AI Brokers are being extensively adopted throughout industries, however what number of brokers are wanted for an Agentic AI system? The reply could be 1 or extra. What actually issues is that we choose the proper variety of Brokers for the duty at hand. Right here, we’ll attempt to take a look at the instances the place we are able to deploy Single-Agent techniques and Multi-Agent techniques, and weigh the positives and negatives. This weblog assumes you have already got a primary understanding of AI brokers and are accustomed to the langgraph agentic framework. With none additional ado, let’s dive in.
Single-Agent vs Multi-Agent
If we’re utilizing a very good LLM beneath the hood for the Agent, then a Single-Agent Agentic system is sweet sufficient for a lot of duties, supplied an in depth step-by-step immediate and all the mandatory instruments are current.
Observe: A Single-Agent system has one agent, however it could actually have any variety of instruments. Additionally, having a single agent doesn’t imply there might be just one LLM name. There could be a number of calls.
And we use a Multi-Agent Agentic when we have now a fancy job at hand, as an illustration, instances the place a couple of steps can confuse the system and lead to hallucinated solutions. The concept right here is to have a number of brokers the place every agent performs solely a single job. We orchestrate the brokers in a sequential or hierarchical method and use the responses of every agent to supply the ultimate output.
One would possibly ask, why not use Multi-Agent techniques for all use instances? The reply is prices; it’s necessary to maintain the prices beneath verify by selecting solely the required variety of brokers and utilizing the proper mannequin. Now let’s check out use instances and examples of each Single-Agent and Multi-Agent agentic techniques within the following techniques.
Overview of Single-Agent vs Multi-Agent System
| Side | Single-Agent System | Multi-Agent System |
|---|---|---|
| Variety of Brokers | One agent | A number of specialised brokers |
| Structure Complexity | Easy and simple to handle | Complicated, requires orchestration |
| Activity Suitability | Easy to reasonably complicated duties | Complicated, multi-step duties |
| Immediate Design | Extremely detailed prompts required | Less complicated prompts per agent |
| Software Utilization | Single agent makes use of a number of instruments | Every agent can have devoted instruments |
| Latency | Low | Greater resulting from coordination |
| Price | Decrease | Greater |
| Error Dealing with | Restricted for complicated reasoning | Higher through agent specialization |
| Scalability | Restricted | Extremely scalable and modular |
| Finest Use Instances | Code technology, chatbots, summarization | Content material pipelines, enterprise automation |
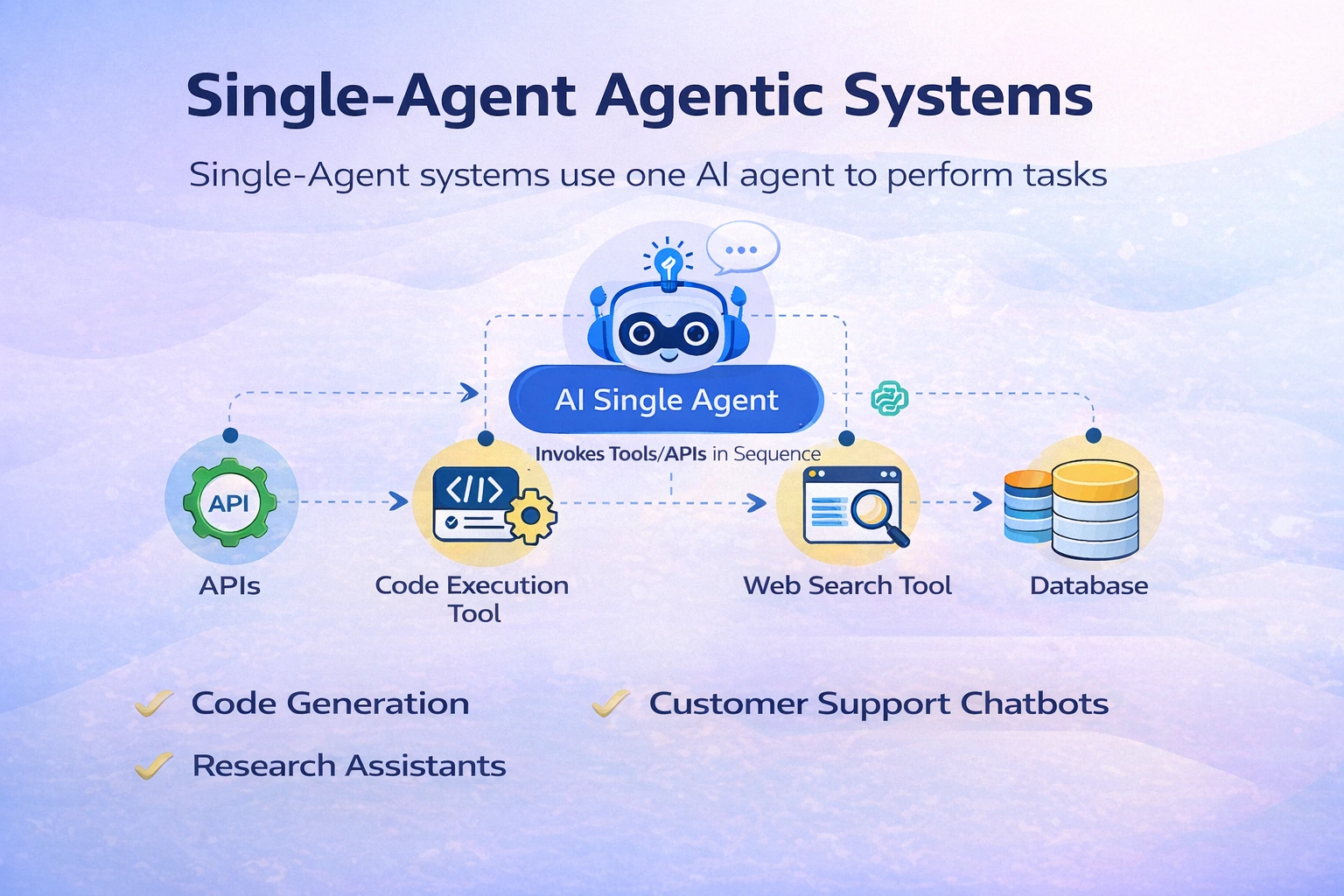
Single-Agent Agentic System
