Trendy purposes depend on structured storage techniques that may scale, keep dependable, and maintain knowledge constant. On the coronary heart of all of it sits the information mannequin. It defines how info is organized, saved, and retrieved. Get the mannequin incorrect and efficiency suffers, integrity breaks down, and future modifications grow to be painful. Get it proper and every little thing else turns into simpler to handle.
Right here, we’ll take a sensible have a look at database knowledge fashions, from sorts and abstraction ranges to normalization and design. We’ll stroll by way of how an ER diagram turns into actual tables, utilizing SQL and actual situations to floor the idea. On this article, we’ll bridge DBMS ideas with hands-on database design.
What Is a Knowledge Mannequin in DBMS?
An information mannequin defines the logical construction of a database. The system defines how knowledge components throughout the database system will join with one another whereas sustaining particular constraints. For instance, a knowledge mannequin demonstrates {that a} pupil entity comprises attributes akin to StudentID and Identify whereas displaying {that a} Course entity connects to Pupil by way of an enrollment relationship. The mannequin defines which knowledge we maintain and the foundations that regulate its administration.
Knowledge fashions allow groups to create knowledge illustration plans by way of logical design as an alternative of beginning with SQL tables. The strategy decreases errors whereas enhancing communication and making subsequent modifications simpler.
Key roles of a knowledge mannequin embody:
- Construction: The system wants to rearrange knowledge into entities and fields which characterize tables and columns in a coherent construction.
