
Final Up to date on: twenty fifth Might 2025, 03:15 pm
For the primary time, the expansion in China’s clear energy era has precipitated the nation’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions to fall regardless of fast energy demand progress.
The brand new evaluation for Carbon Transient exhibits that China’s emissions have been down 1.6% year-on-year within the first quarter of 2025 and by 1% within the newest 12 months.
Electrical energy provide from new wind, photo voltaic and nuclear capability was sufficient to chop coal-power output at the same time as demand surged, whereas earlier falls have been resulting from weak progress.
The evaluation, primarily based on official figures and industrial knowledge, exhibits that China’s CO2 emissions have now been steady, or falling, for greater than a 12 months.
Nonetheless, they continue to be just one% under the newest peak, implying that any short-term soar might trigger China’s CO2 emissions to rise to a brand new document.
Different key findings embrace:
- Development in clear energy era has now overtaken the present and long-term common progress in electrical energy demand, pushing down fossil gasoline use.
- Energy-sector emissions fell 2% year-on-year within the 12 months to March 2025.
- If this sample is sustained, then it will herald a peak and sustained decline in China’s power-sector emissions.
- The commerce “conflict” initiated by US president Donald Trump has prompted renewed efforts to shift China’s financial system in the direction of home consumption, moderately than exports.
- A brand new pricing coverage for renewables has precipitated a rush to put in earlier than it takes impact.
- There’s a rising hole that might have to be bridged if China is to fulfill the 2030 emissions targets it pledged underneath the Paris Settlement.
If sustained, the drop in power-sector CO2 on account of clean-energy progress might presage the kind of structural decline in emissions anticipated in earlier evaluation for Carbon Transient.
The development of falling power-sector emissions is more likely to proceed in 2025.
Nonetheless, the outlook past that relies upon strongly on the clear vitality and emissions targets set in China’s subsequent five-year plan, resulting from be revealed subsequent 12 months, in addition to the financial coverage response to the Trump administration’s hostile commerce coverage.
China’s emissions decline resulting from clear energy
Over the previous decade, China’s CO2 emissions from fossil fuels and cement have risen by practically a fifth, however there have been ups and downs alongside the way in which.
The shallow decline in 2015 and 2016 was resulting from a droop that adopted a spherical of stimulus measures, whereas zero-Covid controls precipitated a sharper fall in 2022. General, nonetheless, emissions have continued to extend, pausing solely during times of financial stress.
Extra not too long ago, there have been indicators that China’s CO2 emissions might be near reaching a peak and plateau, or perhaps a interval of structural decline.
The most recent knowledge, for the primary quarter of 2025, exhibits that China’s CO2 emissions have now been steady or falling for greater than a 12 months, as proven within the determine under.
Nonetheless, with emissions remaining simply 1% under the latest peak, it stays doable that they might soar as soon as once more to a brand new document excessive.
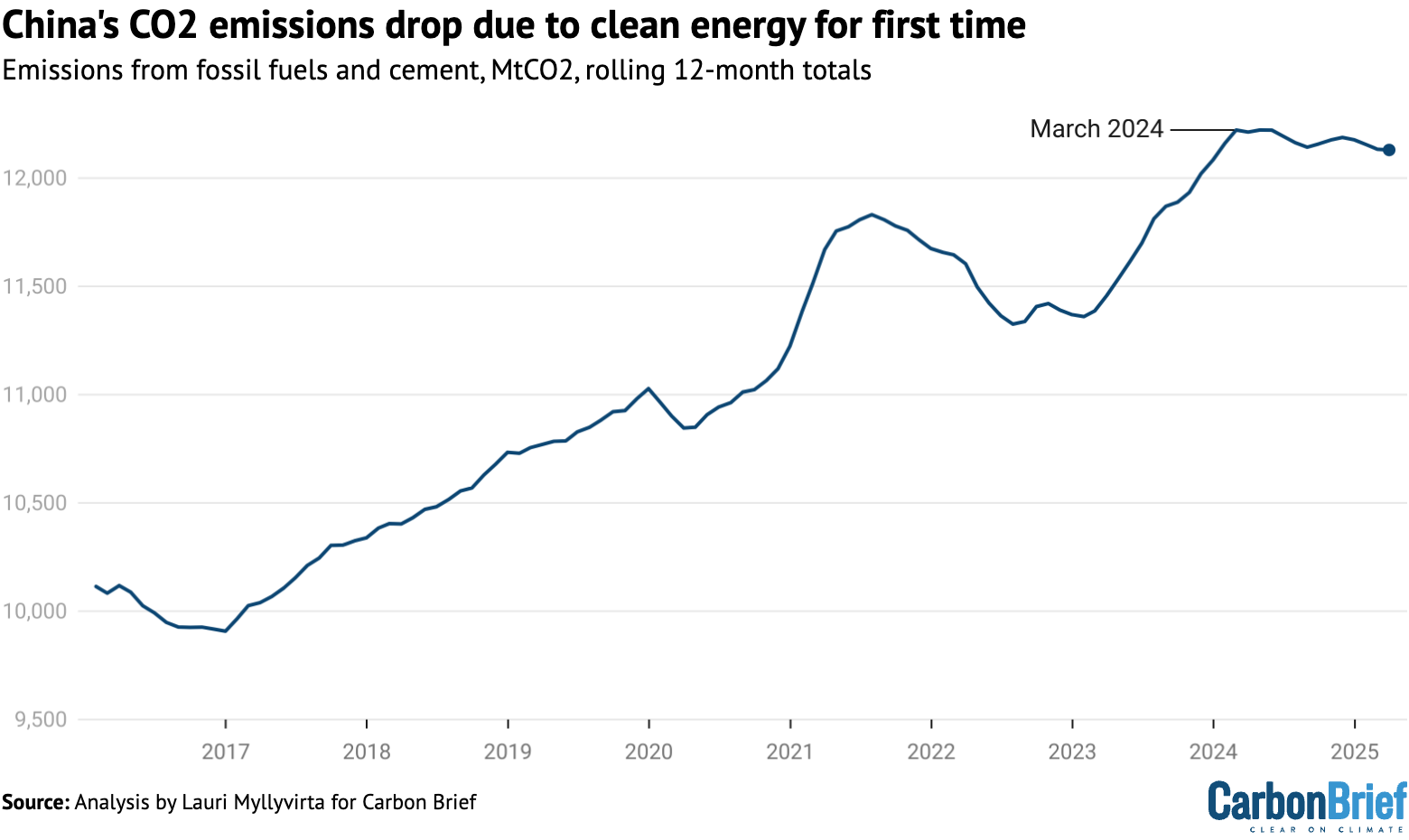