Single-Agent techniques depend on solely a single AI Agent to hold out duties, usually by invoking instruments or APIs in a sequence. This easier structure is quicker and in addition simpler to handle. Let’s check out a couple of functions of Single-Agent workflows:
- Code Technology: An AI coding assistant can generate or refactor code utilizing a single agent. For instance, given an in depth description, a single agent (LLM together with a code execution instrument) can write the code and in addition run checks. Nonetheless, one-shot technology can miss edge instances, which could be mounted by utilizing few-shot prompting.
- Buyer Help Chatbots: Help Chatbots can use a single agent that retrieves info from a data base and solutions the person queries. A buyer Q&A bot can use one LLM that calls a instrument to fetch related info, then formulates the response. It’s easier than orchestrating a number of brokers, and infrequently ok for direct FAQs or duties like summarizing a doc or composing an e mail reply primarily based on supplied information. Additionally, the latency might be a lot better when in comparison with a Multi-Agent system.
- Analysis Assistants: Single-Agent techniques can excel in guided analysis or writing duties, supplied the prompts are good. Let’s take an instance of an AI researcher agent. It may possibly use instruments (net search, and so on.) to assemble info after which summarize findings for the ultimate reply. So, I like to recommend a Single-Agent system for duties like analysis automation, the place one agent with dynamic instrument use can compile info right into a report.
Now, let’s stroll by means of a code-generation agent applied utilizing LangGraph. Right here, we’ll implement a single agent that makes use of GPT-5-mini and provides it a code execution instrument as nicely.
Pre-requirements
If you wish to run it as nicely, guarantee that you’ve got your OpenAI key, and you should use Google Colab or Jupyter Pocket book. Simply make sure you’re passing the API key within the code.
Python Code
Installations
!pip set up langchain langchain_openai langchain_experimentalImports
from langchain.brokers import create_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.instruments import instrument
from langchain.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_experimental.instruments.python.instrument import PythonREPLTool Defining the instrument, mannequin, and agent
# Outline the instrument
@instrument
def run_code(code: str) -> str:
'''Execute python code and return output or error'''
return repl.invoke(code)
# Create mannequin and agent
mannequin = ChatOpenAI(mannequin="gpt-5-mini")
agent = create_agent(
mannequin=mannequin,
instruments=[run_code],
system_prompt="You're a useful coding assistant that makes use of the run_code instrument. If it fails, repair it and check out once more (max 3 makes an attempt)."