- Relationships: The system exhibits how knowledge components join with one another by way of its means to precise that college students can enroll in a number of programs whereas programs can have a number of college students enrolled in them.
- Constraints: The system establishes knowledge validation requirements by way of major keys which guarantee distinctive knowledge identification and international keys which keep referential knowledge relationships.
- Abstraction: The system offers customers with a knowledge idea interface which permits them to entry knowledge by way of ideas like “pupil” as an alternative of needing to know file storage or disk association.
Varieties of Knowledge Fashions in DBMS
Various kinds of knowledge fashions exist in DBMS. This displays the best way during which knowledge is saved in accordance with the character of the information. Every mannequin has its personal manner of representing knowledge:
Knowledge exists in a hierarchical construction which kinds a tree sample. Each file within the system requires one father or mother connection aside from the foundation file whereas the file might have a number of little one connections. Hierarchical constructions describe each XML paperwork and organizational charts. The system performs quick one-to-many searches however struggles with a number of connections between two entities.
John Carter
The community construction shops knowledge as a graph which represents a community of interconnected data. The system helps a number of father or mother and little one hyperlinks for every file which creates pure many-to-many relationships. The system allows customers to create connections between components but it surely requires customers to deal with complicated strategies for each querying and system repairs.
The vast majority of database administration techniques use the relational mannequin as their major database construction. Databases keep knowledge in tables that are structured as relations that include each rows and columns. Overseas keys set up connections between tables. The database mannequin affords customers a number of versatile choices which allow them to create complicated SQL database queries.
SELECT e.EmployeeName, p.ProjectID, p.StartDate
FROM Worker e
JOIN Mission p ON e.EmployeeID = p.EmployeeID;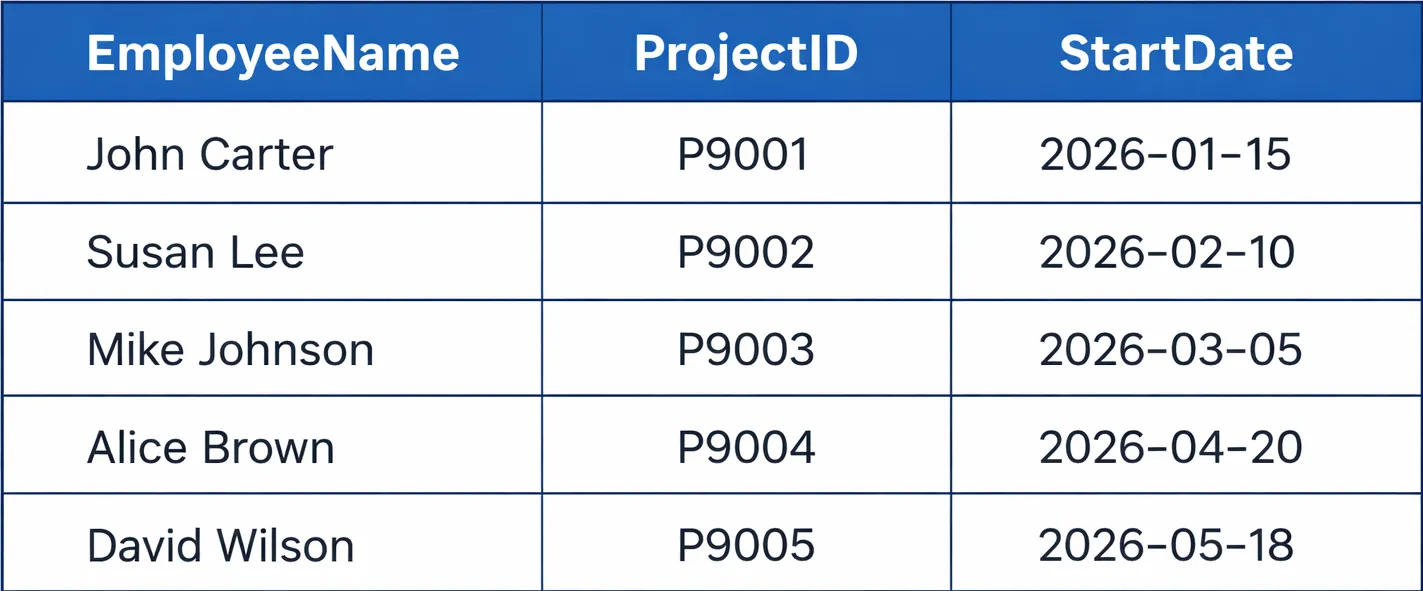
The item-oriented mannequin combines database know-how with object-oriented programming. The system shops knowledge as objects which include each state info and operational strategies. The item mannequin allows purposes to make use of commonplace inheritance and encapsulation mechanisms which assist them handle complexity.
- NoSQL and Different Fashions:
Organizations require NoSQL database techniques as a result of their knowledge necessities demand each intensive capability and versatile storage. The techniques function with out strict schema constructions. Doc shops use digital paperwork which observe the JSON construction as the idea for his or her record-keeping system whereas key-value shops present fundamental search capabilities. Column-family shops use huge desk constructions whereas graph databases use node and edge fashions to characterize their knowledge.
{
"EmployeeName": "John Carter",
"Tasks": [
{
"ProjectName": "AI Dashboard",
"DurationMonths": 6
}
]
}Knowledge Modeling Abstraction Ranges
