A brand new assault dubbed ‘SmartAttack’ makes use of smartwatches as a covert ultrasonic sign receiver to exfiltrate knowledge from bodily remoted (air-gapped) programs.
Air-gapped programs, generally deployed in mission-critical environments equivalent to authorities services, weapons platforms, and nuclear energy vegetation, are bodily remoted from exterior networks to forestall malware infections and knowledge theft.
Regardless of this isolation, they continue to be weak to compromise by means of insider threats equivalent to rogue workers utilizing USB drives or state-sponsored provide chain assaults.
As soon as infiltrated, malware can function covertly, utilizing stealthy methods to modulate the bodily traits of {hardware} parts to transmit delicate knowledge to a close-by receiver with out interfering with the system’s common operations.
SmartAttack was devised by Israeli college researchers led by Mordechai Guri, a specialist within the subject of covert assault channels who beforehand introduced strategies to leak knowledge utilizing LCD display screen noise, RAM modulation, community card LEDs, USB drive RF alerts, SATA cables, and energy provides.
Whereas assaults on air-gapped environments are, in lots of instances, theoretical and very troublesome to attain, they nonetheless current attention-grabbing and novel approaches to exfiltrate knowledge.
How SmartAttack works
SmartAttack requires malware to someway infect an air-gapped pc to assemble delicate data equivalent to keystrokes, encryption keys, and credentials. It might probably then use the pc’s built-in speaker to emit ultrasonic alerts to the setting.
By utilizing a binary frequency shift keying (B-FSK), the audio sign frequencies could be modulated to symbolize binary knowledge, aka ones and zeroes. A frequency of 18.5 kHz represents “0,” whereas 19.5 kHz denotes “1.”
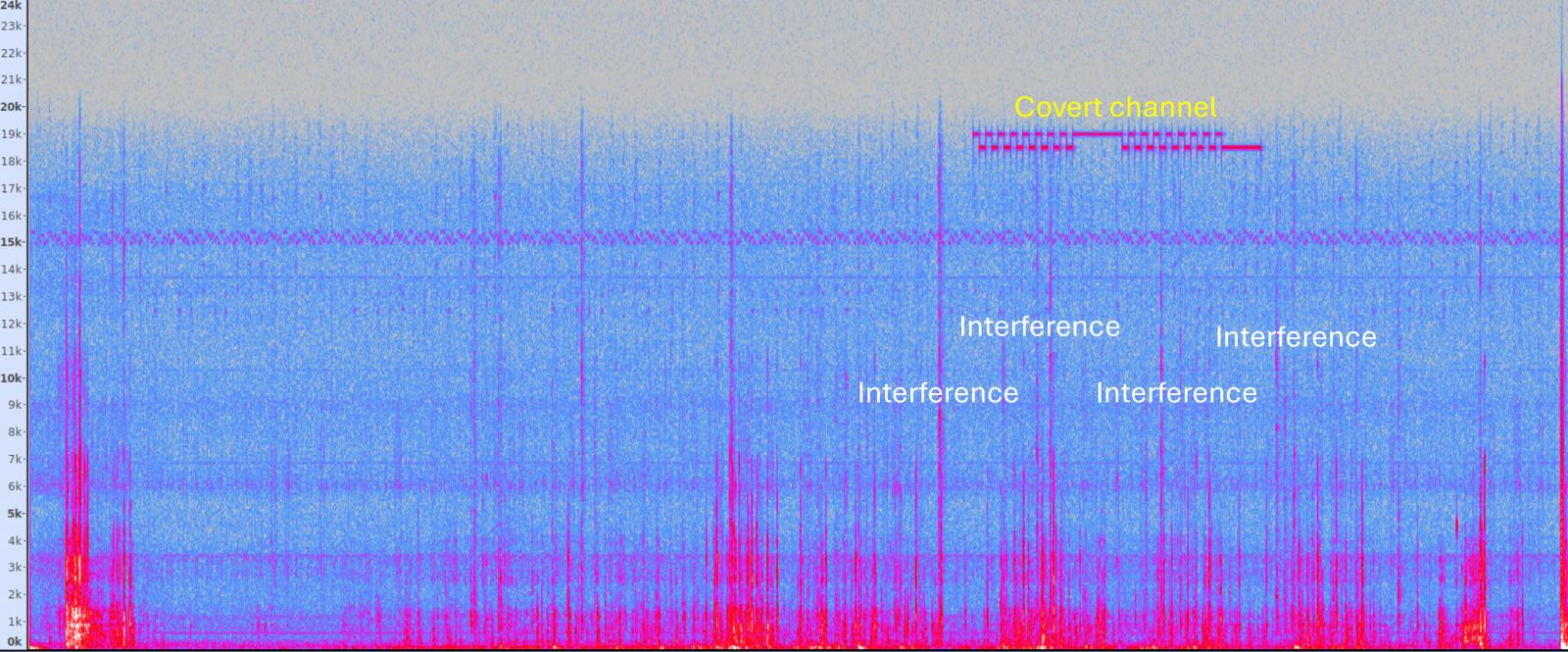
Supply: arxiv.org
Frequencies at this vary are inaudible to people, however they’ll nonetheless be caught by a smartwatch microphone worn by an individual close by.