) Operating the agent
# Invoking the agent
consequence = agent.invoke({
"messages": [
HumanMessage(
content="""Write python code to calculate fibonacci of 10.
- Return ONLY the final working code
"""
)
]
})
# Displaying the output
print(consequence["messages"][-1].content material) Output:
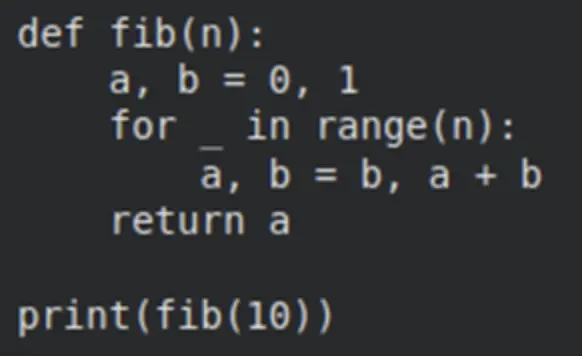
We received the response. The agent reflection helps verify if there’s an error and tries fixing it by itself. Additionally, the immediate could be personalized for the naming conventions within the code and the detailing of the feedback. We are able to additionally move the take a look at instances as nicely together with our immediate.
Observe: create_agent is the advisable method within the present LangChain model. Additionally value mentioning is that it makes use of the LangGraph runtime and runs a ReAct-style loop by default.
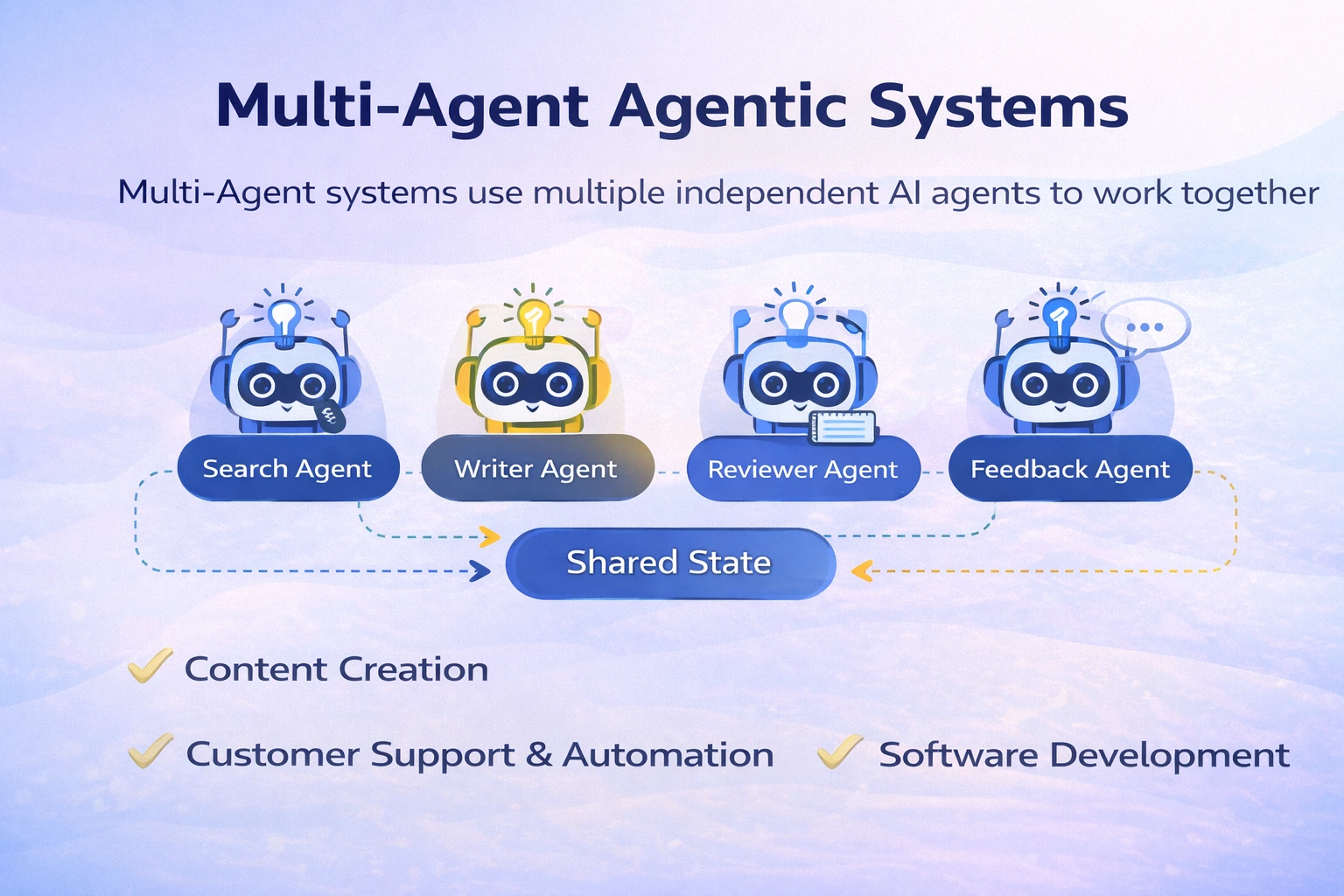
Multi-Agent Agentic System
In distinction to Single-Agent techniques, Multi-Agent techniques, as mentioned, could have a number of impartial AI brokers, every with its personal function, immediate, and possibly every with a unique mannequin, working collectively in a coordinated method. In a multi-agent workflow, every agent makes a speciality of a subtask; for instance, one agent would possibly concentrate on writing, and the opposite does fact-checking. These brokers move info through a shared state. Listed below are some instances the place we are able to use the Mult-Agent techniques:
- Content material Creation: We are able to make a Multi-Agent system for this function, as an illustration, if we’re making a system to craft Information Articles: It’ll have a Search Agent to fetch the most recent info from the net, a Curator Agent that may filter the findings by relevance, and a Author Agent to draft the articles. Then, a Suggestions Agent critiques every draft, offering suggestions, and the author can then revise till the article passes high quality checks. Extra brokers could be added or eliminated based on the necessity in content material creation.
- Buyer Help and Service Automation: Multi-Agent architectures can be utilized to construct extra sturdy help bots. For instance, let’s say we’re constructing an insurance coverage help system. If a person asks about billing, the question is mechanically handed to the “Billing Agent,” or if it’s about claims, it will likely be routed to the “Claims Agent.” Equally, they’ll have many extra brokers on this workflow. The workflow can contain passing prompts to a number of brokers directly if there’s a want for faster responses.