Knowledge modeling is commonly described in three abstraction layers (generally referred to as the three-schema structure):
The best degree of this technique offers full knowledge protection with none technical facets. The conceptual mannequin defines high-level entities and relationships in enterprise phrases.
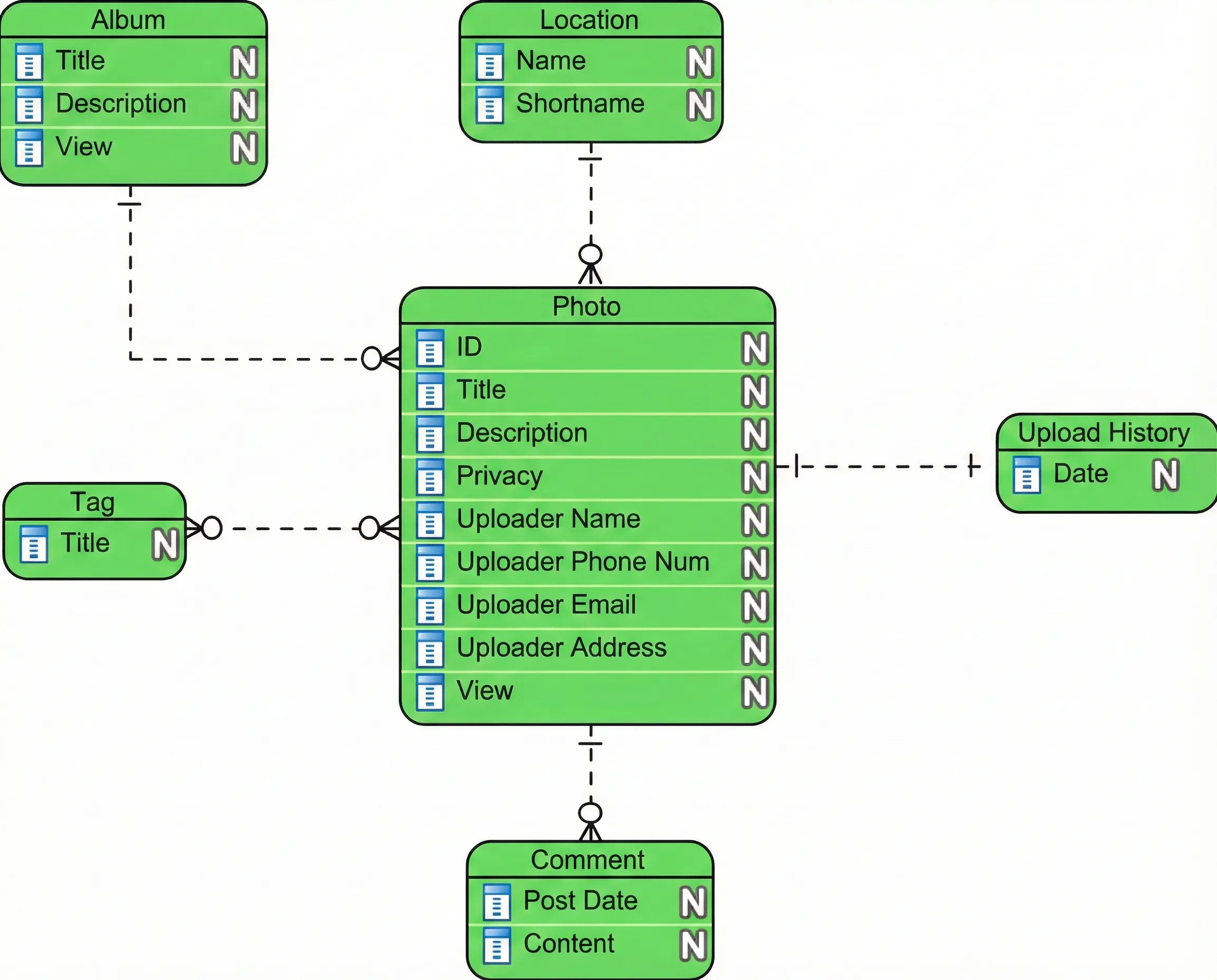
The reason expands by way of the identification of particular tables which include specific columns and their related knowledge sorts whereas remaining impartial from any specific database administration system. The logical mannequin takes the conceptual entities and lists their attributes and keys. The system shows major keys along with international keys whereas it offers knowledge sort specs that embody integer and string sorts with out addressing bodily implementation particulars.
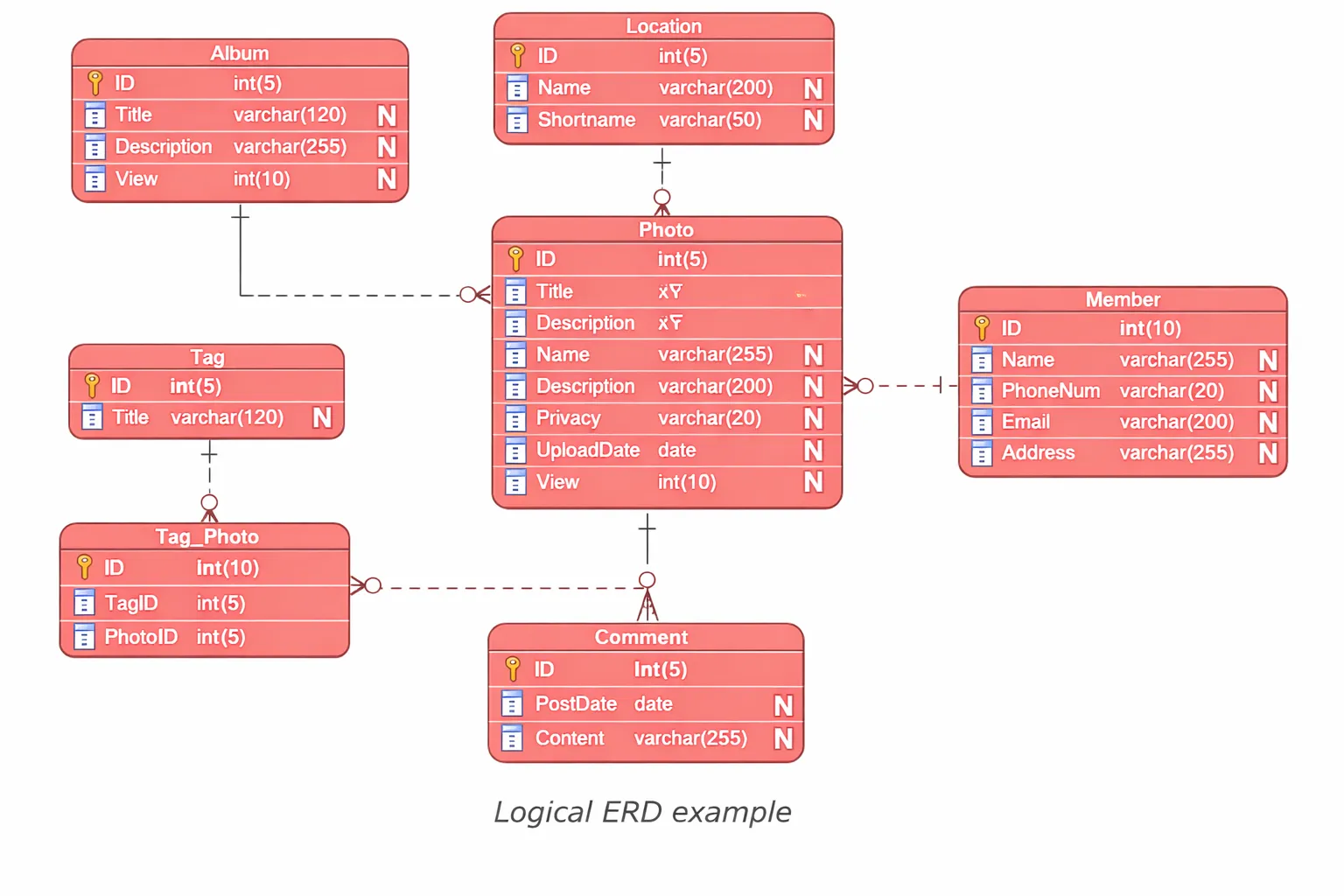
Probably the most full degree of element connects to a selected database administration system. The execution defines desk construction by way of its implementation particulars which embody specs for column sorts and indexes and storage engines and partitions and different components.
CREATE INDEX idx_order_customer ON Orders(CustomerID);
SELECT indexname, indexdef
FROM pg_indexes
WHERE tablename="orders";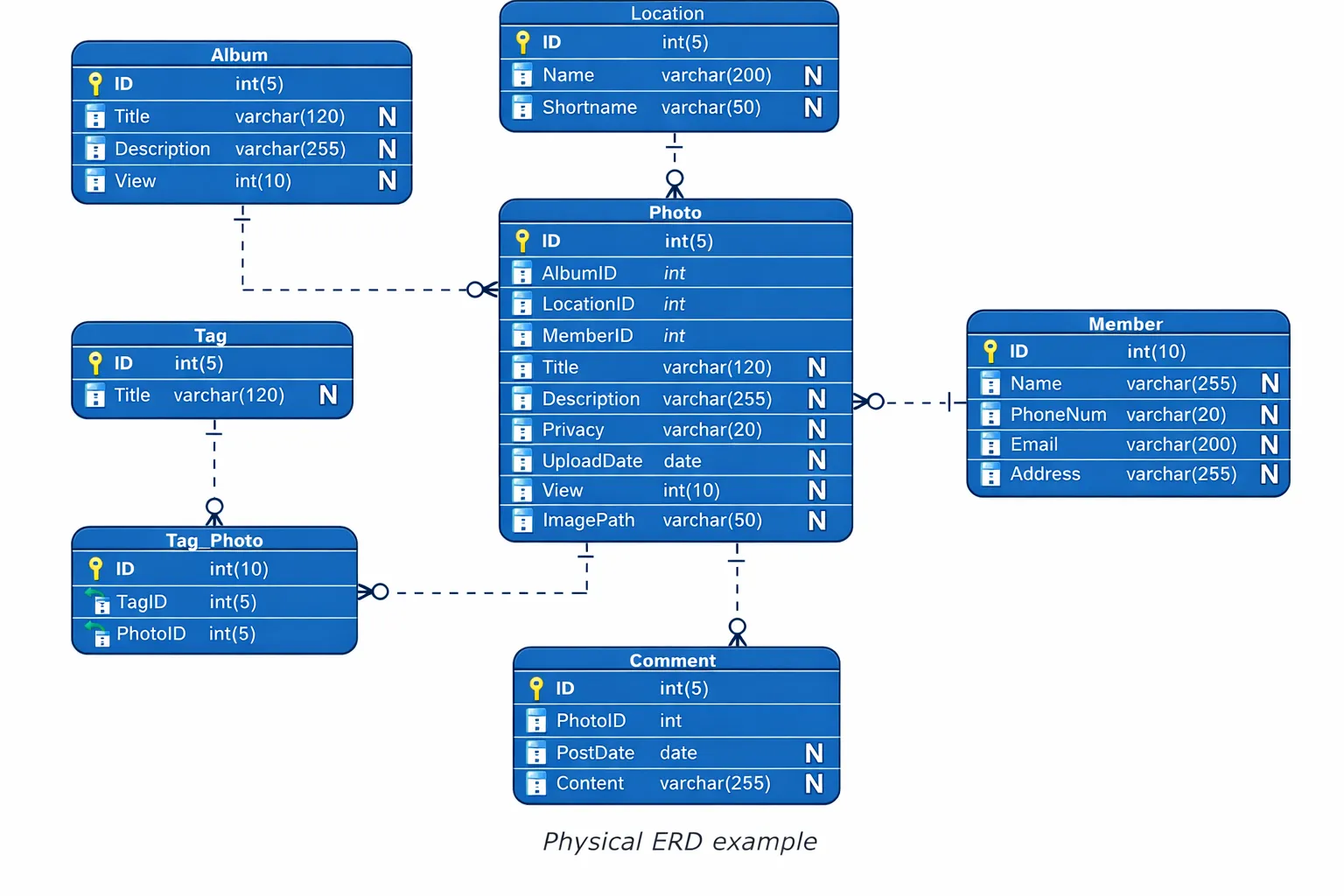
Key Elements of a DBMS Knowledge Mannequin
The elemental components of information fashions function their important parts. The examine of those parts offers design capabilities that may obtain excessive efficiency and exact outcomes.
