The current explosion in massive language mannequin (LLM) know-how has highlighted the challenges of utilizing public generative synthetic intelligence (AI) instruments in categorised environments, particularly for software program evaluation. Presently, software program evaluation falls on the shoulders of heuristic static evaluation (SA) instruments and handbook code evaluate, which have a tendency to supply restricted technical depth and are sometimes time-consuming in follow. As this submit particulars, a gaggle of SEI researchers sought to show that LLMs can be utilized in unclassified environments to quickly develop instruments that might then be used to speed up software program evaluation in categorised environments. The ensuing instruments have been a plugin-based structure that allows analysts to develop buyer checkers (i.e., plugins) and a visualization instrument that leverages CodeQL to carry out management circulate and taint evaluation to assist analysts carry out CSA. The instruments created an preliminary time financial savings of roughly 40 % and improved accuracy of roughly 10 %, primarily based on experiments carried out with a group of software program analysts.
On this weblog submit, tailored from a not too long ago revealed paper, we spotlight our method, which can be utilized to develop static evaluation instruments in categorised and unclassified environments, in addition to the 2 current instruments. This work is a part of ongoing SEI analysis to use synthetic intelligence (AI) throughout software program engineering actions, together with software program evaluation.
Points with Static Evaluation Tolls within the Software program Growth Lifecycle
Whereas LLMs are comparatively new, SA instruments have lengthy been current within the software program growth lifecycle. Regardless of their utility, out-of-the-box heuristic SA instruments usually fail to supply the standard evaluation required for advanced techniques. These SA instruments have a tendency to make use of sample matching and different approximate methods and lack full comprehension of code semantics, resulting in gaps within the depth of their evaluation. Conversely, handbook code evaluate, regardless of its effectiveness in figuring out points that automated instruments would possibly miss, is time consuming, demanding of human consideration, and scales poorly with the scale of contemporary software program tasks. These shortcomings current a big bottleneck within the SDLC, impacting the velocity and high quality of software program supply.
To resolve these bottlenecks, we sought to show how LLMs can be utilized to develop instruments that streamline historically handbook features of software program evaluation. Not like current analysis on straight making use of LLMs to software program evaluation duties, our analysis means that leveraging public LLMs (i.e., an web accessible, business/open-source mannequin reminiscent of ChatGPT) for SA instrument technology gives elevated effectivity and a better technical depth for software program evaluation duties. Our work targeted on enhancing code verification in categorised environments (i.e., any space that handles delicate data and/or has an air-gapped community).
Points with LLMs in Software program Evaluation
LLM-generated code might be error-prone, which highlights the necessity for sturdy verficiation and testing frameworks. LLM reliability points are notably regarding when LLMs are utilized to important duties, reminiscent of vulnerability and high quality evaluation. These subtle duties usually require a contextual understanding of software program’s logic and execution circulate. LLMs, constrained by their coaching information, usually lack the subject material experience of educated software program professionals and should fail to totally grasp the intricacies of advanced techniques. For instance, experiments by researchers within the SEI CERT Division’s Safe Growth initiative demonstrated the constraints of LLMs in figuring out and correcting C code that was noncompliant with a coding normal.
A Methodology for Incorporating LLMs in Static Evaluation Instrument Growth
Though there was an excessive amount of work on the efficacy of LLMs for direct software program evaluation, their present limitations prompted us to research their utility in creating instruments for software program evaluation. This new analysis course leverages pure language prompting to permit LLMs to help with creating SA instruments that may function in categorised environments. As well as, it permits finish customers with minimal software program expertise to customise SA instruments.
In our methodology, we enter public (i.e., overtly revealed) materials associated to software program verification duties into public LLMs, and used them to help within the design, implementation, and customization of SA instruments. We later reviewed and migrated the ensuing instruments to a categorised surroundings. For sure, software program instruments developed utilizing our method should be reviewed as described in software program safety verification requirements earlier than being deployed in categorised environments.
The particular insurance policies for reviewing software program earlier than deployment on a categorised system observe authorities rules and are usually proportional to the extent of required safety. Though these safety critiques should nonetheless be carried out with our method, our use of LLMs to create SA instruments offers important management over the software program deployed in a categorised surroundings.