The sound monitoring app within the smartwatch applies sign processing methods to detect frequency shifts and demodulate the encoded sign, whereas integrity assessments will also be utilized.
The ultimate exfiltration of the information can happen by way of Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or mobile connectivity.
The smartwatch can both be purposefully geared up with this device by a rogue worker, or outsiders might infect it with out the wearer’s information.
Efficiency and limitations
The researchers word that smartwatches use small, lower-SNR microphones in comparison with smartphones, so sign demodulation is kind of difficult, particularly at larger frequencies and decrease sign intensities.
Even wrist orientation was discovered to play a vital function within the feasibility of the assault, working greatest when the watch has “line-of-sight” with the pc speaker.
Relying on the transmitter (speaker kind), the utmost transmission vary is between 6 and 9 meters (20 – 30 ft).
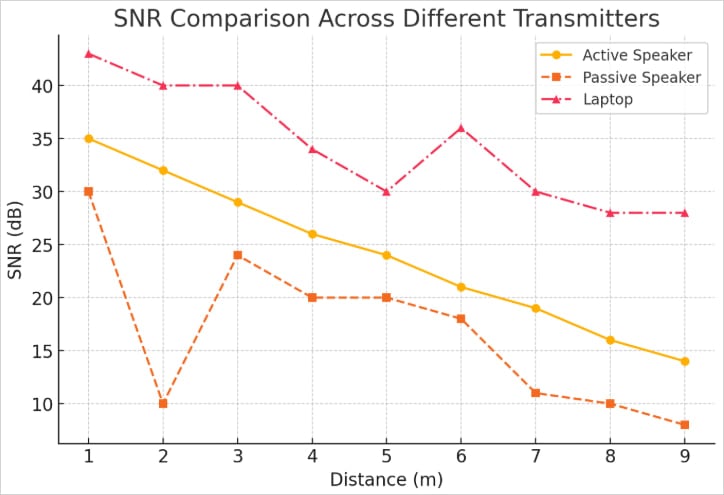
Supply: arxiv.org
The info transmission price ranges from 5 bits per second (bps) to 50 bps, decreasing reliability as the speed and distance improve.
.jpg)
Supply: arxiv.org
The researchers say one of the simplest ways to counter the SmartAttack is to ban utilizing smartwatches in safe environments.
One other measure could be to take away in-built audio system from air-gapped machines. This is able to eradicate the assault floor for all acoustic covert channels, not simply SmartAttack.
If none of that is possible, ultrasonic jamming by means of the emission of broadband noise, software-based firewalls, and audio-gapping may nonetheless show efficient.
Patching used to imply advanced scripts, lengthy hours, and infinite fireplace drills. Not anymore.
On this new information, Tines breaks down how fashionable IT orgs are leveling up with automation. Patch quicker, cut back overhead, and give attention to strategic work — no advanced scripts required.



