
A brand new class of provide chain assaults named ‘slopsquatting’ has emerged from the elevated use of generative AI instruments for coding and the mannequin’s tendency to “hallucinate” non-existent package deal names.
The time period slopsquatting was coined by safety researcher Seth Larson as a spin on typosquatting, an assault technique that tips builders into putting in malicious packages through the use of names that carefully resemble well-liked libraries.
Not like typosquatting, slopsquatting would not depend on misspellings. As a substitute, risk actors may create malicious packages on indexes like PyPI and npm named after ones generally made up by AI fashions in coding examples.
A analysis paper about package deal hallucinations printed in March 2025 demonstrates that in roughly 20% of the examined instances (576,000 generated Python and JavaScript code samples), really helpful packages did not exist.
The state of affairs is worse on open-source LLMs like CodeLlama, DeepSeek, WizardCoder, and Mistral, however industrial instruments like ChatGPT-4 nonetheless hallucinated at a price of about 5%, which is important.
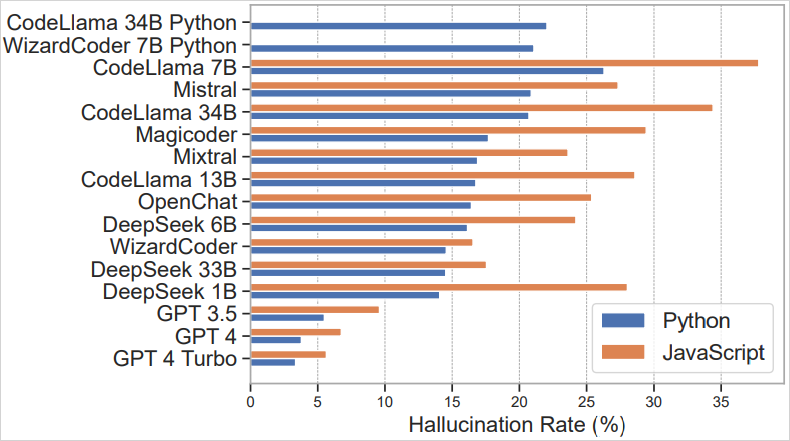
Supply: arxiv.org
Whereas the variety of distinctive hallucinated package deal names logged within the examine was giant, surpassing 200,000, 43% of these had been constantly repeated throughout comparable prompts, and 58% re-appeared no less than as soon as once more inside ten runs.
The examine confirmed that 38% of those hallucinated package deal names appeared impressed by actual packages, 13% had been the outcomes of typos, and the rest, 51%, had been fully fabricated.
Though there aren’t any indicators that attackers have began making the most of this new kind of assault, researchers from open-source cybersecurity firm Socket warn that hallucinated package deal names are frequent, repeatable, and semantically believable, making a predictable assault floor that could possibly be simply weaponized.
“General, 58% of hallucinated packages had been repeated greater than as soon as throughout ten runs, indicating {that a} majority of hallucinations aren’t simply random noise, however repeatable artifacts of how the fashions reply to sure prompts,” explains the Socket researchers.
“That repeatability will increase their worth to attackers, making it simpler to establish viable slopsquatting targets by observing only a small variety of mannequin outputs.”
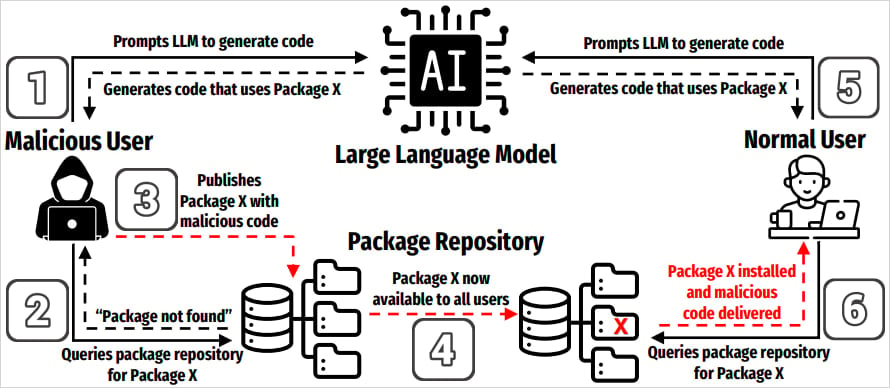
Supply: arxiv.org
The one option to mitigate this threat is to confirm package deal names manually and by no means assume a package deal talked about in an AI-generated code snippet is actual or protected.
Utilizing dependency scanners, lockfiles, and hash verification to pin packages to recognized, trusted variations is an efficient approach to enhance safety
The analysis has proven that reducing AI “temperature” settings (much less randomness) reduces hallucinations, so for those who’re into AI-assisted or vibe coding, this is a crucial issue to think about.
Finally, it’s prudent to at all times check AI-generated code in a protected, remoted atmosphere earlier than working or deploying it in manufacturing environments.



