Analyst home ABI Analysis seems to be at how full duplex microwave improvements are boosting 5G spectrum effectivity, serving to operators meet rising backhaul calls for, overcome spectrum limitations, and allow high-capacity, cost-effective wi-fi connectivity.
Wi-fi backhaul is a important element of any cell community, as it’s the hyperlink supporting voice and information transport between the core community and radio entry community (RAN) websites. Wi-fi backhaul, corresponding to microwave and millimeter wave (mmWave), continues to be a key spine know-how, with ABI Analysis forecasting that over 50% of backhaul site visitors is carried over microwave and mmWave hyperlinks.
Backhaul capability necessities are anticipated to proceed rising, so the microwave gear sector has been spearheading a number of key developments and improvements.
Key business tendencies
1. Demand for backhaul capability
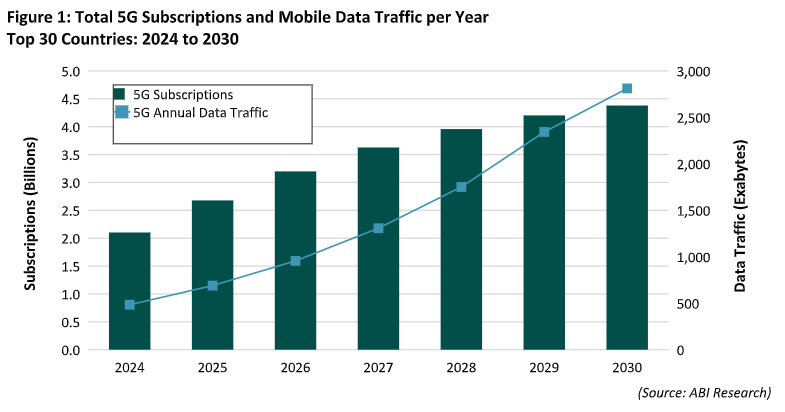
Exceeding earlier forecasts, annual 5G subscriptions from the highest 30 international locations monitored by ABI Analysis reached 2.1 billion on the finish of 2024 and they’re anticipated to develop to over 4.3 billion by the top of 2030. Accordingly, 5G information site visitors is forecast to extend from over 480 exabytes in 2024 to 2,800 exabytes in 2030 – a compound annual development charge (CAGR) of 32%. This development is pushed by growing consumption of high-resolution video streaming companies, each downloads and uploads, in addition to greater adoption of generative AI (gen AI) cell functions.
The above developments are anticipated to drive demand for greater backhaul capacities, particularly in city areas. ABI Analysis expects backhaul capability throughput necessities to develop shortly, reaching 25 Gbps in city eventualities. That is pushed by site visitors carried over 5G mid-band, a selective deployment of 5G high-band, and the lowering put in base of 4G finish customers by 2030.
2. Elevated competitors for spectrum
Current developments on the World Radiocommunication Convention 2023 (WRC-23) additionally launched new challenges to the microwave business by way of spectrum availability. Area 1 and Area 3 have recognized the 6,425-7,125 MHz and seven,025-7,125 MHz spectrum ranges for Worldwide Cell Telecommunications (IMT) companies, respectively. Moreover, to facilitate 6G deployment, the WRC-23 agreed to review the 7,125-8,400 MHz frequency band of (or components thereof) and 14.8-15.35 GHz for IMT, thus creating much more competitors for spectrum use in conventional microwave frequency bands.
On the identical time, different international locations, such because the US, Canada, Saudi Arabia, and South Korea, have recognized the whole 6 GHz band (5,925-7,125 MHz) for license-exempt entry, which is able to help different wi-fi entry applied sciences corresponding to Wi-Fi. This additionally creates a problem for microwave deployment as a consequence of interference issues.
3. Inadequate spectrum channel sizes
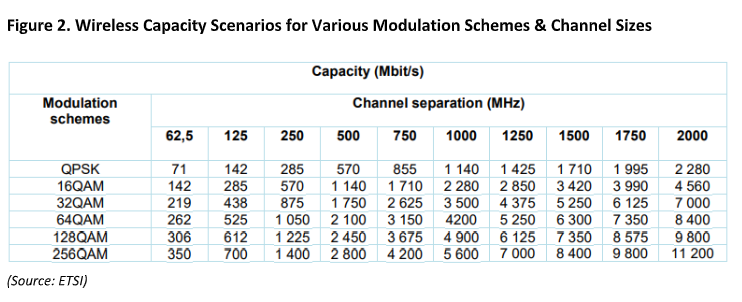
Limitations to microwave channel sizes is one other problem for wi-fi backhaul deployments. Based on the European Telecommunications Requirements Institute (ETSI), nearly all of international locations surveyed (74%) had most E-band channel sizes of 1,000 MHz and under. This restriction, which restricted E-band deployments to five,600 Mbps at 256 quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), prevented operators from realizing the complete potential of the know-how.
Microwave spectrum tendencies
To adequately deal with communications service suppliers’ (CSPs’) issues on backhaul capability, microwave options suppliers have been in a position to rise to the problem and ship enhanced spectrum efficiencies. These developments are largely centered across the following key applied sciences.
1. Increased / adaptive modulation schemes
QAM is a often used approach for microwave backhaul functions that mixes amplitude and section modulation to transmit extra information in a single sign. Moderately than solely sending 0s and 1s, this know-how makes use of factors on a constellation diagram, with completely different values assigned to every level. For instance, 4 QAM has 4 factors, which permits the transmission of two bits per image, whereas 16 QAM has 16 factors within the constellation, which helps 4 bits per image.
