Our eyes naturally regulate to the visible world. From studying small fonts on a display to scanning lush greenery within the nice outside, they routinely change their focus to see every thing close to and much.
It is a far cry from digital camera programs. Even top-of-the-line choices, reminiscent of full-frame mirrorless cameras, require a number of cumbersome lenses to cowl a variety of focal lengths. For instance, photographers use telephoto lenses to movie wildlife at a distance and macro lenses to seize the superb particulars of small issues up shut—say, a drop of morning dew on a flower.
In distinction, our eyes are made from “tender, versatile tissues in a extremely compact type,” Corey Zhang and Shu Jia at Georgia Institute of Expertise not too long ago wrote.
Impressed by nature, the duo engineered a extremely versatile robotic lens that adjusts its curvature in response to gentle, no exterior energy wanted. Added to a normal microscope, the lens might zero in on particular person hairs on an ant’s leg and the lobes of single pollen grains.
Known as a photoresponsive hydrogel tender lens (PHySL), the system may very well be particularly helpful for mimicking human imaginative and prescient in tender robots. It might additionally open the door to a spread of makes use of in medical imaging, environmental monitoring, and even in its place digital camera in ultra-light cell gadgets.
Synthetic Eyes
We’re extremely visible creatures. Roughly 20 % of the mind’s cortex—4 to 6 billion neurons—is dedicated to processing imaginative and prescient.
The method begins when gentle hits the cornea, a transparent dome-shaped construction on the entrance of our eyes. This layer of tissue begins focusing the sunshine. The following layer is the coloured a part of the attention and the pupil. The latter dilates at evening and shrinks by day to regulate the quantity of sunshine reaching the lens, which sits instantly behind the pupil.
A versatile construction paying homage to an M&M, the lens focuses gentle onto the retina, which then interprets it into electrical alerts for the mind to interpret. Eye muscle groups change focal size by bodily pulling the lens into totally different shapes. Working in tandem with the cornea, this flexibility permits us to alter what we’re specializing in with out aware thought.
Regardless of their delicate nature and every day use, our eyes can stay in working order for many years. It’s no marvel scientists have tried to engineer synthetic lenses with comparable properties. Biologically impressed eyes may very well be particularly useful in tender robots navigating harmful terrain with restricted energy. They might additionally make surgical endoscopes and different medical instruments extra appropriate with our squishy our bodies or assist tender grippers decide fruit and different delicate objects with out bruising or breaking them.
“These options have prompted substantial efforts in bioinspired optics,” wrote the group. A number of earlier makes an attempt used a fluid-based technique, which modifications the curvature—and therefore, focal size—of a tender lens with exterior strain, {an electrical} zap, or temperature. However these are liable to mechanical harm. Different contraptions utilizing strong {hardware} are sturdier, however they require heavier motors to function.
“The optics wanted to type a visible system are nonetheless sometimes restricted to inflexible supplies utilizing electrical energy,” wrote the group.
New Perspective
The brand new system introduced two fields collectively: Adjustable lenses and tender supplies.
The system’s lens is made from PDMS, a light-weight and versatile silicon-based materials used within the likes of contact lenses and catheters.
The opposite part acts like synthetic muscle groups to alter the curvature of the lens. It’s fabricated with a biocompatible hydrogel and dusted with a light-sensing chemical. Heating the chemical sensor causes the gel to alter its form.
The group mixed these two components right into a tender robotic eye, with the hydrogel surrounding the central lens. When uncovered to warmth—reminiscent of that stemming from gentle—the gel releases water and contracts. Because it shrinks, the lens flattens and its focal size will increase, permitting the attention to resolve objects at higher distances.
Depriving the system of sunshine—basically like closing your eyes—cools the gel. It then swells to its authentic plumpness, releases stress, and the lens resets.
The design gives higher mechanical stability than earlier variations, wrote the group. As a result of the gel constricts with gentle, it may possibly type a stronger supporting construction that stops the fragile lens from bending or collapsing because it modifications form. The robotic eye labored as anticipated throughout the sunshine spectrum, with decision and focus similar to the human eye. It was additionally sturdy, sustaining efficiency after a number of cycles of bending, twisting, and stretching.