We discovered that our methodology can be utilized to generate SA instruments for unclassified environments as properly. In such instances, the general public LLM might have entry to the codebase, take a look at instances, and software program output, probably growing its worth in producing SA instruments. Our methodology might be break up into two totally different workflows:
- a instrument developer workflow
- a software program analyst workflow
Determine 1 exhibits the workflow for a instrument developer.

Determine 1: AVASST Instrument Developer Workflow
On this workflow, the instrument developer collaborates with software program analysts to develop a set of software program necessities (e.g., high quality attributes, programming paradigms) that drive the prompts fed right into a public LLM. The LLM is then used to assist design instrument architectures from which a instrument developer can down choose primarily based on the analysts’ priorities (e.g., effectivity, maintainability). As soon as the ultimate structure is chosen, the LLM may help instrument builders implement varied prototypes, from which the instrument developer can additional down-select primarily based on high quality attribute necessities (e.g., interoperability, scalability).
Upon completion, instrument builders ought to have a instrument that may assist to confirm some or all the necessities that embody the verification process. To check the instrument, builders can use quite a lot of approaches, together with utilizing an LLM to generate take a look at code. After rigorously testing the generated SA instrument, it may be safely deployed in a categorised surroundings. In a case research, we utilized this workflow and leveraged an LLM to shortly iterate by means of varied prototype architectures for a SA instrument. After down choosing to a plugin-based structure, which might facilitate the seamless integration of future instrument expansions, we leveraged LLMs to assist us implement our SA instrument.
Determine 2 exhibits the workflow for a software program analyst.
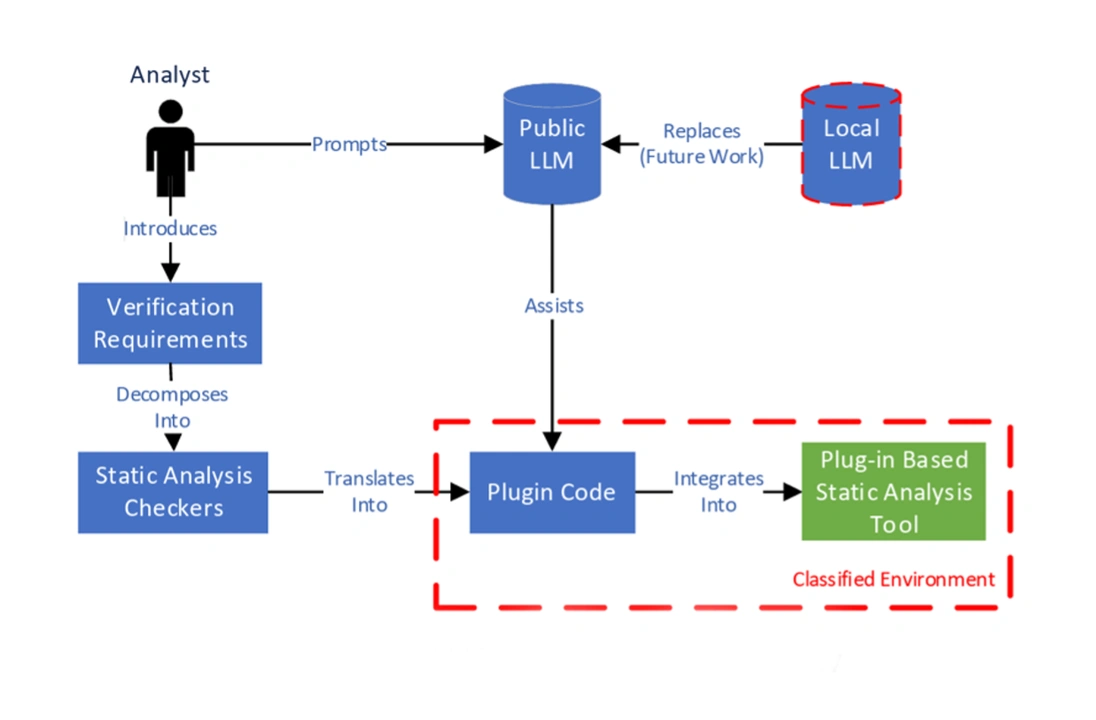
Determine 2: AVASST Analyst Workflow
On this workflow, a software program analyst leverages a public LLM to decompose the beforehand developed necessities into a set of plugins (i.e., SA checkers). As soon as these plugins are migrated to a categorised surroundings, they will combine into our beforehand developed SA instrument. Then, analysts can run the improved SA instrument over categorised code and use its output to assist confirm a codebase meets specified necessities.