- Software program Improvement: Multi-Agent techniques can help with complicated programming workflows that may transcend a single code technology or refactoring job. Let’s take an instance the place we have now to make a complete pipeline from creating take a look at instances to writing code and working the take a look at instances. We are able to have three brokers for this: ‘Check Case Technology Agent’, ‘Code Technology Agent’, and ‘Tester Agent’. The Tester Agent can delegate the duty once more to the ‘Code Technology Agent’ if the checks fail.
- Enterprise Workflows & Automation: Multi-Agent techniques can be utilized in enterprise workflows that contain a number of steps and resolution factors. One instance is safety incident response, the place we would want a Search Agent that scans the logs and risk intel, an Analyzer Agent that critiques the proof and hypotheses concerning the incident, and a Reflection Agent that evaluates the draft report for high quality or gaps. They work in concord to generate the ultimate response for this use case.
Now let’s stroll by means of the code of the Information Article Creator utilizing the Multi-Brokers, that is to get a greater concept of agent orchestration and the workflow creation. Right here additionally, we’d be utilizing LangGraph, and I’ll be taking the assistance of Tavily API for net search.
Pre-Requisites
- You’ll want an OpenAI API Key
- Join and create your new Tavily API Key in the event you already don’t have one: https://app.tavily.com/dwelling
- If you’re utilizing Google Colab, I’d suggest you add the keys to the secrets and techniques as ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’ and ‘TAVILY_API_KEY’ and provides entry to the pocket book, or you possibly can straight move the API key within the code.

Python Code
Installations
!pip set up -U langgraph langchain langchain-openai langchain-community tavily-pythonImports
from typing import TypedDict, Checklist
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_community.instruments.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
from langchain.messages import HumanMessage
from google.colab import userdata
import osLoading the API keys into the surroundings
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = userdata.get('TAVILY_API_KEY') Initialize the instrument and the mannequin
llm = ChatOpenAI(
mannequin="gpt-4.1-mini"
)
search_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=5) Outline the state
class ArticleState(TypedDict):
matter: str
search_results: Checklist[str]
curated_notes: str
article: str
suggestions: str
permitted: bool This is a vital step and helps retailer the intermediate outcomes of the brokers, which may later be accessed and modified by different brokers.