Entities and Attributes: Entities characterize real-world objects akin to college students or programs. Attributes describe entity properties like identify, electronic mail, or course title. The attribute definitions present clear descriptions which assist to remove uncertainty and make knowledge validation simpler.
Relationships and Cardinality: Relationships set up the connections that hyperlink totally different entities. Cardinality defines the variety of components that may exist inside a specific relationship.
The three most important relationship sorts encompass:
- One-to-One relationships
- One-to-Many relationships
- Many-to-Many relationships
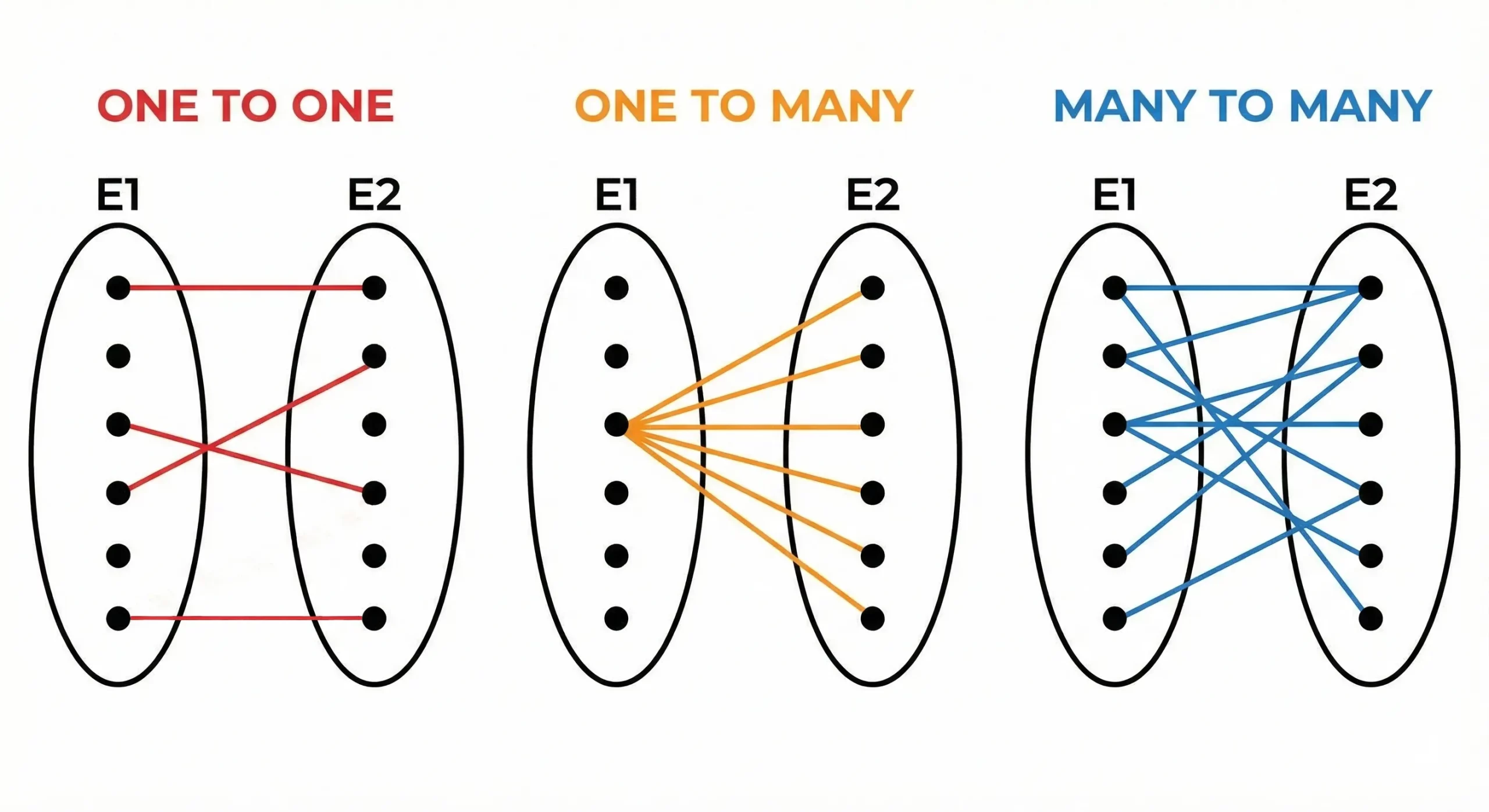
The system enforces constraints which safeguard knowledge integrity by way of their established guidelines.
- Major Key: The first key capabilities as a novel identifier that distinguishes all data inside a desk. The system prevents duplicate entries whereas it offers quick entry by way of indexing.
- Overseas Key: The international key establishes a connection between two related tables. The system maintains referential integrity by blocking any makes an attempt to create invalid hyperlinks.
- Distinctive and Examine Constraints: Distinctive constraints stop duplicate values. Examine constraints validate knowledge ranges or codecs.
The Entity-Relationship (ER) Mannequin
The Entity-Relationship (ER) mannequin serves as a extensively used technique for creating conceptual fashions. The mannequin allows the illustration of precise objects by way of entities which show their inside construction. An entity corresponds to an object or idea (e.g. Pupil or Course), every with attributes (like StudentID, Identify, Age).
A number of entities join by way of a relationship (like Enrollment) which exhibits their relationship by describing their mutual actions (as an illustration, “a pupil enrolls in programs”).
