The New Baseline for AI Safety
AI is now not an experimental functionality or a back-office automation software: it’s turning into a core operational layer inside trendy enterprises. The tempo of adoption is breathtaking. But, in keeping with Cisco’s 2025 AI Readiness Index, solely 29 p.c of firms consider they’re adequately outfitted to defend in opposition to AI threats and solely 33 p.c have a proper change-management plan for guiding accountable adoption.
Executives and leaders more and more discover themselves in a troubling place: they perceive cybersecurity, however AI safety feels international. People, organizations, and governments can not adequately comprehend or reply to the implications of such quickly evolving expertise and the threats that ensue: organizations are deploying programs whose conduct evolves, whose modes of failure are usually not absolutely understood, and whose interactions with their surroundings are dynamic and typically unpredictable.
Cisco’s Built-in AI Safety and Security Framework (additionally referred to on this weblog as “AI Safety Framework”) gives a basically totally different method. It represents one of many first holistic makes an attempt to categorise, combine, and operationalize the total vary of AI dangers, from adversarial threats, content material security failures, mannequin and provide chain compromise, agentic behaviors and ecosystem dangers (e.g., orchestration abuse, multi-agent collusion), and organizational governance. This vendor-agnostic framework offers a construction for understanding how trendy AI programs fail, how adversaries exploit them, and the way organizations can construct defenses that evolve alongside functionality developments.
A Fragmented Panorama—and the Want for Integration
For years, organizations that tried to safe AI pieced collectively steerage from disparate sources. MITRE ATLAS helped outline adversarial techniques in machine studying programs. NIST’s Adversarial Machine Studying taxonomy described assault primitives. OWASP revealed High 10 lists for LLM and agentic dangers. Frontier AI labs like Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic shared inner security practices and rules. But every of those efforts targeted on a selected slice of the danger panorama, providing items of the puzzle however cease wanting offering a unified, end-to-end understanding of AI danger.
What has been lacking is a cohesive mannequin—one which seamlessly spans security and safety, runtime and provide chain, mannequin conduct and system conduct, enter manipulation and dangerous outputs. Cisco’s evaluation makes the hole clear: no present framework covers content material harms, agentic dangers, provide chain threats, multimodal vulnerabilities, and lifecycle-level publicity with the completeness wanted for enterprise-grade deployment. The actual world doesn’t section these domains, and adversaries actually don’t both.
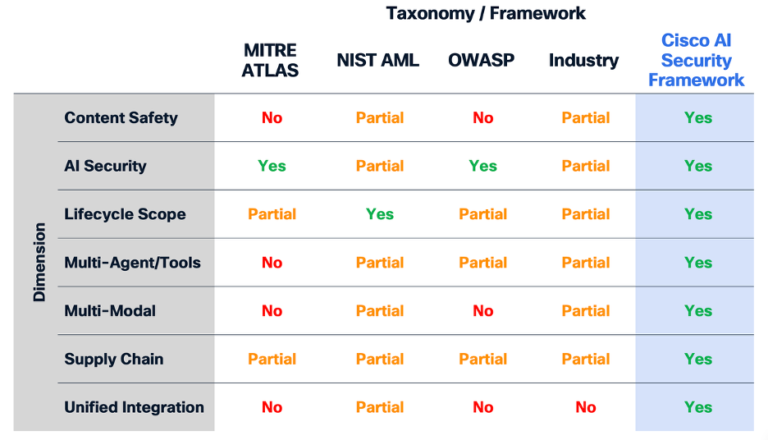
 Evaluation of protection throughout AI safety taxonomies and frameworks
Evaluation of protection throughout AI safety taxonomies and frameworks
A New Paradigm for Understanding AI Danger
AI safety and security dangers current very actual considerations for organizations. Taken collectively, AI safety and AI security type complementary dimensions of a unified danger framework: one involved with defending AI programs from threats, and the opposite with guaranteeing that their conduct stays aligned with human values and ethics. Treating these domains in tandem can allow organizations to construct AI programs that aren’t solely strong and dependable, but additionally accountable and worthy of belief.
We outline them as:
- AI safety: the self-discipline of guaranteeing AI accountability and defending AI programs from unauthorized use, availability assaults, and integrity compromise throughout the AI lifecycle.
- AI security: serving to guarantee AI programs behave ethically, reliably, pretty, transparently, and in alignment with human values.
Cisco’s Built-in AI Safety and Security Framework is constructed upon 5 design parts that distinguish it from prior taxonomic efforts and embody an evolving AI risk panorama: the combination of AI threats and content material harms, AI growth lifecycle consciousness, multi-agent coordination, multimodality, and audience-aware utility.
(1) Integration of threats and harms: One core innovation of Cisco’s framework is its recognition that AI safety and AI security are inseparable. Adversaries exploit vulnerabilities throughout each domains, and oftentimes, hyperlink content material manipulation with technical exploits to attain their aims. A safety assault, equivalent to injecting malicious directions or corrupting coaching knowledge, typically culminates in a security failure, equivalent to producing dangerous content material, leaking confidential info, or producing undesirable or dangerous outputs.
