forCellWithReuseIdentifier: "Cell")
Anyway, after you register the programmatically created cell you’ll have a pleasant means of displaying round photographs. Utilizing this system is sort of difficult, nevertheless it positively works in each case. You may obtain the instance from The.Swift.Dev. tutorials on GitHub.