The ER mannequin captures the essence of the information with out committing to a desk structure. The connection between Pupil and Course exhibits a many-to-many connection which we are able to characterize by way of a diagram.
A relational system transforms entities into tables whereas attributes grow to be columns, and international keys serve to ascertain relationships between entities.
Key Elements (Major/Overseas Keys, Constraints)
- A Major Secret’s a novel identifier for desk rows. For instance, StudentID uniquely identifies every pupil. A major key column can not include NULL and should be distinctive. It ensures we are able to all the time inform data aside.
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY - A Overseas Secret’s a column or set of columns that hyperlinks to the first key of one other desk. This creates a referential integrity rule: the DBMS won’t enable an enrollment that factors to a non-existent pupil. In SQL, we’d write:
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Pupil(StudentID) - Different constraints like NOT NULL, UNIQUE, or CHECK can implement knowledge guidelines (e.g., a grade column should be between 0 and 100). These constraints maintain the information legitimate in accordance with the mannequin
ALTER TABLE Pupil
ADD CONSTRAINT unique_name UNIQUE (student_name);Pattern Pupil Administration Database (MySQL Instance)
So for demonstration let’s use a fundamental Pupil Administration System. The system consists of three entities that are Pupil and Course and Enrollment that serves because the hyperlink between college students and programs. We exhibit the MySQL relational schema setup by way of the next course of.