Nonetheless, this method has a limitation in that it sees diminishing returns as QAM ranges enhance. It was reported that past 1024 QAM, spectral effectivity acquire is lower than 10% for every incremental step (i.e., to 2048 QAM and past). Operators might want to stability between enhancing capability through growing QAM ranges in opposition to lowering radio frequency efficiency as a consequence of elevated interference dangers.
Adaptive modulation is a software used to regulate the modulation of a sign relying on the prevailing situation of the channel between the transmitter and receiver. For instance, when the channel is experiencing sub-optimal situations, corresponding to rain, adaptive modulation permits for the adjustment of modulation schemes to extend sign throughput, a characteristic that’s not accessible with fastened modulation schemes.
2. Spectral effectivity – through interference cancelling
Cross-polarization interference cancelling (XPIC) can doubtlessly double the capability of a microwave hyperlink by doubling its spectral effectivity. That is achieved by propagating two indicators horizontally and vertically over the identical channel, growing channel reusability. This permits for a rise in each protection and the variety of hyperlinks utilizing the identical spectrum band.
XPIC additionally cancels interference led to by atmospheric attenuation (e.g., raindrops, which trigger polarization rotation as they fall, skewing a sign’s polarization out of alignment and inflicting interference with different polarized indicators). XPIC samples indicators in each polarizations to cancel the results of any interference. Primarily, hyperlink capability may be doubled by means of XPIC by using each polarizations to transmit twice the info in the identical channel.
3. Spectral effectivity – through antenna separation
Line-of-sight (LOS) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) enhances hyperlink capability by means of growing spectral effectivity. That is achieved by permitting extra information to be transmitted although the identical frequency by optimizing the separation between the antennas within the transmit and obtain arrays. LOS MIMO hyperlinks can both be 2X2, with two transmitters and receivers which can be related to 2 antennas on either side, or 4X4 through the use of 4 transmitters and receivers in each horizontal and vertical polarization.
A 4X4 LOS MIMO scheme can allow transmission of 4 completely different information streams in the identical frequency channel with an efficient acquire of 4X extra capability than a typical 1+0 single-input, single-output (SISO) hyperlink. Nonetheless, a problem with this deployment mode is that double the variety of antennas should be put in on a single tower, with a minimal separation distance between them to optimize sign high quality. Because of this, scaling out such LOS MIMO deployments is difficult as a consequence of issues on accumulating tower-related telco gear rental prices.
4. Built-in entry and backhaul
Built-in Entry and Backhaul (IAB) makes use of entry spectrum to backhaul cell information site visitors to the core community. IAB has greater gear price efficiencies, as each entry and backhaul share the identical radio {hardware} unit and have comparable operation/upkeep programs. IAB may also assist decrease gear prices, as cell websites don’t require separate transmitter-antennas for backhaul hyperlinks.
Nonetheless, a limitation to this know-how is that it makes use of the identical entry spectrum for backhaul, doubtlessly affecting buyer community experiences. Moreover, there are additionally dangers of IAB interference between entry and backhaul hyperlinks, which can trigger half-duplexing.
5. Two-way transmissions
Conventional strategies of communication sometimes use: 1) time division duplex (TDD) know-how, the place indicators are transmitted and acquired utilizing the identical frequency however at completely different time intervals; and a pair of) frequency division duplex (FDD) know-how, the place indicators are transmitted and acquired concurrently, however utilizing completely different frequencies. Nonetheless, a typical subject confronted by each TDD and FDD applied sciences is that spectrum utilization shouldn’t be totally maximized.
“Full duplex” is a revolutionary know-how that improves spectrum utilization by enabling simultaneous sending of information in each instructions (i.e., transmitting and receiving) utilizing the identical frequency band, successfully doubling spectrum effectivity. This know-how additionally avoids the challenges confronted by LOS MIMO deployments by simplifying deployments right into a single antenna.
Whereas full duplex transmission introduces elevated dangers of co-channel interference, numerous options, corresponding to excessive isolation and interference cancellation, have been developed to maximise the efficiency of full duplex options.
Listed below are a few of the newest developments for full duplex know-how:
Huawei: In 2025, Huawei launched the world’s first industrial full duplex microwave answer, MAGICSwave, that may double spectral effectivity with using: 1) extremely remoted antennas (inside a single field); and a pair of) superior interference cancellation algorithms to take away interference brought on by the atmosphere. In a reside take a look at carried out with Turkcell, the complete duplex answer was in a position to help a knowledge throughput of fifty Gbps using the E-band (80 GHz) spectrum.
Nokia: In 2024, Nokia introduced the profitable demonstration of full duplex fastened point-to-point wi-fi hyperlinks within the D-Band (130 – 175 GHz) frequency vary. The corporate reviews that its answer achieved 10 Gbps for the uplink and 10 Gbps for the downlink over a single 2 GHz channel. Research to develop requirements governing using the D-Band by ETSI and the Worldwide Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) are ongoing.
Abstract conclusions
Microwave backhaul know-how continues to evolve with the altering necessities of cell entry know-how. With growing competitors for spectrum sources, spectral effectivity stands out as a important element to maximizing backhaul capacities with the restricted accessible spectrum.
On the identical time, lowering tower load, operational expenditure, and power consumption will proceed to be key issues for CSPs. The evolution of microwave know-how towards full duplex options is well timed for serving to backhaul networks meet future cell necessities.


