
North Korean risk actors planted 67 malicious packages within the Node Package deal Supervisor (npm) on-line repository to ship a brand new malware loader referred to as XORIndex to developer techniques.
The packages collectively rely greater than 17,000 downloads and have been found by researchers at package deal safety platform Socket, who assess them to be a part of the continued Contagious Interview operation.
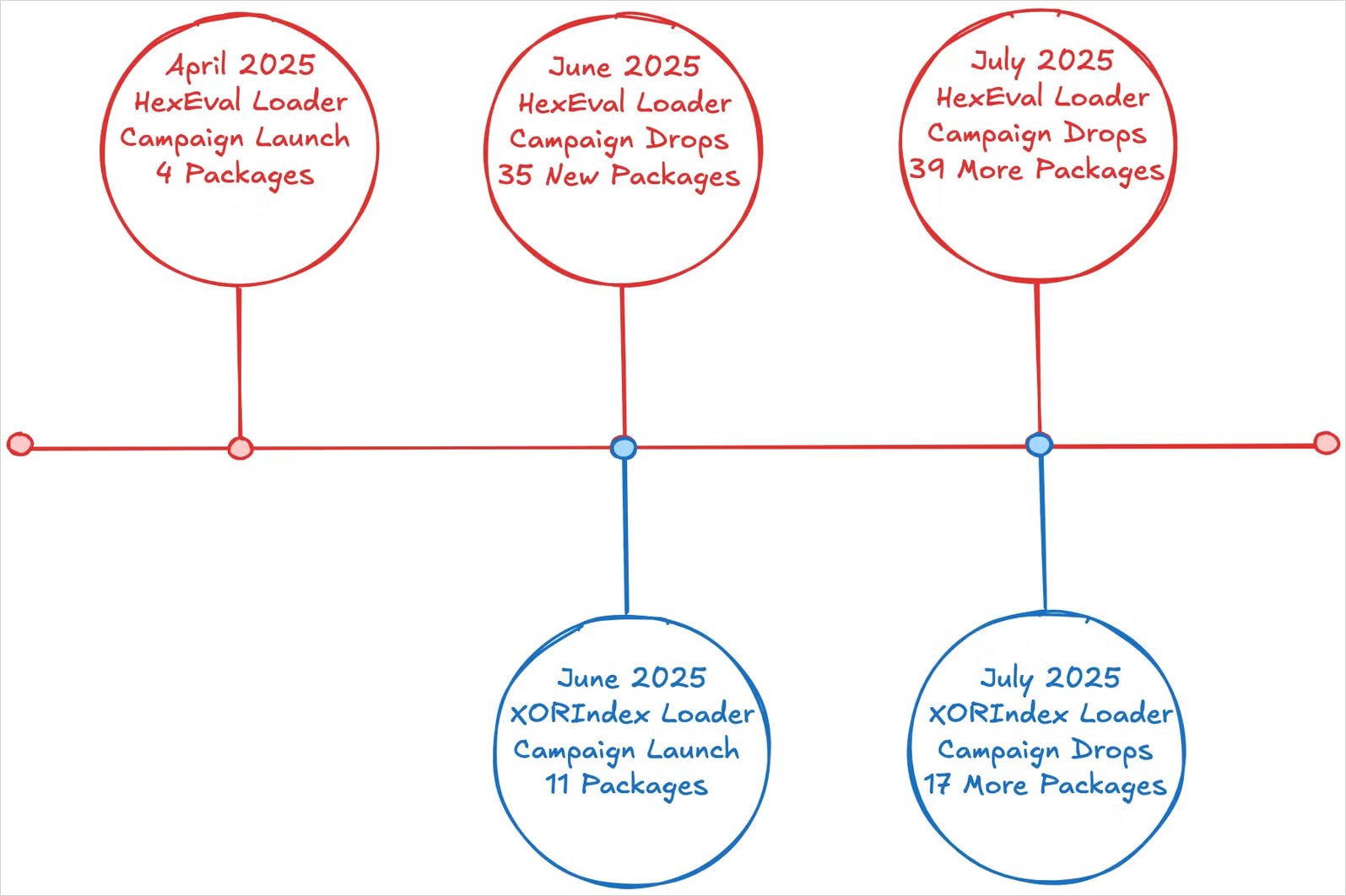
Socket researchers say that the marketing campaign follows risk exercise detected since April. Final month, the identical actor infiltrated npm with 35 packages that dropped data stealers and backdoors onto builders’ units.
Supply: Socket
Overview of the assaults
Contagious Interview is a North Korean state-backed marketing campaign that targets principally builders with pretend job presents to trick them into working malicious code on their techniques.
The aim varies from gathering delicate data that enables breaching corporations to stealing cryptocurrency property.
The Node Package deal Supervisor (npm) is the default package deal supervisor for Node.js, a platform the place builders publish and set up JavaScript libraries and instruments. It’s extensively utilized in internet growth, but additionally ceaselessly exploited by risk actors for malware distribution.
Out of the 67 packages the risk actors uploaded onto npm this time, there are a number of that seem to imitate or mix the names of reputable software program initiatives and libraries, like:
- vite-meta-plugin
- vite-postcss-tools
- vite-logging-tool
- vite-proc-log
- pretty-chalk
- postcss-preloader
- js-prettier
- flowframe
- figwrap
- midd-js, middy-js
When victims set up any of those packages, a ‘postinstall’ script executes to launch XORIndex Loader, a novel instrument that seems for use in parallel with HexEval Loader, a malware dropper noticed in previous assaults.
XORIndex Loader collects host knowledge to profile every sufferer and sends it to a hardcoded command and management (C2) deal with, hosted on infrastructure from Vercel cloud software firm.
The C2 server responds with a number of JavaScript payloads, that are executed on the sufferer’s system utilizing eval(). These payloads are usually the BeaverTail and the InvisibleFerret backdoor, each attributed to North Korean Contagious Interview operations.
The 2 items of malware present entry to compromised machines, enable knowledge exfiltration, and may obtain extra payloads.
Based on the researchers, the North Korean hackers mix previous and new instruments with delicate modifications to evade detection, and each time npm cleans an an infection, they return by way of completely different npm accounts and package deal names.
“Contagious Interview risk actors will proceed to diversify their malware portfolio, rotating by new npm maintainer aliases, reusing loaders reminiscent of HexEval Loader and malware households like BeaverTail and InvisibleFerret, and actively deploying newly noticed variants together with XORIndex Loader” – Socket
“Defenders ought to anticipate continued iterations of those loaders throughout newly revealed packages, usually with slight variations to evade detection,” the researchers warn.
Socket researchers say that they reported to npm all malicious packages from the most recent marketing campaign however a few of them should still be out there within the repository.
You will need to double-check sourced packages to make sure they’re not typosquatting decoys, solely belief well-known initiatives and publishers with a confirmed document, and scrutinize latest repository exercise for indicators of automation.
When potential, at all times look at the supply code for obfuscation and execute new libraries in remoted environments to judge their security.