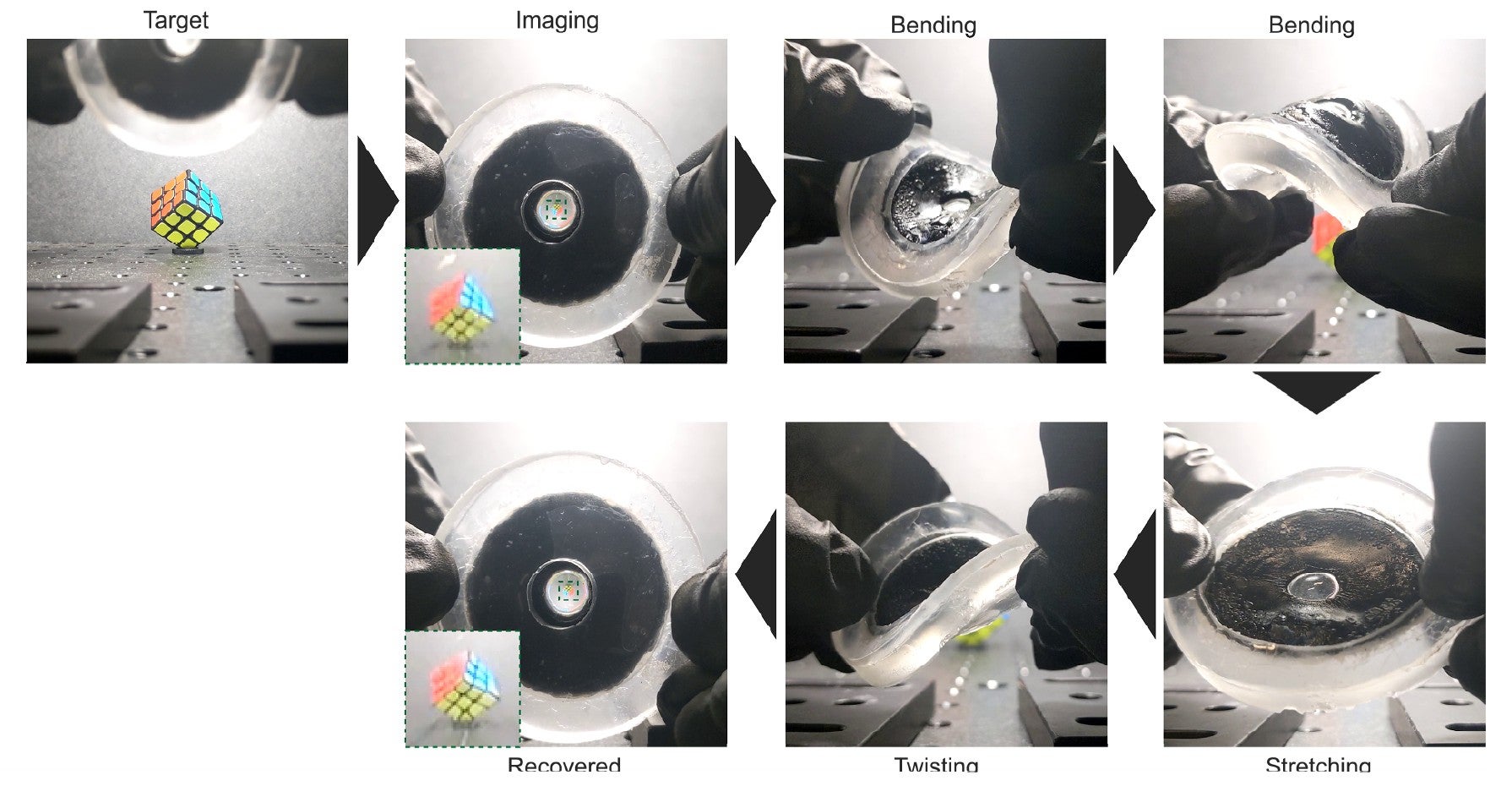
Picture Credit score: Shu Jia
With extra tinkering, the system proved to be an environment friendly substitute for conventional glass-based lenses in optical devices. The group hooked up the squishy lens to a normal microscope and visualized a spread of organic samples. These included fungal fibers, microscopic hairs on an ant’s leg, and the hole between a tick’s claws—all sized roughly a tenth of the width of a human hair.
The group desires to enhance the system too. Just lately developed hydrogels reply sooner to gentle with extra highly effective mechanical forces, which might enhance the robotic eye’s focal vary. The system’s heavy dependence on temperature fluctuations might restrict its use in excessive environments. Exploring totally different chemical components might doubtlessly shift its working temperature vary and tailor the hydrogel to explicit makes use of.
And since the robotic eye “sees” throughout the sunshine spectrum, it might in idea mimic different creature’s eyes, reminiscent of mantis shrimp, which might detect shade variations invisible to people, or reptilian eyes that may seize UV gentle.
A subsequent step is to include it right into a tender robotic as a biologically impressed digital camera system that doesn’t depend on electronics or further energy. “This method can be a big demonstration for the potential of our design to allow new kinds of tender visible sensing,” wrote the group.