Our methodology is iterative, enabling analysts to customise current plugins to extend their efficacy and develop new plugins to suit the altering wants of their group. In Determine 1 and Determine 2, a pink dotted boundary highlights the instruments or actions that may be transitioned into categorised environments. Future analysis would possibly contain the introduction of a neighborhood, on-premises LLM into the categorised surroundings to increase the categorised boundary and probably enhance the efficacy of our workflows.
Utilizing Our Methodology to Create Static Evaluation Instruments
To show the effectiveness of our hybrid methodology, we developed a set of customized SA instruments and collaborated with software program analysts working in a categorised surroundings. From discussions with analysts, we discovered two major ache factors that have been considerably impacting their productiveness:
- authorities software program necessities validation entails validating that software program complies with authorities security and/or safety necessities
- important sign evaluation (CSA) entails verifying the integrity of security important information because it flows by means of this system.
We leveraged our methodology to develop two customized SA instruments in these two areas:
- AVASST Plugin Suite is a instrument with a plugin-based structure that allows analysts to develop customized checkers (i.e., plugins) utilizing the Clang-Tidy framework to assist confirm authorities software program necessities.
- FlowFusion is a visualization instrument that leverages CodeQL to carry out management circulate and taint evaluation to assist analysts carry out CSA.
The AVASST Plugin Suite leverages Clang-Tidy to supply customized SA checkers for analysts. Clang-Tidy is a linter instrument for C and C++ that’s constructed on high of the Clang compiler frontend. It’s used to carry out SA on code to catch errors, implement coding requirements, and recommend enhancements. It features a library of normal checkers out-of-the-box and helps the creation of customized checkers that seek for structural options of the compiled software program’s summary syntax tree (AST) by way of the ASTMatcher library. We leveraged LLMs to help with our understanding of the ASTMatcher library and generate skeleton code for utilizing current Clang-Tidy checkers.
Then we used LLMs to iteratively develop a plugin structure that helps the straightforward integration of future LLM- or human- generated customized checkers. We additionally used LLMs to assist consider the viability of current Clang-Tidy checkers for validating authorities software program necessities. The place we discovered gaps, we prompted LLMs to assist us translate high-level software program necessities into ASTMatcher queries. This helped us develop an preliminary set of customized checkers for validating the integrity of message information.
LLMs additionally helped us develop a Command Line Interface (CLI) and GUI to boost usability and permit customers to graphically mix checkers into teams to confirm chosen authorities software program necessities.
CodeQL, a instrument developed by GitHub, makes use of a proprietary AST parser and different methods to statically analyze a codebase and supply a question language to allow customers to seek for structural code options that manifest in an AST. CodeQL can be utilized to carry out taint evaluation—the monitoring of information that has been influenced (i.e., tainted) by an exterior, probably untrusted supply because it flows by means of a program. Taint evaluation can be utilized to detect vulnerabilities reminiscent of injection assaults, the place tainted information impacts delicate elements of a program missing correct enter validation. We leveraged LLMs to help with the event of CodeQL taint evaluation queries that monitor important indicators flowing by means of the software program. Nonetheless, taint evaluation alone solely supplied a slim view of the important sign pathway. Analysts discovered that there have been extra operate calls and situations involving untainted information that weren’t absolutely captured however nonetheless essential for a radical CSA. This was not a flaw within the idea of taint circulate, which isn’t designed to trace untainted information. Nonetheless, we wanted to include extra data into our instrument’s output for it to be helpful for analysts. Thus, we proposed FlowFusion, the novel idea of overlaying a taint circulate graph on high of a management circulate graph. FlowFusion provided a extra full image of the important sign pathway and enabled analysts to proceed with extra confidence of their evaluation. Determine 3 exhibits a FlowFusion visualization containing gray rectangle and orange oval nodes. The gray rectangles signify capabilities, and edges between rectangles signify management circulate. As well as, the orange ovals signify tainted information, and edges between them signify taint circulate.