CREATE TABLE Pupil (
StudentID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
StudentName VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
Main VARCHAR(50),
Age INT
);
CREATE TABLE Course (
CourseID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
CourseName VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
Division VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Enrollment (
EnrollmentID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
StudentID INT NOT NULL,
CourseID INT NOT NULL,
Grade CHAR(2),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Pupil(StudentID),
FOREIGN KEY (CourseID) REFERENCES Course(CourseID)
);On this schema:
- The StudentID and CourseID function major keys for his or her respective tables which leads to each pupil and course receiving distinct identification numbers.
- The Enrollment desk has two international keys (StudentID, CourseID) that reference the respective major keys. This enforces that each enrollment entry corresponds to a legitimate pupil and course.
- The AUTO_INCREMENT attribute (MySQL-specific) routinely generates distinctive IDs. The NOT NULL constraint ensures these ID fields will need to have values.
- Different constraints like
NOT NULLon names stop lacking knowledge.
This design is helps in creating normalization, so pupil and course info isn’t duplicated in every enrollment row, lowering redundancy
Inserting Pattern Knowledge
INSERT INTO Pupil (StudentName, Main, Age) VALUES
('Alice', 'Biology', 20),
('Bob', 'Laptop Science', 22);
INSERT INTO Course (CourseName, Division) VALUES
('Database Methods', 'Laptop Science'),
('Calculus I', 'Arithmetic');
INSERT INTO Enrollment (StudentID, CourseID, Grade) VALUES
(1, 1, 'A'),
(1, 2, 'B'),
(2, 1, 'A');These inserts add two college students and two programs. Then we add enrollments linking them: for instance, (1,1,’A’) means Alice (StudentID=1) takes Database Methods (CourseID=1) and earned an A grade. MySQL enforces international key constraints which stop customers from including enrollments that include non-existent StudentID or CourseID values. Our pattern knowledge exists in third Regular Kind (3NF) as a result of each knowledge aspect exists as a single storage merchandise.
Normalization in DBMS
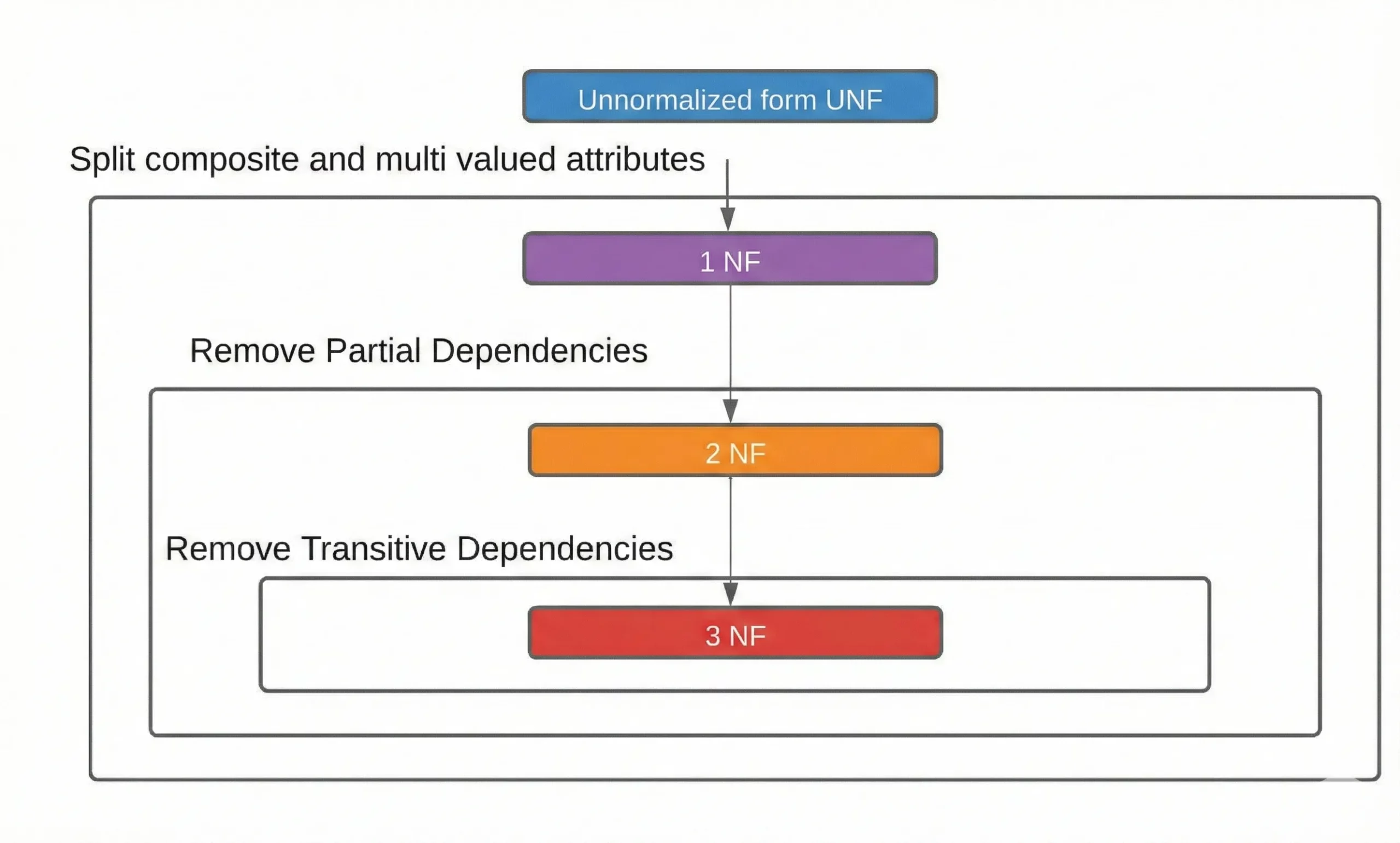
Normalization organizes tables by way of its course of which eliminates duplicate knowledge and prevents points throughout updates. The conventional kinds guidelines which we make the most of to implement our system embody the next definitions:
- 1NF (First Regular Kind): Every desk cell ought to maintain a single worth (no repeating teams).
- 2NF (Second Regular Kind): In tables with composite keys, non-key columns should rely upon the entire key, not simply a part of it.
