Speaking to software program feels pure now, till you want actual enterprise information. That’s the place issues often break. MCPToolbox to Databases fixes this by giving AI brokers protected, dependable entry to manufacturing databases by means of a standardized MCP interface. Databases change into first-class instruments that brokers can examine, question, and purpose over utilizing clear, production-ready pure language to SQL. On this article, we clarify why MCP issues and present the right way to construct your individual AI database agent.
MCPToolbox to Databases runs as a server that turns database operations into instruments AI brokers can safely use. Initially constructed by Google and LangChain, it helps the Mannequin Context Protocol and sits between your LLM app and the database.
You configure connections as soon as, and it handles pooling and SQL execution for the agent. Builders use it wherever AI wants actual information, from help bots querying CRMs to brokers inspecting schemas, throughout databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, and Cloud Spanner.
Key options embrace:
- Open Protocol & Open Supply: It makes use of Open Mannequin Context Protocol. The Toolbox is all open-source. This may guarantee that you’re not sure to a single provider.
- Multi-Database Assist: The multi-database connects to quite a few databases. These are SQL Server and graph databases similar to Neo4j.
- Enterprise Prepared: The Toolbox has safe authentication. It additionally gives observability within the type of OpenTelemetry to log and monitor.
Merely, MCPToolbox to Databases gives a standardized central entry level to offer entry to AI fashions to databases. This enables builders to focus on the AI logic slightly than integration code.
The Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP) Defined
To see the ability of MCPToolkit, the very first thing it’s a must to know is the Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP). Previous to MCP, it was customary to tie LLMs into exterior instruments by means of ad-hoc approaches. This brought on non-standardized brittle integration.
MCP offers an AI mannequin a common language to speak with exterior programs similar to databases and APIs. Right here’s why that issues:
- Commonplace Interface: Within the case of MCP, the AI has no thought the right way to join with a selected database. It merely should have details about which instrument to invoke, e.g., question menu.
- Decoupling AI and Instruments: MCP divides tasks. The LLM is anxious with reasoning and planning (e.g., I need to know the worth of an Espresso). Our Toolbox (the MCP server) is the place the place the execution (e.g. “Hook up with the database and run the SQL question) is carried out.
- Interoperability: Any instrument server that’s MCP-compatible, such because the Gemini by Google, could also be used with any MCP-compatible mannequin.
MCPToolkit is a database-specific MCP server and, subsequently, the most effective choices to a really sturdy integration of LLM and databases.
Learn extra: What’s Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP)?
Fingers-on Information: Construct an AI Agent for a Espresso Store Database
Concept is nice, however development makes concepts come true. Let’s get began with it.
Step 1: Setting Up Your Workspace
The very first thing you want to do is create a brand new challenge folder. Open the terminal in that folder and set up the required Python libraries.
pip set up google-genai toolbox-core Here’s a breakdown of those libraries:
google-genai: The Python SDK for speaking with Google Gemini fashions (the mind).toolbox-core: The library gives your utility with contact to the MCPToolkit server (linking the “mind” with the “palms”).
Step 2: Create Your Native “Database”
Our clever agent should have one thing to work with. The next Python script can be utilized to generate a easy SQLite database file espresso store.db. This file shall have a menu desk with a number of pattern information, which shall simulate a real-life supply of information.
File: setup_db.py
import sqlite3
# Create the database file and a desk
conn = sqlite3.join("coffee_shop.db")
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS menu (
id INTEGER,
merchandise TEXT,
worth REAL
)
""")
cursor.executemany(
"INSERT INTO menu VALUES (?, ?, ?)",
[
(1, "Espresso", 3.50),
(2, "Latte", 4.75),
(3, "Cappuccino", 4.25),
(4, "Blueberry Muffin", 3.00),
],
)
conn.commit()
conn.shut()
print("Success! 'coffee_shop.db' created regionally.")Run the script out of your terminal:
python setup_db.py Step 3: Outline the “Instruments” in a YAML File
The subsequent step might be to tell the Toolbox server in regards to the actions that the AI can do. That is accomplished in a naked configuration file. That is protected for the reason that database connection data shouldn’t be seen to the AI, however slightly the instruments the AI is allowed to make the most of.