Due to this fact, the longer term path of China’s CO2 emissions hangs within the stability, relying on tendencies inside every sector of its financial system, in addition to China’s response to Trump’s tariffs.
These sectoral tendencies are explored additional within the sections under, together with indicators on what might be coming subsequent from Chinese language policymakers as they take into account the nation’s worldwide local weather pledge for 2035 and the five-year plan for 2026-2030.
Energy-sector emissions fall whereas different sectors rebound
The discount in China’s first-quarter CO2 emissions in 2025 was resulting from a 5.8% drop within the energy sector. Whereas energy demand grew by 2.5% total, there was a 4.7% drop in thermal energy era — primarily coal and gasoline.
Will increase in photo voltaic, wind and nuclear energy era, pushed by investments in new producing capability, greater than lined the expansion in demand. The rise in hydropower, which is extra associated to seasonal variation, helped push down fossil energy era.
Energy-sector emissions fell by greater than whole era from fossil fuels, because the share of biomass and gasoline elevated, whereas common coal energy plant effectivity improved.
Particularly, the typical quantity of coal wanted to generate every unit of electrical energy at coal-fired energy vegetation fell by 0.9% year-on-year.
The primary-quarter discount in CO2 emissions from coal use within the energy sector is proven on the backside of the determine under, under CO2 modifications in different sectors.

Outdoors of the ability sector, emissions elevated 3.5%, with the biggest rises in the usage of coal within the metals and chemical compounds industries.
The coal-to-chemicals business is present process fast enlargement, pushed by considerations about dependence on imported oil and gasoline. In the course of the first quarter of 2025, it was additionally benefiting from extra beneficial economics resulting from decrease coal costs and comparatively excessive oil costs.
Crude metal manufacturing elevated 0.6% year-on-year, metallic merchandise output by 6% and non-ferrous metals manufacturing by 2%. All of those will increase have been primarily resulting from a soar in March. Metals demand was boosted by the bump in exports forward of the tariffs, however excessive output has continued effectively into April.
Actual-estate development “begins” fell by 24% and gross sales of latest properties by 3%, indicating that the demand for cement, metal and glass from the development sector continues to say no.
In distinction, financial output in car and equipment manufacturing elevated by 12% and 13%, respectively, signalling elevated demand for metals.
Cement manufacturing fell by 1.4%, a slower charge of lower than in earlier years, seemingly resulting from an earlier begin to weather-dependent development exercise because of heat climate.
Gasoline consumption elevated by an estimated 6% within the energy sector, resulting from a 14% enhance in gas-fired energy era capability, at the same time as the typical utilisation of the vegetation fell. Nonetheless, gasoline consumption fell in different sectors, outweighing the rise for energy.
Oil merchandise consumption elevated barely, as proven by the bar on the high within the determine above. Hotter climate meant that weather-dependent development and agricultural exercise rose earlier within the 12 months than standard.