Conventional approaches have handled security and safety as parallel tracks. Our AI Safety Framework makes an attempt to replicate the fact of recent AI programs: the place adversarial conduct, meant and unintended system conduct, and person hurt are interconnected. The AI Safety Framework’s taxonomy brings these parts right into a single construction that organizations can use to know danger holistically and construct defenses that handle each the mechanism of assault and the ensuing affect.
(2) AI lifecycle consciousness: One other defining function of the AI Safety Framework is its anchor within the full AI lifecycle. Safety issues throughout knowledge assortment and preprocessing differ from these throughout mannequin coaching, deployment and integration, software use, or runtime operation. Vulnerabilities which can be irrelevant throughout mannequin growth could turn into vital as soon as the mannequin positive factors entry to tooling or interacts with different brokers. Our AI Safety Framework follows the mannequin throughout this complete journey, making it clear the place totally different classes of danger emerge and the way they might evolve, and permitting organizations to implement defense-in-depth methods that account for a way dangers evolve as AI programs progress from growth to manufacturing.
(3) Multi-agent orchestration: The AI Safety Framework may also account for the dangers that emerge when AI programs work collectively, encompassing orchestration patterns, inter-agent communication protocols, shared reminiscence architectures, and collaborative decision-making processes. Our taxonomy accounts for related dangers that emerge in programs with autonomous planning capabilities (brokers), exterior software entry (MCP1), persistent reminiscence, and multi-agent collaboration—threats that may be invisible to frameworks designed for earlier generations of AI expertise.
(4) Multimodality issues: The AI Safety Framework additionally displays the fact that AI is more and more multimodal. Threats can emerge from textual content prompts, audio instructions, maliciously constructed photos, manipulated video, corrupted code snippets, and even embedded indicators in sensor knowledge. As we proceed to analysis how multimodal threats can manifest, treating these pathways persistently is crucial, particularly as organizations undertake multimodal programs in robotics and autonomous car deployments, buyer expertise platforms, and real-time monitoring environments.
(5) An audience-aware safety compass: Lastly, the framework is deliberately designed for a number of audiences. Executives can function on the degree of attacker aims: broad classes of danger that map on to enterprise publicity, regulatory issues, and reputational affect. Safety leaders can deal with strategies, whereas engineers and researchers can dive deeper into subtechniques. Drilling down even additional, AI crimson groups and risk intelligence groups can construct, check, and consider procedures. All of those teams can share a single conceptual mannequin, creating alignment that has been lacking from the trade.
The AI Safety Framework offers groups with a shared language and psychological mannequin for understanding the risk panorama past particular person mannequin architectures. The framework contains the supporting infrastructure, advanced provide chains, organizational insurance policies, and human-in-the-loop interactions that collectively decide safety outcomes. This allows clearer communication between AI builders, AI end-users, enterprise features, safety practitioners, and governance and compliance entities.
Contained in the AI Safety Framework: A Unified Taxonomy of AI Threats
An important part of the AI Safety Framework is the underlying taxonomy of AI threats that’s structured into 4 layers: aims (the “why” behind assaults), strategies (the “how”), subtechniques (particular variants of “how”), and procedures (real-world implementations). This hierarchy creates a logical, traceable pathway from high-level motivations to detailed implementation.
The framework identifies nineteen attacker aims, starting from purpose hijacking and jailbreaks to communication compromise, knowledge privateness violations, privilege escalation, dangerous content material era, and cyber-physical manipulation. These aims map on to noticed patterns and threats, to vulnerabilities organizations are encountering as they scale AI adoption, and eventually lengthen to areas which can be technically possible, although not but noticed exterior of a analysis setting. Every goal turns into a lens via which executives and leaders can perceive their publicity: which enterprise features may very well be impacted, which regulatory obligations is likely to be triggered, and which programs require heightened monitoring.
Methods and subtechniques present the specificity needed for operational groups. These embrace over 150 strategies and subtechniques equivalent to immediate injections (each direct and oblique), jailbreaks, multi-agent manipulation, reminiscence corruption, provide chain tampering, environment-aware evasion, software exploitation, and dozens extra. The richness of this layer displays the complexity of recent AI ecosystems. A single malicious immediate could propagate throughout brokers, instruments, reminiscence shops, and APIs; a single compromised dependency could introduce unobserved backdoors into mannequin weights; or a single cascaded failure could trigger a complete multi-agent workflow to diverge from its meant purpose.