File: instruments.yaml
sources:
my-coffee-db:
sort: sqlite
database: "coffee_shop.db"
instruments:
query_menu:
sort: sqlite-sql
supply: my-coffee-db
description: "Use this to lookup objects and costs on the espresso store menu."
assertion: "SELECT * FROM menu WHERE merchandise LIKE ?"
parameters:
- title: item_name
kind: string
description: "The title of the merchandise (e.g. 'Latte')"
toolsets:
coffee-tools:
- query_menuLet’s break down this file:
- sources: this part gives your database connections. We develop a supply which we name my-coffee-db which factors to our coffee-shop.db file.
- instruments: On this case, we declare a instrument referred to as
query_menu. - description: It’s the most vital part to the LLM. It reads this textual content to grasp when and the right way to use the instrument. A transparent description is significant.
- assertion: That is the SQL question the server might be really executing. The P is an emblem that represents what the LLM will provide.
- parameters: That is what one of many instruments desires as enter on this case, an item-name.
- toolsets: This lets you bundle related instruments. We kind a set of coffee-tools which has our single instrument.
Step 4: Begin the Toolbox Server (The “Fingers”)
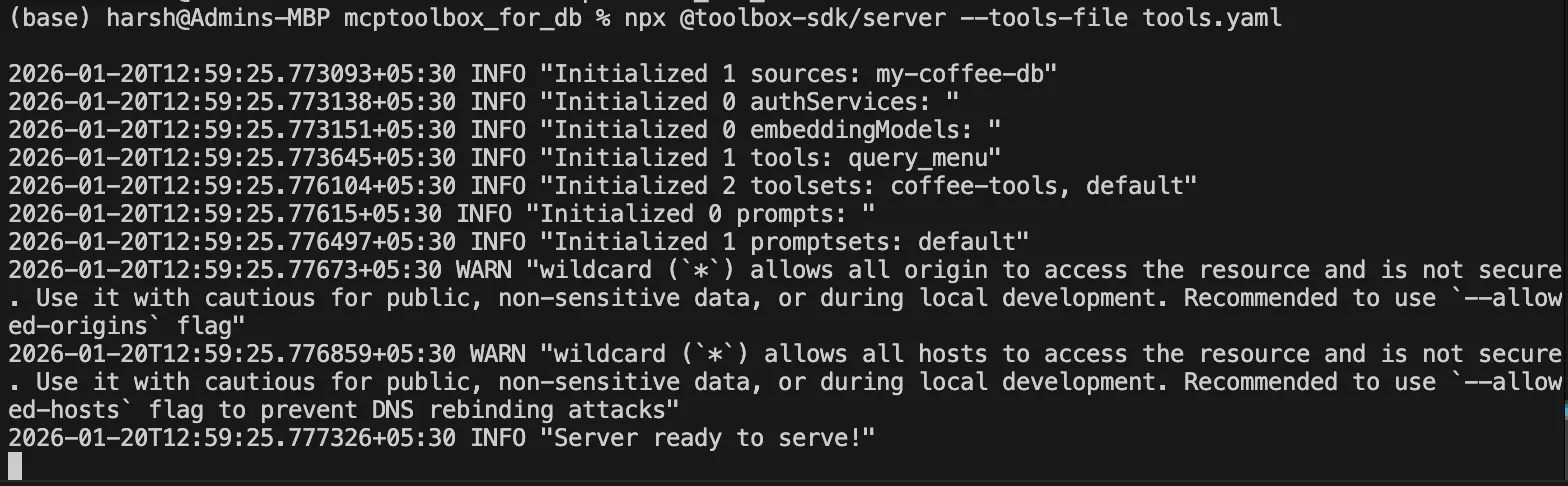
At this level, begin the Toolbox server in your terminal. This command then launches the MCP server that reads your instruments.yaml file, after which connects to the database and waits to be referred to as by the AI to execute its instruments.
npx @toolbox-sdk/server --tools-file instruments.yaml Preserve this terminal window open. You must see a message confirming that the server is listening on port 5000.
Output:
Step 5: Write the LLM Shopper (The “Mind”)
The server is now operational and now we are able to write the Python script that can make use of the LLM to speak with our database. The script might be related to the Toolbox server, load the out there instruments, and supply a sign to the Gemini mannequin.
You’ll require a Gemini API Key on Google AI Studio, which often could be very beneficiant to builders.