Agent Nodes
Search Agent (Has entry to the search instrument):
def search_agent(state: ArticleState):
question = f"Newest information about {state['topic']}"
outcomes = search_tool.run(question)
return {
"search_results": outcomes
} Curator Agent (Processes the knowledge acquired from the search agent):
def curator_agent(state: ArticleState):
immediate = f"""
You're a curator.
Filter and summarize essentially the most related info
from the next search outcomes:
{state['search_results']}
"""
response = llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=prompt)])
return {
"curated_notes": response.content material
} Author Agent (Drafts a model of the Information Article):
def writer_agent(state: ArticleState):
immediate = f"""
Write a transparent, participating information article primarily based on the notes under.
Notes:
{state['curated_notes']}
Earlier draft (if any):
{state.get('article', '')}
"""
response = llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=prompt)])
return {
"article": response.content material
} Suggestions Agent (Writes suggestions for the preliminary model of the article):
def feedback_agent(state: ArticleState):
immediate = f"""
Evaluation the article under.
Test for:
- factual readability
- coherence
- readability
- journalistic tone
If the article is sweet, reply with:
APPROVED
In any other case, present concise suggestions.
Article:
{state['article']}
"""
response = llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=prompt)])
permitted = "APPROVED" in response.content material.higher()
return {
"suggestions": response.content material,
"permitted": permitted
} Defining the Routing Perform
def feedback_router(state: ArticleState):
return "finish" if state["approved"] else "revise" It will assist us loop again to Author Agent if the Article just isn’t ok, else it willbe permitted as the ultimate article.
LangGraph Workflow
graph = StateGraph(ArticleState)
graph.add_node("search", search_agent)
graph.add_node("curator", curator_agent)
graph.add_node("author", writer_agent)
graph.add_node("suggestions", feedback_agent)
graph.set_entry_point("search")
graph.add_edge("search", "curator")
graph.add_edge("curator", "author")
graph.add_edge("author", "suggestions")
graph.add_conditional_edges(
"suggestions",
feedback_router,
{
"revise": "author",
"finish": END
}
)
content_creation_graph = graph.compile() 
We outlined the nodes and the perimeters, and used a conditional edge close to the suggestions node and efficiently made our Multi-Agent workflow.
Operating the Agent
consequence = content_creation_graph.invoke({
"matter": "AI regulation in India"
})
from IPython.show import show, Markdown