Nonetheless, structural elements, significantly car electrification and the shift to liquified pure gasoline (LNG) within the freight sector, level to continued declines in oil demand.
Have China’s emissions peaked?
Following the 1.6% decline within the first quarter of 2025, China’s emissions have now been steady or falling for greater than a 12 months, ranging from the start of March 2024.
Nonetheless, emissions within the 12 months to the top of March 2025 have been down just one% from their latest peak, implying that any short-term soar might result in a brand new document excessive.
After the sharp discount within the first quarter, emissions from energy era at the moment are down year-on-year for the latest 12 months.
This has occurred 4 occasions earlier than over the previous 4 many years — in 2009, 2012, 2015 and 2022. Nonetheless, the present drop is the primary time that the principle driver is progress in clear energy era.
The falls in 2009 and 2012 have been associated to the worldwide monetary disaster and the Euro space disaster, whereas the drop in 2015 was pushed by the development and industrial sector droop that adopted the 2008-12 stimulus program.
These financial shocks resulted within the sharp discount in electrical energy demand proven within the determine under. The drop in 2022 was a mix of gradual energy demand progress resulting from strict “zero-Covid” measures and comparatively sturdy clean-power additions.
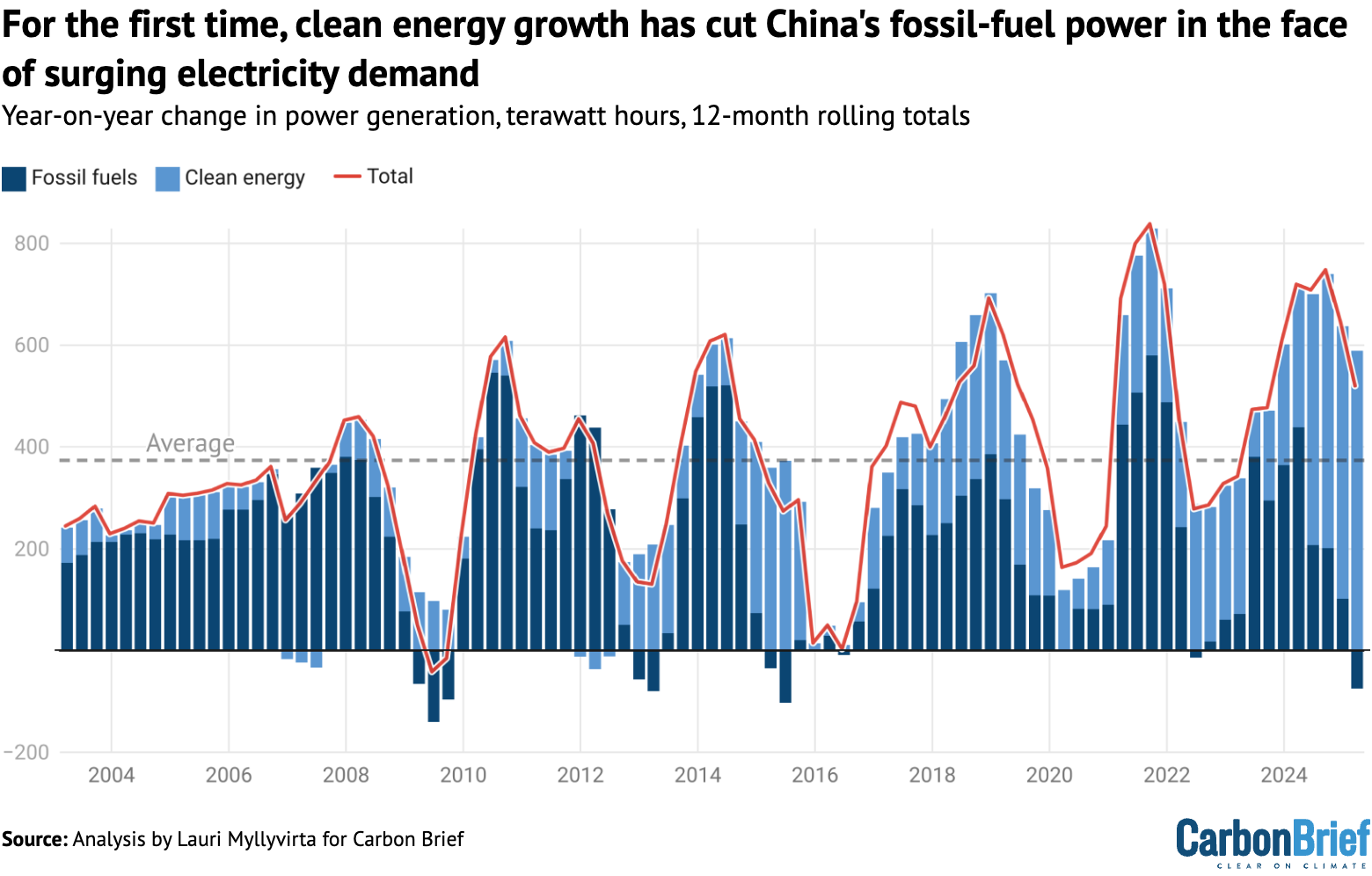
Importantly, the expansion in clear energy era within the first quarter of 2025 was not solely bigger than the rise in demand total, it was additionally greater than the typical enhance in demand over the previous 15 years, marked by the dashed line within the determine above.