File: ask_llm.py
import asyncio
from google import genai
from toolbox_core import ToolboxClient
# Change along with your free API Key from AI Studio
API_KEY = "YOUR_GOOGLE_API_KEY"
async def foremost():
async with ToolboxClient("http://127.0.0.1:5000") as toolbox:
# 1. Get the instruments we outlined earlier
instruments = await toolbox.load_toolset("coffee-tools")
# 2. Arrange the LLM
shopper = genai.Shopper(api_key=API_KEY)
# 3. Ask the query
immediate = (
"I've $4.00. Can I afford an Espresso? "
"Have a look at the menu instrument to test."
)
print("--- LLM is checking the database file... ---")
response = shopper.fashions.generate_content(
mannequin="gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=immediate,
config={"instruments": instruments},
)
print("nANSWER:")
print(response.textual content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(foremost())Explaining the Code:
- We initialize a ToolboxClient to speak with our server working on localhost:5000.
toolbox.load_toolset("coffee-tools")fetches the instrument definitions (title, description, parameters) from the working server.- We initialise the GenerativeModel utilizing our API key, and extra importantly, the instruments that we’ve loaded.
- After we name
generate_content_async, we ship each the immediate and the instrument definitions to the Gemini mannequin. The mannequin will then make a good move on whether or not or not it ought to make use of a instrument to answer the query.
The Consequence: What Occurs Behind the Scenes
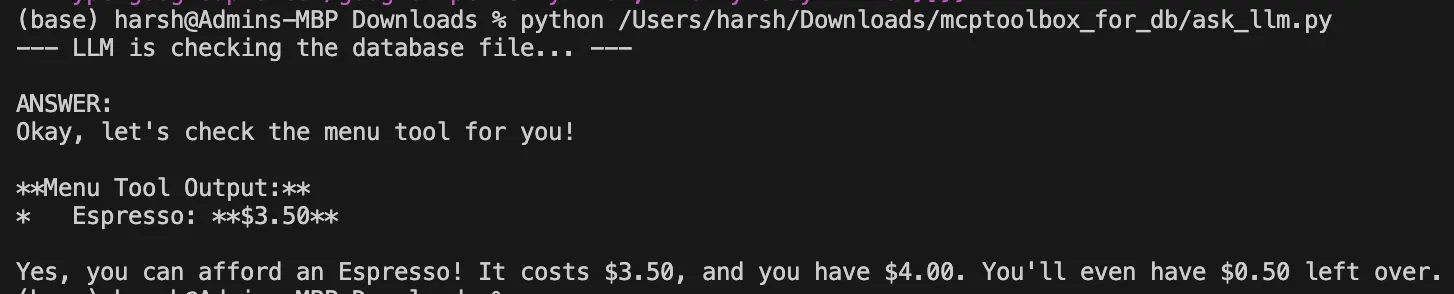
Open a second terminal and run the shopper script:
python ask_llm.pyThe query and outline of the querymenu instrument might be analyzed with the assistance of the LLM. It’ll set up that it requires checking the worth of an “Espresso.” Gemini API, in flip, will automatize the next steps:
- It sends a request to make use of querymenu with the parameter itemname= Espresso which is able to give a instrument name request.
- This request is executed by the ToolboxClient by utilizing the google-genai library.
- The request is shipped by the shopper to your native Toolbox server by means of port 5000.
- The Toolbox server runs the SQL question that has been predefined:
SELECT * FROM menu WHERE merchandise=Espresso. - The results of the database is returned to the Gemini mannequin by way of the chain.
- Now outfitted with the worth, the mannequin formulates a remaining, useful reply.
Output:
Conclusion
MCPToolkit of Databases affords a chic and safe format of the important job of the mixing of the LLCM-database. You have got now realized how its easy YAML-based configuration, server-based design and compliance with the Mannequin Context Protocol make AI and structured information a formidable bridge. With this strategy, you may create complicated functions during which an open-source AI mannequin will be safely and successfully used to course of your individual information to present sensible responses.
Steadily Requested Questions
A. It’s an open-source server that connects Giant Language Fashions (LLMs) to databases utilizing a typical protocol, permitting AI brokers to securely question and work together with structured information.
A. MCP is an open customary and a typical mannequin of how AI fashions ought to work together with exterior programs and instruments, together with databases and APIs.
A. In our instance, the SQL was predefined within the instruments.yaml file for safety and predictability. Extra refined configurations could also be used to permit the LLM to provide SQL, but the strategy affords extra management.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.


