Vulnerabilities affecting a Bluetooth chipset current in additional than two dozen audio units from ten distributors could be exploited for eavesdropping or stealing delicate info.
Researchers confirmed that 29 units from Beyerdynamic, Bose, Sony, Marshall, Jabra, JBL, Jlab, EarisMax, MoerLabs, and Teufel are affected.
The checklist of impacted merchandise consists of audio system, earbuds, headphones, and wi-fi microphones.
The safety issues could possibly be leveraged to take over a susceptible product and on some telephones, an attacker inside connection vary could possibly extract name historical past and contacts.
Snooping over a Bluetooth connection
On the TROOPERS safety convention in Germany, researchers at cybersecurity firm ERNW disclosed three vulnerabilities within the Airoha methods on a chip (SoCs), that are extensively utilized in True Wi-fi Stereo (TWS) earbuds.
The problems will not be essential and apart from shut bodily proximity (Bluetooth vary), their exploitation additionally requires “a excessive technical talent set.” They obtained the next identifiers:
- CVE-2025-20700 (6.7, medium severity rating) – lacking authentication for GATT providers
- CVE-2025-20701 (6.7, medium severity rating) – lacking authentication for Bluetooth BR/EDR
- CVE-2025-20702 (7.5, excessive severity rating) – essential capabilities of a customized protocol
ERNW researchers say they created a proof-of-concept exploit code that allowed them to learn the presently enjoying media from the focused headphones.
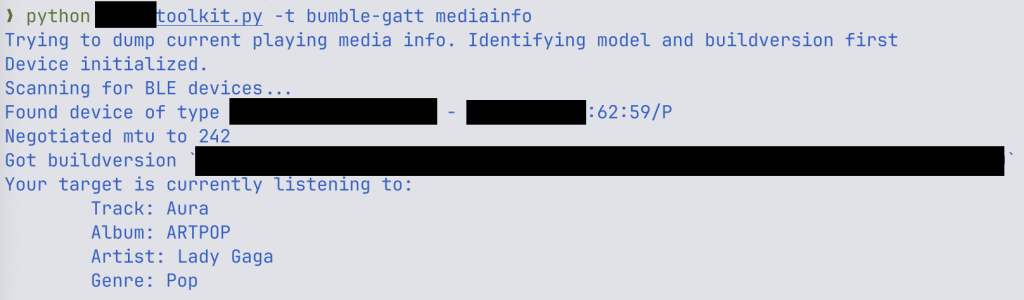
supply: ERWN
Whereas such an assault might not current an excellent danger, different eventualities leveraging the three bugs may let a risk actor hijack the connection between the cell phone and an audio Bluetooth gadget and use the Bluetooth Arms-Free Profile (HFP) to subject instructions to the telephone.
“The vary of accessible instructions is determined by the cell working system, however all main platforms help at the least initiating and receiving calls” – ERNW
The researchers had been in a position to set off a name to an arbitrary quantity by extracting the Bluetooth hyperlink keys from a susceptible gadget’s reminiscence.
They are saying that relying on the telephone’s configuration, an attacker may additionally retrieve the decision historical past and contacts.
They had been additionally in a position to provoke a name and “efficiently snoop on conversations or sounds inside earshot of the telephone.”
Moreover, the susceptible gadget’s firmware may probably be rewritten to allow distant code execution, thereby facilitating the deployment of a wormable exploit able to propagating throughout a number of units.
Assault restrictions apply
Though the ERNW researchers current critical assault eventualities, sensible implementation at scale is constrained by sure limitations.
“Sure — the concept somebody may hijack your headphones, impersonate them in the direction of your telephone, and probably make calls or spy on you, sounds fairly alarming.”
“Sure — technically, it’s critical,” the researchers say, including that “actual assaults are advanced to carry out.”
The need of each technical sophistication and bodily proximity confines these assaults to high-value targets, equivalent to these in diplomacy, journalism, activism, or delicate industries.
Airoha has launched an up to date SDK incorporating needed mitigations, and gadget producers have began patch improvement and distribution.
Nonetheless, German publication Heise says that the newest firmware updates for greater than half of the affected units are from Might 27 or earlier, which is earlier than Airoha delivered the up to date SDK to its clients.