Furthermore, hydropower has been steady year-on-year up to now six months, implying that the clean-energy progress has been pushed by will increase in photo voltaic, wind and nuclear energy capability, not year-to-year variation in hydropower output.
Wanting past electrical energy era, all sectors registered a fall in emissions over the latest 4 months from December 2024 to March 2025, aside from coal-to-chemicals.
To ensure that China’s emissions total to peak after which begin declining, CO2 cuts in declining sectors might want to outweigh continued progress elsewhere.
For instance, course of emissions from cement manufacturing peaked in 2021 and have declined by 27% since then, as proven within the high left chart within the determine under.
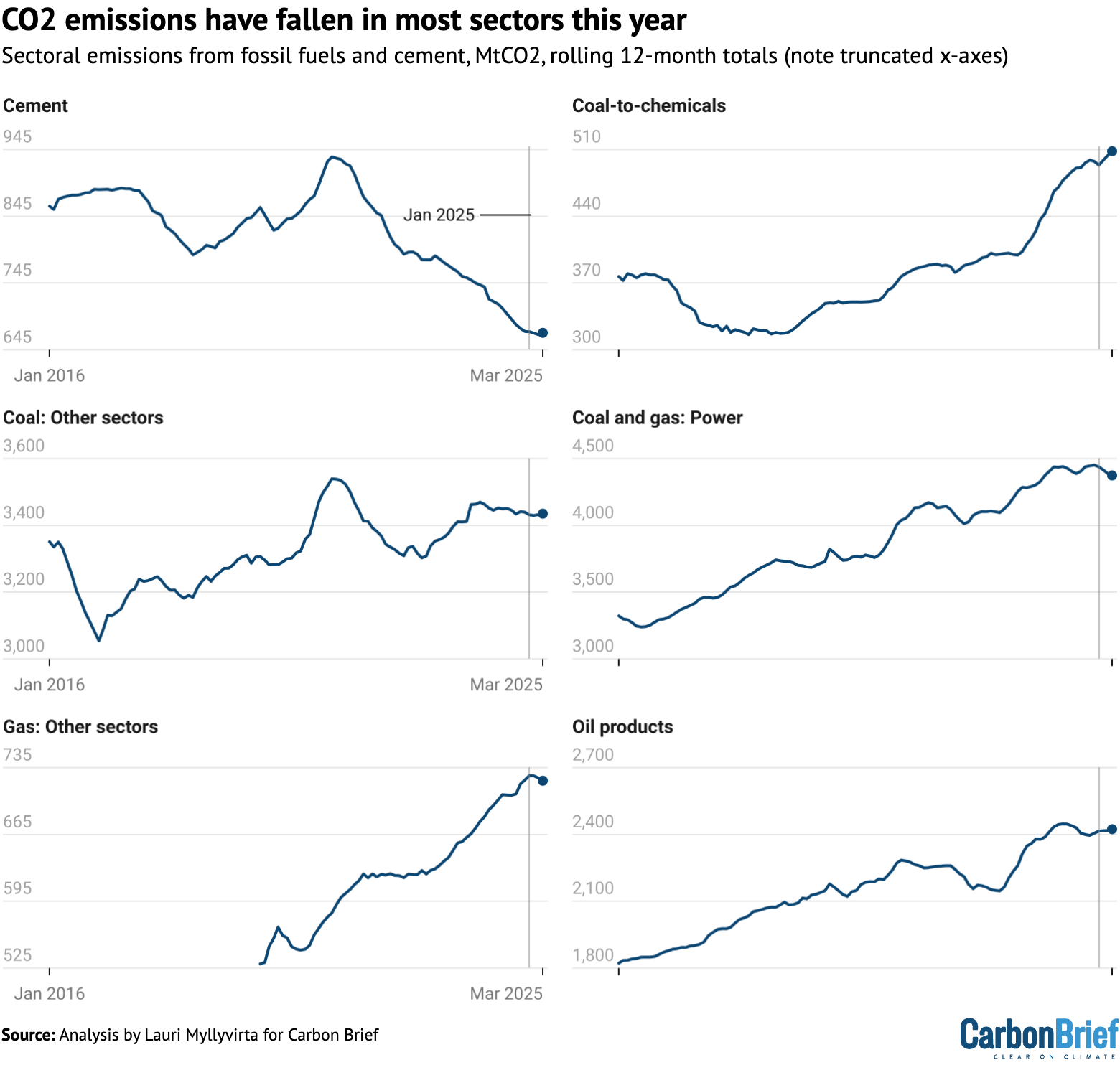
Coal use exterior the ability and chemical compounds sectors peaked similtaneously cement, however has been rebounding since then and is now near earlier peak ranges.