- 3NF (Third Regular Kind): Non-key columns should rely solely on the first key, not on different non-key columns.
The method of normalization brings two advantages as a result of it decreases knowledge duplication which results in storage financial savings and prevents knowledge inconsistencies whereas making knowledge upkeep simpler. The Pupil desk serves as the one supply for updating Alice’s main and age info. The method of information normalization creates advantages however its extremely standardized schemas require a number of JOIN to construct report knowledge which causes delays in executing complicated queries.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Knowledge Fashions
| Benefits | Disadvantages |
| Guarantee correct and constant illustration of information | Preliminary design requires important time for complicated techniques |
| Cut back knowledge redundancy and keep away from duplication | Massive schemas grow to be obscure |
| Major and international keys set up clear relationship definitions | Minor structural modifications can impression your entire system |
| Enhance knowledge integrity by way of constraints and guidelines | Requires experience in each area data and database techniques |
| Make databases extra comprehensible for builders and analysts | Extremely dynamic techniques might endure from over-engineered fashions |
| Assist ongoing upkeep and future growth |
Conclusion
The muse of any reliable database system relies on its knowledge fashions which function elementary parts. They help in creating databases which meet precise wants by way of their structured design and talent to deal with growing knowledge volumes and obtain operational effectivity. Understanding conceptual and logical and bodily fashions lets you handle system knowledge conduct. Database upkeep turns into less complicated and question execution quickens by way of correct implementation of modeling and normalization and indexing strategies. Knowledge modeling requires funding of time as a result of it advantages each small purposes and enormous enterprise techniques.
Incessantly Requested Questions
A. It defines how knowledge is structured, associated, and constrained, serving as a blueprint for constructing dependable and environment friendly databases.
A. Conceptual focuses on enterprise entities, logical defines tables and keys, and bodily specifies implementation particulars like knowledge sorts and indexes.
A. It reduces redundancy, prevents replace anomalies, and improves knowledge integrity by organizing knowledge into well-structured tables.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.