show(Markdown(consequence["article"])) 
Sure! We now have the output from our Agentic System right here, and the output seems to be good to me. You may add or take away brokers from the workflow based on your wants. As an illustration, you possibly can add an Agent for picture technology as nicely to make the article look extra interesting.
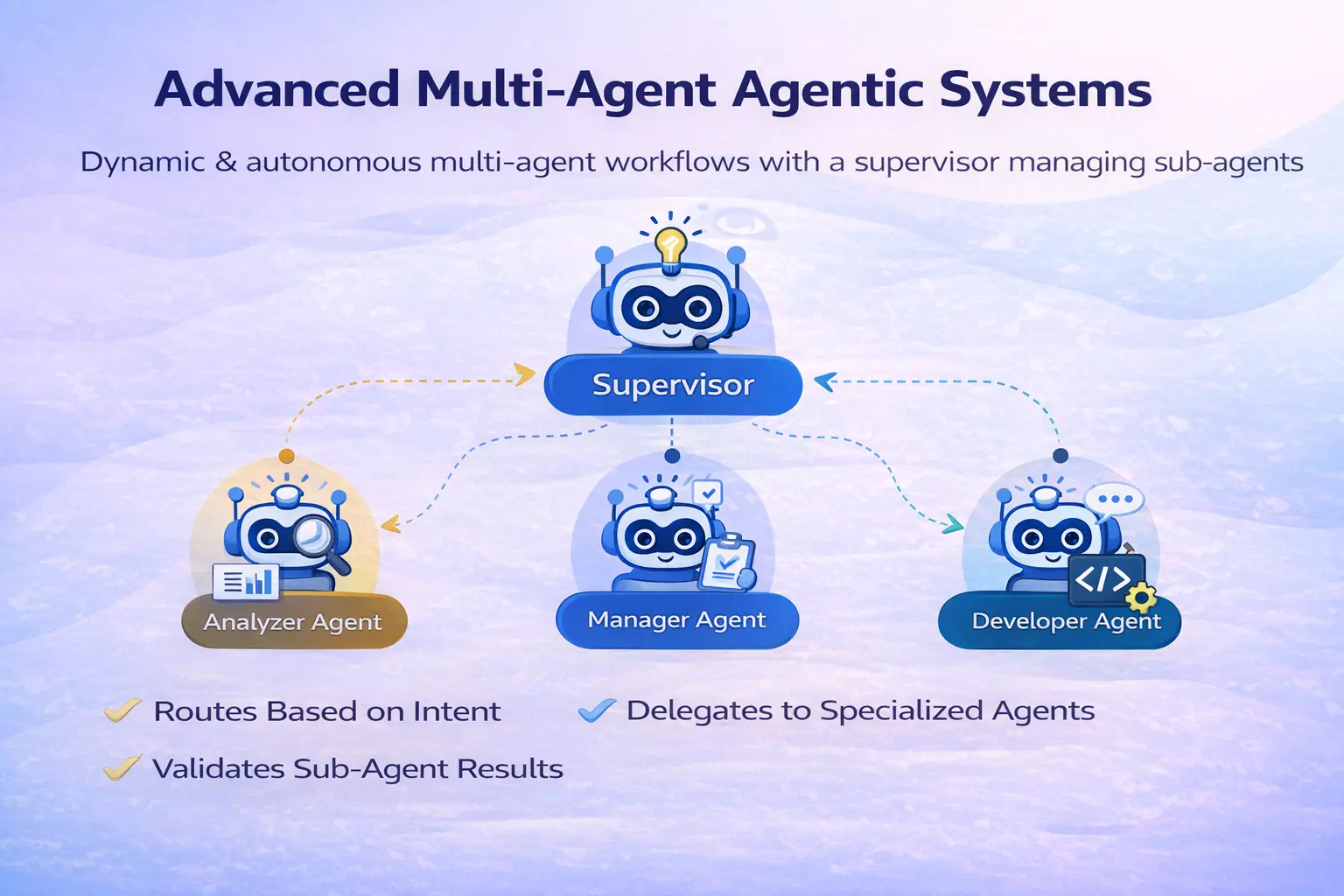
Superior Multi-Agent Agentic System
Beforehand, we checked out a easy sequential Multi-Agent Agentic system, however the workflows can get actually complicated. Superior Multi-Agent techniques could be dynamic, with intent-driven architectures the place the workflow could be autonomous with the assistance of an Agent.
In LangGraph, you implement this utilizing the Supervisor sample, the place a lead node can dynamically route the state between specialised sub-agents or normal Python capabilities primarily based on the outputs. Equally, AutoGen achieves dynamic orchestration by means of the GroupChatManager. And CrewAI leverages the Course of.hierarchical, requiring a manager_agent to supervise delegation and in addition validation.
Let’s create a workflow to grasp supervisor brokers and dynamic flows higher. Right here, we’ll create a Author & Researcher agent and a Supervisor agent that may delegate duties to them and full the method.
Python Code
Installations
!pip set up -U langgraph langchain langchain-openai langchain-community tavily-python Imports
import os
from typing import Literal
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START, END
from langgraph.varieties import Command
from langchain.brokers import create_agent
from langchain_community.instruments.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
from google.colab import userdata Loading the API Keys to the Surroundings
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = userdata.get('TAVILY_API_KEY') Initializing the mannequin and instruments
manager_llm = ChatOpenAI(mannequin="gpt-5-mini")
llm = ChatOpenAI(mannequin="gpt-4.1-mini")
tavily_search = TavilySearchResults(max_results=5) Observe: We might be utilizing a unique mannequin for the supervisor and a unique mannequin for the opposite brokers.
Defining the instrument and agent capabilities
def search_tool(question: str):
"""Fetches market information."""
question = f"Fetch market information on {question}"
outcomes = tavily_search.invoke(question)
return outcomes
# 2. Outline Sub-Brokers (Employees)
research_agent = create_agent(
llm,
instruments=[tavily_search],
system_prompt="You're a analysis agent that finds up-to-date, factual info."
)
writer_agent = create_agent(
llm,
instruments=[],
system_prompt="You're a skilled information author."