The China Coal Affiliation expects coal use within the metal and constructing supplies industries to fall, whereas coal consumption within the chemical business is projected to proceed rising.
Hopes of future progress in demand for coal are pinned on the chemical sector, described as a shift from utilizing coal primarily as a gasoline to a job as each a gasoline and a uncooked materials.
The affiliation additionally believes that coal-fired energy era will resume progress — not less than within the brief time period — however it not too long ago revised down its projections for 2025 in contrast with the outlook on the finish of 2024.
The tariff “conflict” might have affected expectations. One evaluation suggests a 0.5 to 1 proportion level discount in China’s GDP progress charge because of the tariffs might lead to the same discount in demand for thermal coal — primarily used at energy stations.
Oil product consumption has been declining for the reason that post-Covid rebound led to March 2024, falling 2% from its peak. The long-term development is anticipated to be downwards, because of the electrification of transportation, regardless of rising demand for chemical compounds and aviation.
Gasoline use has been falling for a number of months, however the development is probably going nonetheless growing.
The desk under lists the 12-month intervals with the best emissions for every sector, in addition to the discount for the reason that newest peak in every case.
For all the sectors apart from cement manufacturing, it’s too early to declare a definitive peak in emissions. Nonetheless, there are indicators that different sectoral peaks might be previous their peak, too.
Certainly, for oil merchandise consumption and metal manufacturing, business projections point out that the longer term development is more likely to be falling.
For the ability sector, clean-energy additions at or above present ranges would seemingly result in a structural peak, as clean-energy progress would greater than cowl electrical energy demand progress.
Collectively, these sectors cowl greater than 80% of China’s whole emissions. If all of them enter a structural decline, then whole emissions are very seemingly to take action too.
China pushes home demand in response to US tariffs
The financial and emissions outlook for this 12 months and past will likely be affected by the Trump administration’s unprecedented commerce tariffs — and China’s counter-measures.
The preliminary impression was a drop in emissions resulting from decrease manufacturing facility output in export-oriented coastal provinces and doable knock-on impacts on funding and client spending.
Conversely, the momentary easing of tariffs for 90 days will lead to a rush of orders from the US to make up for the short-lived slowdown in commerce and to stockpile items earlier than the aid ends.
China’s reactions to the tariffs targeted on counteracting the financial impacts with stimulus.
An nameless remark piece in Individuals’s Every day, the principle Communist celebration affiliated newspaper, says the nation ought to “try to make consumption the principle driving drive and ballast stone of financial progress”, leveraging China’s giant home market.
(The piece has the byline “Individuals’s Every day commentator”, which suggests that it’s written by somebody with authority.)
The article says that it will contain growing client earnings, whereas easing monetary and social burdens to spice up buying energy and willingness to eat.
Whereas the momentary easing of tariffs will cut back the urgency of those measures, the US tariff charge on China, at 40%, stays a lot greater than it was earlier than Trump’s presidency — and China’s leaders will seemingly need to put together towards the chance of renewed tariff hikes.
The main focus will likely be creating home markets for the merchandise China exports to the US. The long-held purpose of rebalancing China’s financial system in the direction of consumption might lastly change into actuality in consequence. A profitable rebalancing might imply much less energy-intensive progress.
China’s response additionally contains redoubling its give attention to “new high quality productive forces”, an idea that emphasises new know-how.
The idea contains the clean-energy business, which has change into such an necessary financial driver in China that it will be laborious to depart out of stimulus plans.
A brand new listing of low-carbon demonstration initiatives, revealed by the Nationwide Improvement and Reform Fee, gives a have a look at China’s priorities for clean-energy funding. Inexperienced hydrogen, vitality storage, “digital energy vegetation” and industrial decarbonisation primarily based on hydrogen are new progress areas.
When it comes to the emissions implications of China’s response to Trump’s tariffs, the large query is whether or not stimulus targeted at these favoured sectors — together with the brand new low-carbon focus areas and different clean-energy industries — is deemed ample.
Some conventional recipients of stimulus spending, akin to shipbuilding and public infrastructure, have already posted sturdy progress within the first quarter of this 12 months on account of stimulus measures introduced in 2024.
