
A brand new “Department Privilege Injection” flaw in all trendy Intel CPUs permits attackers to leak delicate knowledge from reminiscence areas allotted to privileged software program just like the working system kernel.
Usually, these areas are populated with data like passwords, cryptographic keys, reminiscence of different processes, and kernel knowledge buildings, so defending them from leakage is essential.
In accordance with ETH Zurich researchers Sandro Rüegge, Johannes Wikner, and Kaveh Razavi, Spectre v2 mitigations held for six years, however their newest “Department Predictor Race Circumstances” exploit successfully bypasses them.
The flaw, which is known as ‘department privilege injection’ and tracked below CVE-2024-45332, is a race situation on the subsystem of department predictors utilized in Intel CPUs.
Department predictors like Department Goal Buffer (BTB) and Oblique Department Predictor (IBP) are specialised {hardware} parts that attempt to guess the result of a department instruction earlier than it is resolved to maintain the CPU pipeline full for optimum efficiency.
These predictions are speculative, that means they’re undone in the event that they find yourself being flawed. Nonetheless, if they’re appropriate, it will increase efficiency.
The researchers discovered that Intel’s department predictor updates aren’t synchronized with instruction execution, leading to these updates traversing privilege boundaries.
If a privilege swap occurs, like from consumer mode to kernel mode, there’s a small window of alternative throughout which the replace is related to the flawed privilege stage.
Because of this, isolation between consumer and kernel is damaged, and a non-privileged consumer can leak knowledge from privileged processes.
ETH Zurich’s workforce developed an exploit that trains the CPU to foretell a particular department goal, then makes a system name to maneuver execution into the OS kernel, resulting in speculative execution utilizing the attacker-controlled goal (“gadget”).
This code accesses secret knowledge loaded into the cache, and utilizing a side-channel methodology, the contents are leaked to the attacker.
The researchers demonstrated their assault on Ubuntu 24.04 with default mitigations enabled to learn the contents of the ‘/and so on/shadow/’ file containing hashed account passwords. The exploit can obtain peak leak charges of 5.6 KB/sec at 99.8% accuracy.
Impression and fixes
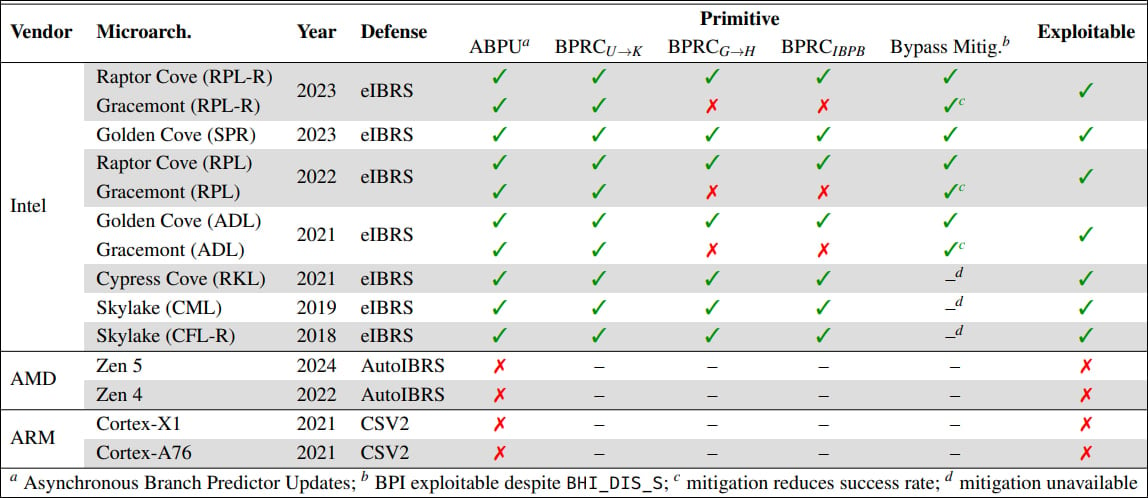
CVE-2024-45332 impacts all Intel CPUs from the ninth era onward, together with Espresso Lake, Comet Lake, Rocket Lake, Alder Lake, and Raptor Lake.
“All intel processors because the ninth era (Espresso Lake Refresh) are affected by Department Privilege Injection,” explains the researchers.
“Nonetheless, we now have noticed predictions bypassing the Oblique Department Prediction Barrier (IBPB) on processors way back to seventh era (Kaby Lake).”
ETH Zurich researchers didn’t check older generations at the moment, however since they don’t assist Enhanced Oblique Department Restricted Hypothesis (eIBRS), they’re much less related to this particular exploit and sure extra liable to older Spectre v2-like assaults.
Arm Cortex-X1, Cortex-A76, and AMD Zen 5 and Zen 4 chips had been additionally examined, however they don’t exhibit the identical asynchronous predictor conduct, so they don’t seem to be susceptible to CVE-2024-45332.
Supply: ETH Zurich
Though the assault was demonstrated on Linux, the flaw is current on the {hardware} stage, so it is theoretically exploitable on Home windows too.
The researchers reported their findings to Intel in September 2024, and the tech large launched microcode updates that mitigate CVE-2024-45332 on impacted fashions.
The firmware-level mitigations introduce a 2.7% efficiency overhead, whereas software program mitigations have a efficiency impression between 1.6% and eight.3%, relying on the CPU.
The danger is low for normal customers, and assaults have a number of sturdy stipulations to open up real looking exploitation situations. That being stated, making use of the most recent BIOS/UEFI and OS updates is really useful.
ETH Zurich will current the total particulars of their exploit in a technical paper on the upcoming USENIX Safety 2025.
BleepingComputer contacted Intel to see if an advisory could be launched immediately, and can replace the article with a response.



