
Safety researchers have recognized a minimum of 187 npm packages compromised in an ongoing provide chain assault, with a malicious self-propagating payload to contaminate different packages.
The coordinated worm-style marketing campaign dubbed ‘Shai-Hulud’ began yesterday with the compromise of the @ctrl/tinycolor npm bundle, which receives over 2 million weekly downloads.
Since then, the marketing campaign has expanded considerably and now contains packages revealed below CrowdStrike’s npm namespace.
From tinycolor to CrowdStrike
Yesterday, Daniel Pereira, a senior backend software program engineer, alerted the group to a large-scale software program provide chain assault affecting the world’s largest JavaScript registry, npmjs.com.
“There’s a [sic] malware spreading dwell in npm as you learn this,” wrote the engineer, cautioning everybody to chorus from putting in the newest variations of the @ctrl/tinycolor venture.
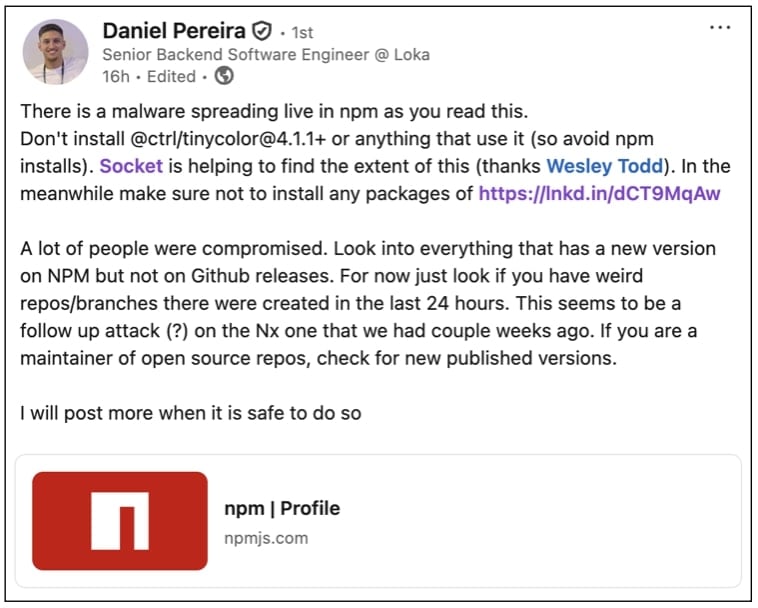
Pereira had been attempting to get GitHub’s consideration within the final 24 hours by way of extra discreet channels to debate the continued assault as “a lot of repos have been focused,” and disclosing the assault publicly might put individuals in danger.
“However contacting GitHub is simply too onerous. As an example, secrets and techniques are being uncovered in repos. That is critical,” wrote the engineer.
Software program provide chain safety agency Socket started investigating the compromise and recognized a minimum of 40 packages that have been compromised on this marketing campaign. Immediately, each Socket and Aikido researchers have recognized further packages, bringing the depend as much as a minimum of 187.
StepSecurity additionally revealed a technical breakdown with deobfuscated snippets and attack-flow diagrams, largely confirming Socket’s preliminary findings.
Affected packages embrace a number of ones revealed by CrowdStrike’s npmjs account crowdstrike-publisher.
BleepingComputer reached out to the cybersecurity options supplier for remark:
“After detecting a number of malicious Node Bundle Supervisor (NPM) packages within the public NPM registry, a third-party open supply repository, we swiftly eliminated them and proactively rotated our keys in public registries,” a CrowdStrike spokesperson shared with BleepingComputer.
“These packages will not be used within the Falcon sensor, the platform will not be impacted and clients stay protected. We’re working with NPM and conducting an intensive investigation.”
Self-propagating worm makes use of TruffleHog to steal secrets and techniques
The compromised variations embrace a self-propagating mechanism that targets different packages by the identical maintainer.
The malware downloads every bundle by a maintainer, modifies its bundle.json, injects a bundle.js script (proven under), repacks the archive, and republishes it, thereby “enabling computerized trojanization of downstream packages,” as Socket researchers defined.

The bundle.js script makes use of TruffleHog, a reliable secret scanner that can be utilized by builders and safety professionals to seek out by accident leaked delicate info like API keys, passwords, and tokens inside code repositories and different information sources.
The malicious script, nonetheless, abuses the device to go looking the host for tokens and cloud credentials.
“It validates and makes use of developer and CI credentials, creates a GitHub Actions workflow inside repositories, and exfiltrates outcomes to a hardcoded webhook (hxxps://webhook[.]website/bb8ca5f6-4175-45d2-b042-fc9ebb8170b7),” explains Socket.
The identify ‘Shai-Hulud’ comes from the shai-hulud.yaml workflow recordsdata utilized by malware discovered within the compromised variations, and is a reference to the big sandworms in Frank Herbert’s Dune collection.
“Whereas not a novel reference, its presence reinforces that the attacker intentionally branded the marketing campaign ‘Shai-Hulud,'” said Socket researchers Kush Pandya and Peter van der Zee right this moment.
The malware present in further packages recognized right this moment is similar to the earlier strand that used bundle.js to:
- Obtain and execute the reliable secret scanning device, TruffleHog
- Search the host for secrets and techniques like tokens and cloud credentials
- Examine if the found developer and CI credentials are legitimate
- Create unauthorized GitHub Actions workflows inside repositories
- Exfiltrate delicate information to a hardcoded webhook endpoint
Incident follows ongoing large-scale assaults like nx ‘s1ngularity’
What makes this supply-chain assault stand out, past the favored packages it hit, is its timing.
The assault follows two high-profile provide chain assaults occurring in the identical month.
The primary week of September, AI-powered malware hit 2,180 GitHub accounts in what was dubbed the ‘s1ngularity’ assault.
Whereas the foundation reason behind right this moment’s assault remains to be being investigated, practitioners, together with Pereira, hypothesize that right this moment’s assault could have been orchestrated by the attackers behind ‘s1ngularity’.
Earlier this month, maintainers of the favored chalk and debug npm packages additionally fell sufferer to phishing, in a separate assault, resulting in their initiatives being compromised.
The ripple results of those assaults lengthen deep into the dependency chain, probably impacting broadly used initiatives comparable to Google Gemini CLI, which launched a press release over the weekend:
“We wish to be clear: The Gemini CLI supply code itself was not compromised, and our servers stay safe,” wrote Ryan J. Salva, Google’s Senior Director of Product Administration.
“Nonetheless, this incident could have affected customers who put in or up to date the Gemini CLI throughout the assault window utilizing the NPM set up technique. We’re offering particulars on the incident, clarifying who’s impacted, and outlining the steps customers ought to take to make sure their methods are safe.”
These ongoing assaults reveal the fragility of the trendy software program provide chain, the place a single malicious pull request or compromised maintainer account can ripple out to a whole lot of initiatives.
Whereas distributors like Google and CrowdStrike stress their core platforms stay safe, the incident underscores the pressing want for builders to safeguard their software program builds and pipelines.
Affected customers ought to audit their environments and logs for indicators of compromise, rotate all secrets and techniques and CI/CD tokens, and assessment dependency timber for malicious variations. Pinning dependencies to trusted releases and limiting the scope of publishing credentials stay important steps to cut back publicity to package-level compromises.