)
# 3. Supervisor Logic (Dynamic Routing)
def supervisor_node(state: MessagesState) -> Command[Literal["researcher", "writer", "__end__"]]:
system_prompt = (
"You're a supervisor. Resolve if we want 'researcher' (for information), "
"'author' (to format), or 'FINISH' to cease. Reply ONLY with the node identify."
)
# The supervisor analyzes historical past and returns a Command to route
response = manager_llm.invoke([{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt}] + state["messages"])
resolution = response.content material.strip().higher()
if "FINISH" in resolution:
return Command(goto=END)
goto_node = "researcher" if "RESEARCHER" in resolution else "author"
return Command(goto=goto_node) Employee Nodes (Wrapping brokers to return management to the supervisor)
def researcher_node(state: MessagesState) -> Command[Literal["manager"]]:
consequence = research_agent.invoke(state)
return Command(replace={"messages": consequence["messages"]}, goto="supervisor")
def writer_node(state: MessagesState) -> Command[Literal["manager"]]:
consequence = writer_agent.invoke(state)
return Command(replace={"messages": consequence["messages"]}, goto="supervisor") Defining the workflow
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node("supervisor", supervisor_node)
builder.add_node("researcher", researcher_node)
builder.add_node("author", writer_node)
builder.add_edge(START, "supervisor")
graph = builder.compile() As you possibly can see have solely added the “supervisor” edge and different edges might be dynamically created on execution.
Operating the system
inputs = {"messages": [("user", "Summarize the market trend for AAPL.")]}
for chunk in graph.stream(inputs):
print(chunk) 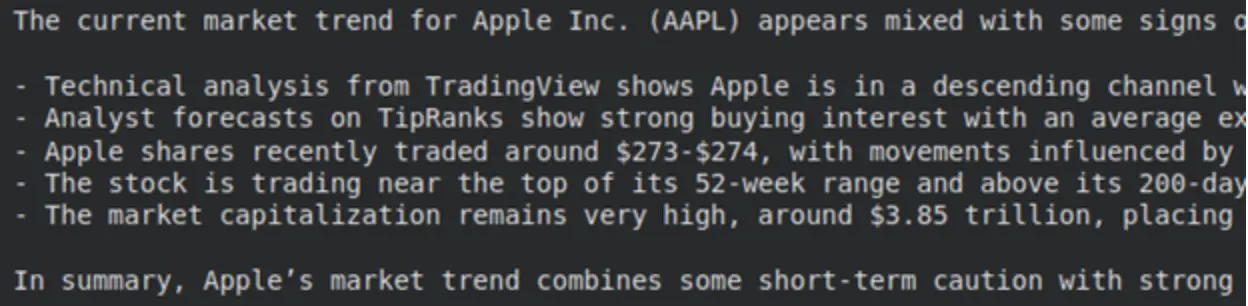
As you possibly can see, the supervisor node executed first, then the researcher, then once more the supervisor, and eventually the graph accomplished execution.
Observe: Supervisor Agent doesn’t return something explicitly, it makes use of ‘Command()’ to resolve whether or not to direct the immediate to different brokers or finish the execution.
Output:
inputs = {"messages": [("user", "Summarize the market trend for AAPL.")]}
consequence = graph.invoke(inputs)
# Print ultimate response
print(consequence["messages"][-1].content material) Nice! We now have an output for our immediate, and we are able to efficiently create a Multi-Agent Agentic Sysem utilizing a Dynamic workflow.
Observe: The output could be improved by utilizing a inventory market instrument as an alternative of a search instrument.
Conclusion
Lastly, we are able to say that there’s no common system for all duties. The reply to picking Single-Agent or Multi-Agent Agentic techniques is determined by the use case and different components. The important thing right here is to decide on a system based on the duty complexity, required accuracy, and in addition the fee constraints. And ensure to orchestrate your brokers nicely if you’re utilizing a Multi-Agent Agentic system. Additionally, keep in mind that it’s equally necessary to choose the proper LLMs on your Brokers as nicely.
Incessantly Requested Questions
Sure. Alternate options embody CrewAI, AutoGen, and lots of extra.
Sure. You may construct customized orchestration utilizing plain Python, but it surely requires extra engineering efforts.
Stronger fashions can cut back the necessity for a number of brokers, whereas lighter fashions can be utilized as specialised brokers.
They are often, however latency will increase with extra brokers and LLM calls, so real-time use instances require cautious optimization and light-weight orchestration.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.