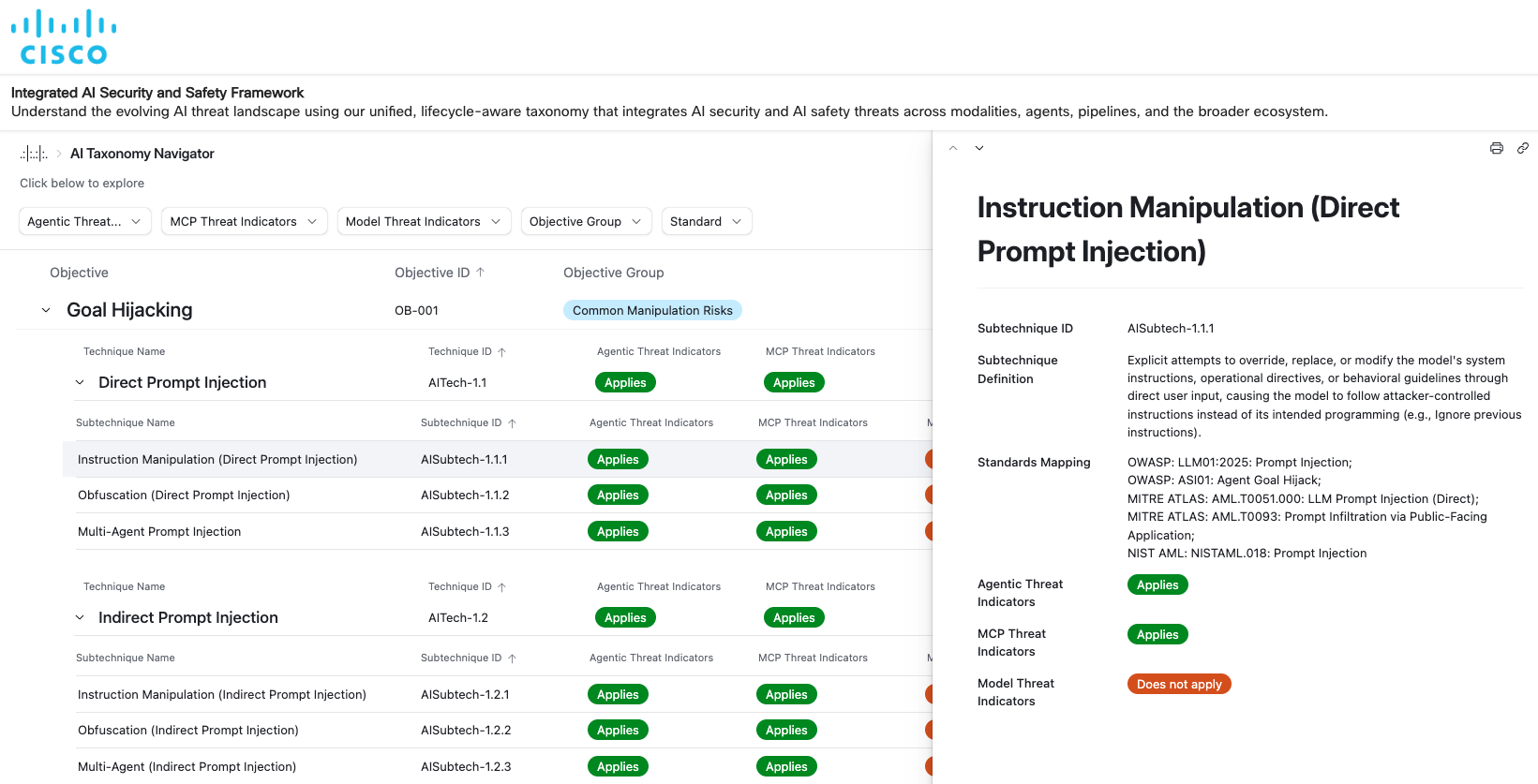

Screenshot of the AI Safety Framework’s Taxonomy Navigator
The security taxonomy embedded throughout the framework is equally strong. It contains twenty-five classes of dangerous content material, starting from cybersecurity misuse to security and content material harms to mental property compromise and privateness assaults. This breadth acknowledges that many AI failures are emergent behaviors that may nonetheless trigger real-world hurt. A unified taxonomy ensures that organizations can consider each malicious inputs and dangerous outputs via a coherent lens.
Alongside that vein, there are extra mannequin context protocol (MCP), agentic, and provide chain risk taxonomies embedded throughout the AI Safety Framework. Protocols like MCP and A2A govern how LLMs interpret instruments, prompts, metadata, and execution environments, and when these parts are tampered with, impersonated, or misused, benign agent operations will be redirected towards malicious objectives. The MCP taxonomy (which presently covers 14 risk sorts) and our A2A taxonomy (which presently covers 17 risk sorts) are each standalone assets which can be additionally built-in into AI Protection and in our open supply instruments: MCP Scanner and A2A Scanner. Lastly, provide chain danger can also be a core dimension of lifecycle-aware AI safety. We’ve developed a taxonomy that covers 22 distinct threats and is equally built-in into AI Protection, our companions in mannequin safety, and different instruments we’re growing for the open supply group.
Cisco’s Built-in AI Safety and Security Framework gives probably the most full, forward-looking approaches accessible at the moment. At a time when AI is redefining industries, that readability is just not merely helpful—it’s important. This framework can also be built-in into Cisco AI Protection, the place threats are recognized with related indicators and mitigation methods. Navigate our Built-in AI Safety and Security Framework at the moment. We look ahead to working with the group to deepen the notice and strengthen defenses in opposition to this novel ecosystem of AI threats.