New wind and photo voltaic pricing coverage will increase uncertainty
An extra supply of uncertainty for China’s emissions comes within the type of its new electrical energy pricing coverage for renewable vitality, which enters into drive in June.
The brand new coverage removes value ensures pegged to coal-power costs, with new wind and photo voltaic initiatives imagined to safe direct contracts with electrical energy patrons. That is more likely to lead to decrease costs being paid to new wind and photo voltaic initiatives.
Nonetheless, it presents extra beneficial pricing — by way of “contracts for distinction” — to the quantity of latest capability wanted to fulfill central authorities vitality targets.
The fast impact of the coverage will seemingly be a rush of initiatives speeding to finish set up earlier than the June deadline, in order to safe assured costs.
This rush was already obvious within the newest knowledge: 23 gigawatts (GW) of photo voltaic and 13GW of wind was added in March alone, up 80% and 110% from earlier data for the month.
Moreover, this 12 months’s installations are more likely to be very sturdy, even topping final 12 months’s document, as lots of centralised solar energy and wind-power initiatives are racing to finish earlier than the top of the 14th five-year plan interval.
The China Wind Vitality Affiliation expects a brand new document of 105-115GW put in this 12 months throughout onshore and offshore wind initiatives — up from the record-breaking 80GW final 12 months — primarily based on very lively bidding final 12 months. It additionally expects volumes to remain at that stage even in 2026 and to then develop additional in the direction of 2030.
The China Electrical energy Council predicts an excellent bigger wind-power capability addition of 120GW in 2025. One other analyst initiatives a 20% drop in wind-power capability additions in 2026, however after an excellent steeper enhance in 2025 to 120-130GW of capability added. So he additionally expects 2026 installations to be far above the present document 12 months of 2024.
For photo voltaic, the China Photovoltaic Trade Affiliation forecasts a drop in installations of 8-23% this 12 months, from the staggering document of 278GW final 12 months. Even the low finish of this projection would see installations keep at 2023 ranges in 2025 after which get better from there. The China Electrical energy Council’s projection for photo voltaic additions in 2025 matches the low finish of the business affiliation’s forecast.
The determine under, primarily based on these varied projections, exhibits that further electrical energy era from new clear energy capability is anticipated to stay above final 12 months’s record-breaking ranges in each 2025 and 2026.
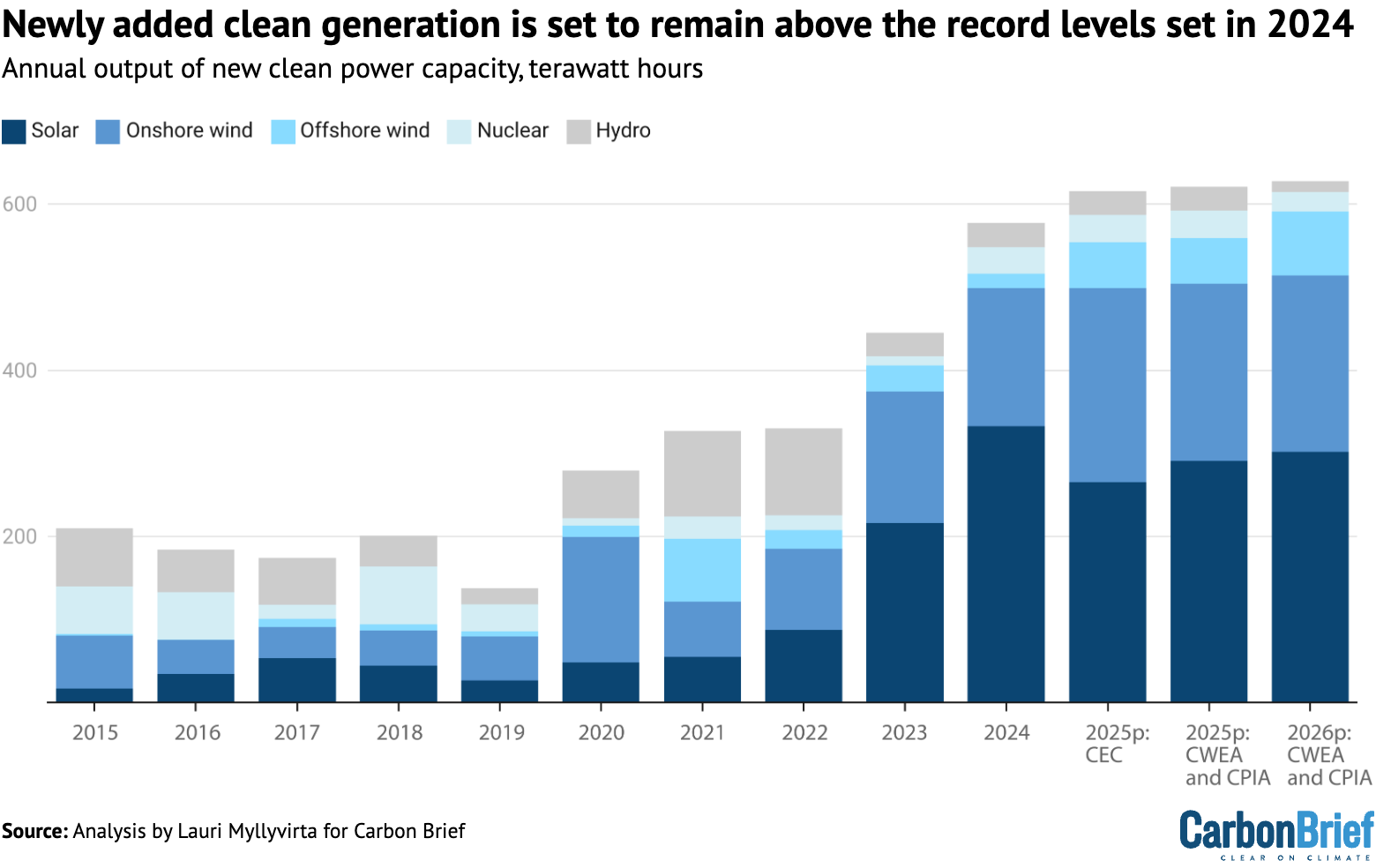
The projections proven within the determine above illustrate that the vitality business expects to have the ability to navigate the brand new renewable pricing coverage and to keep up a excessive stage of wind and photo voltaic additions over the following two years.
The coverage has, nonetheless, created much more uncertainty. The stop-go cycle of a flood of installations within the first half of this 12 months after which a slowdown within the second half — seemingly particularly within the distributed photo voltaic section — is more likely to be a troublesome time for the business.