Determine 3: Instance Visualization from FlowFusion
The assorted graph nodes are additionally interactive, permitting customers to navigate to the precise code places visualized within the graph by merely clicking on a node. By combining the management and taint flows into an interactive overlay visualization, analysts can have a extra complete view of the pathway important information takes by means of this system and speed up their verification of software program necessities. Whereas analysis in human-AI teaming suggests we might be able to introduce LLMs to help analysts with the pink duties, we didn’t pursue this course as a consequence of time constraints however plan to in future work.
Limitations and Influence of Our Strategy
Though our work represents a step ahead in enhancing software program evaluation, it does have some limitations. First, recall that even best-in-class, public SA instruments usually can’t absolutely confirm necessities. Equally, we should always not anticipate our customized instruments to supply a cure-all answer. Nonetheless, our instruments did present some acceleration in necessities verification.
Second, our instruments require analysts to know the structural options they want to seek for within the codebase. Nonetheless, analysts unfamiliar with a codebase could not know what to seek for a priori, making it troublesome to assemble high-quality queries.
Third, our method requires a human-in-the-loop to confirm that the instrument outputs are correct, since LLMs have been used to create the instruments and LLM reliability points (e.g., hallucinations) can generally result in inaccurate output. The instruments themselves may also output false positives or false negatives that require human adjudication, like most SA instruments.
A Frequent Platform for Sharing Customized LLM-Generated Plugins
To judge the long-term usefulness of our instruments, we delivered them to an in-house group of analysts to be used throughout software program evaluation duties. These duties historically require intensive handbook effort, which is each time-consuming and susceptible to human error. We hope that our LLM-augmented instruments considerably velocity up the evaluation course of and produce a better diploma of accuracy than conventional strategies.
We anticipate our instruments to boost collaboration and consistency amongst group members by offering a standard platform for sharing customized LLM-generated plugins. As well as, we undertaking that effectivity beneficial properties achieved by means of our instruments will lengthen throughout your entire SDLC. As analysts obtain a number of variations of software program over time, our instruments ought to allow them to shortly replicate particular evaluation checks and analyze modifications between every model; a handbook evaluation of modifications would seemingly show extra time consuming. Whereas we await long-term efficacy outcomes, now we have developed some preliminary confidence in our instruments by means of preliminary experimentation and surveys.
Future Work Utilizing LLMs in Software program Evaluation
The AVASST Plugin Suite and FlowFusion signify a step ahead in tailoring analyses to guarantee compliance with particular necessities reminiscent of CSA . Our case research show how LLMs might be efficiently built-in into software program evaluation processes to boost productiveness, particularly in categorised environments, which have distinctive connectivity and confidentiality constraints.
Many alternatives exist to increase upon our analysis together with:
- Creating requirements for evaluating SA and LLM-assisted software program growth: To the perfect of our information, there are not any appropriate normal metrics or take a look at information units for evaluating the effectivity or accuracy of our SA instruments or methodology. Future work might discover creating an ordinary to match our work to current methods.
- Customizing LLM options for various programming paradigms: Our present immediate engineering tips, which we element in our paper, are tailor-made to particular code technology duties (i.e., plugin-based structure). Future work might concentrate on integrating steady studying mechanisms or extra versatile immediate engineering methods to tune LLMs to generate code that follows different design patterns (e.g., microservices).
- Integrating human-AI teaming: New analysis within the discipline of human-AI teaming suggests we might be able to introduce LLMs into duties that require human intervention to additional speed up evaluation workflows. Future work can examine finest practices for incorporating human-AI teaming into workflows constrained by the distinctive necessities of categorised environments.