The uncertainty relates above all to 2 issues. First is the native implementation of the coverage, as provincial governments have lots of leeway right here. Given the financial significance of unpolluted vitality for a lot of provinces, they are often anticipated to hunt to implement the coverage in a manner that minimises disruptions to the business.
The opposite supply of uncertainty is central authorities targets. The pricing coverage ties the supply of extra favorable pricing to central authorities vitality targets, after clean-energy progress outpaced these targets by a large margin up to now few years.
This emphasises the significance of the targets set for the following 5 12 months plan. The Nationwide Vitality Administration (NEA) is concentrating on “greater than 200GW” per 12 months of clean-energy capability added, which is way decrease than the 360GW added final 12 months.
The impact of the pricing coverage additionally is dependent upon market situations, after all, with a danger of oversupply of coal-fired energy because of the ongoing fast addition of latest coal-fired energy vegetation.
China’s nuclear development additionally retains accelerating, with one other 10GW of reactor initiatives accepted in April, on high of 10GW accepted in every of the earlier two years. These initiatives will contribute to wash energy provide in the direction of 2030 as they’re accomplished.
China faces widening hole to Paris pledge
The uncertainty round wind and photo voltaic enlargement additionally has implications for China’s worldwide local weather pledges underneath the Paris Settlement.
After exceptionally gradual progress in 2020-23, China is considerably off observe for its 2030 dedication to cut back carbon depth — the emissions per unit of financial output. It’s nearly sure to overlook its 2025 goal. Carbon depth fell by 3.4% in 2024, falling wanting the speed of enchancment wanted to fulfill the 2025 and 2030 targets.
The authorities work plan for 2025 didn’t set a carbon depth goal. It solely included a goal for decreasing the depth per unit of GDP for vitality provide from fossil fuels by 3%, excluding use for uncooked supplies.
This gives an oblique indication of the focused enchancment in carbon depth. In 2024, carbon depth fell by 3.4%, whereas fossil vitality depth fell by 3.8%. If the ratio is analogous in 2025, then carbon depth would wish to fall by round 2.5% at a minimal, permitting CO2 emissions to extend by greater than 2%, if the goal for five% GDP progress can be met.
The absence of a carbon depth goal and the shortage of emphasis on decreasing carbon depth additionally indicators that assembly the goal will not be seen as a precedence in the meanwhile.
The federal government work plan emphasised the “dual-carbon” targets of peaking CO2 emissions earlier than 2030 and attaining carbon neutrality earlier than 2060.
Nonetheless, these targets enable CO2 emissions to proceed to extend till the top of the last decade, implying the potential for a big absolute emission enhance from 2024 ranges by 2030. The “dual-carbon” targets, even when met, due to this fact don’t assure the supply of China’s present key worldwide local weather dedication, the 2030 carbon-intensity goal.
Even when emissions fell this 12 months, enhancements to carbon depth would wish to speed up sharply within the subsequent 5 years to fulfill China’s 2030 Paris dedication.
If China stays dedicated to its 2030 pledge, then this acceleration would have to be mirrored within the targets set within the nation’s subsequent five-year plan.
Outlook for 2025 and past
The previous 12 months mark a doubtlessly important turning level for China’s CO2 emissions, with clean-energy progress for the primary time outpacing demand progress and displacing fossil gasoline use within the energy sector.
Document-breaking clear vitality additions anticipated in 2025, regardless of new pricing coverage uncertainties, recommend that the development will proceed this 12 months.
The longer-term trajectory relies upon closely on the targets set within the upcoming five-year plan and on the financial coverage response to US tariffs and different financial headwinds.
Within the brief time period, the US tariffs will dampen vitality demand progress and emissions. Financial coverage designed to offset the impacts of Trump’s tariffs will seemingly enhance the clean-energy sector additional and may result in a shift in the direction of home consumption as an financial driver, implying decrease vitality consumption progress relative to GDP.
However, earlier rounds of financial stimulus in China have led to sharp will increase in emissions. If China is to ship stimulus that targets consumption and new know-how, moderately than emissions-intensive development and heavy business, then it’s going to require a big break with earlier patterns.
Whether or not power-sector emissions have peaked will likely be decided by a race between progress in clear vitality provide and whole energy demand progress.
The brand new renewable electrical energy pricing coverage, which ties the quantity of “contracts for distinction” given out to new photo voltaic and wind initiatives to nationwide clear vitality targets, additional will increase the significance of target-setting in China’s upcoming 2035 local weather targets underneath the Paris Settlement and within the subsequent fifteenth five-year plan, overlaying 2026-2030.
Sector-by-sector evaluation means that, along with the ability sector, emissions have seemingly additionally peaked within the constructing supplies and metal sectors, in addition to oil merchandise consumption.
These sectors collectively symbolize over 80% of China’s fossil fuel-related CO2 emissions. Nonetheless, there are uncertainties and potential for short-term rebound in all of those sectors.
The sector with remaining potential for substantial emissions progress is coal-to-chemicals. The drop in oil costs after US tariff bulletins will undermine the profitability of this sector and certain result in decrease utilisation of vegetation, at the same time as extra capability is added. China’s counter-tariffs on imports of petrochemical merchandise from the US might have benefited the business — however these have reportedly been waived.
All of this implies that there’s potential for China’s emissions to proceed to fall and for the nation to realize substantial absolute emissions reductions over the following 5 years.
Nonetheless, coverage selections working in the wrong way might simply as simply see emissions enhance additional in the direction of 2030.
In regards to the knowledge
Information for the evaluation was compiled from the Nationwide Bureau of Statistics of China, Nationwide Vitality Administration of China, China Electrical energy Council and China Customs official knowledge releases, and from WIND Data, an business knowledge supplier.
Wind and photo voltaic output, and thermal energy breakdown by gasoline, was calculated by multiplying energy producing capability on the finish of every month by month-to-month utilisation, utilizing knowledge reported by China Electrical energy Council via Wind Monetary Terminal.
Complete era from thermal energy and era from hydropower and nuclear energy was taken from Nationwide Bureau of Statistics month-to-month releases.
Month-to-month utilisation knowledge was not out there for biomass, so the annual common of 52% for 2023 was utilized. Energy sector coal consumption was estimated primarily based on energy era from coal and the common warmth charge of coal-fired energy vegetation throughout every month, to keep away from the challenge with official coal consumption numbers affecting latest knowledge.
When knowledge was out there from a number of sources, completely different sources have been cross-referenced and official sources used when doable, adjusting whole consumption to match the consumption progress and modifications within the vitality combine reported by the Nationwide Bureau of Statistics.
CO2 emissions estimates are primarily based on Nationwide Bureau of Statistics default calorific values of fuels and emissions elements from China’s newest nationwide greenhouse gasoline emissions stock, for the 12 months 2018. Cement CO2 emissions issue is predicated on annual estimates as much as 2024.
For oil consumption, obvious consumption is calculated from refinery throughput, with internet exports of oil merchandise subtracted.
Article courtesy of Carbon Transient. (CC license)
Join CleanTechnica’s Weekly Substack for Zach and Scott’s in-depth analyses and excessive stage summaries, join our day by day e-newsletter, and/or observe us on Google Information!
Whether or not you’ve got solar energy or not, please full our newest solar energy survey.
Have a tip for CleanTechnica? Wish to promote? Wish to recommend a visitor for our CleanTech Discuss podcast? Contact us right here.
Join our day by day e-newsletter for 15 new cleantech tales a day. Or join our weekly one on high tales of the week if day by day is simply too frequent.
CleanTechnica makes use of affiliate hyperlinks. See our coverage right here.
CleanTechnica’s Remark Coverage





