New analysis factors to an sudden approach plastic air pollution could also be influencing Earth’s local weather system.
A latest research means that microscopic plastic air pollution is decreasing the ocean’s capability to soak up carbon dioxide, a pure operate that performs a central position in retaining the planet’s local weather steady.
Microplastics are small plastic particles measuring lower than 5 millimeters. They’ve unfold broadly throughout the setting and are actually detected in deep ocean waters, rivers and lakes, the air, soil, Arctic ice, and even contained in the human physique. As a result of these particles can carry poisonous chemical compounds, their widespread presence poses severe environmental issues. When ingested by dwelling organisms, together with individuals, they’ll contribute to illness, disrupt ecosystems, hurt marine species, and degrade soil high quality.
Regardless of rising concern over local weather change, scientists say the affect of microplastics on this world drawback, particularly in ocean programs, has obtained comparatively little consideration.
“Local weather disruption and plastic air pollution are two main environmental challenges that intersect in complicated methods. MPs (microplastics) affect biogeochemical processes, disrupt oceanic carbon pumps, and contribute on to greenhouse gasoline (GHG) emissions,” the researchers write in a research revealed within the Journal of Hazardous Supplies: Plastics.
In accordance with the authors, microplastics intrude with how marine ecosystems naturally retailer carbon.
“In marine ecosystems, MPs alter the pure carbon sequestration by affecting phytoplankton and zooplankton, that are key brokers of carbon biking. Moreover, the plastisphere, a microbial neighborhood colonizing MPs, performs a big position in GHG (greenhouse gasoline manufacturing) resulting from its numerous microbial networks.”
Though microplastics are already acknowledged as dangerous pollution, the research factors to a broader local weather consequence. “Our research exhibits additionally they intrude with the ocean’s capacity to soak up carbon dioxide, a course of crucial for regulating Earth’s temperature,” mentioned Dr. Ihsanullah Obaidullah, Affiliate Professor of Built-in Water Processing Applied sciences on the College of Sharjah and the research’s corresponding creator.
Dr. Obaidullah added, “Microplastics disrupt marine life, weaken the ‘organic carbon pump,’ and even launch greenhouse gases as they degrade. Over time, these adjustments might result in ocean warming, acidification, and biodiversity loss, threatening meals safety and coastal communities worldwide.”
A hidden local weather menace
Dr. Obaidullah describes the research as a “collaborative perspective” involving scientists from China, Hong Kong, Pakistan, and the United Arab Emirates. “We now have highlighted an neglected hyperlink between microplastics and local weather change. We name for pressing world motion to handle this rising menace.”
Somewhat than presenting new experiments, the authors performed a scoping evaluation to evaluate the scope and course of current analysis. By analyzing the obtainable research and figuring out gaps in present information, they level to a possible greenhouse impact linked to microplastics that has hardly ever been emphasised in previous local weather discussions.
“Oceans are Earth’s largest carbon sink,” defined Dr. Ihsanullah. “Microplastics are undermining this pure defend towards local weather change. Tackling plastic air pollution is now a part of the combat towards world warming.”
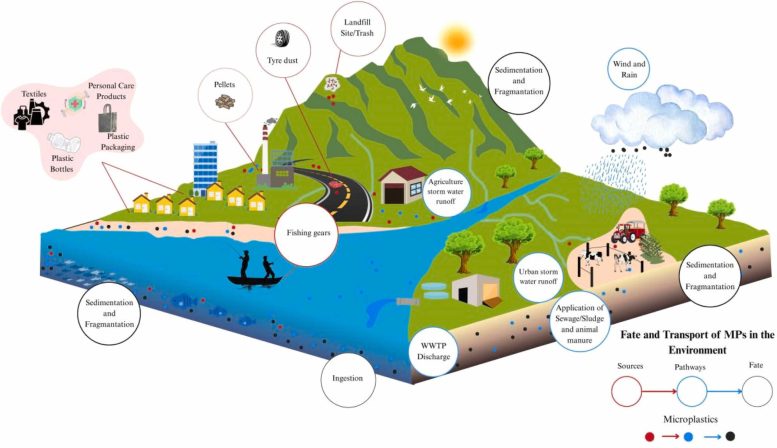
The research emphasizes that “organic carbon pumping” – the ocean’s pure course of that transfers carbon from the ambiance into the deep sea layers – is the first mechanism linking microplastics to world warming and local weather change. “MPs intrude with this course of by decreasing phytoplankton photosynthesis and impairing zooplankton metabolism,” the authors observe.
One other connection, the authors point out, is said to the plastisphere, an meeting of microbes in aquatic settings that type biofilms on surfaces. “The plastisphere is dwelling to quite a lot of microorganisms, the vast majority of that are concerned in organic processes just like the nitrogen and carbon cycles.” Alarmingly, they keep, microplastics additionally emit greenhouse gases throughout degradation, exacerbating their impression on local weather programs.
Unseen connections
The researchers adopted an integrative narrative method to investigate earlier research, fairly than a scientific or scoping evaluation. Their evaluation is grounded in desktop analysis, drawing on peer-reviewed articles, reviews from worldwide organizations, and different authoritative sources to critically synthesize information on microplastics, ocean well being, local weather change, and associated socio-environmental points.
In contrast to protocols equivalent to PRISMA, no inflexible inclusion or exclusion standards had been utilized. As an alternative, the emphasis was positioned on conceptual integration and thematic linkage throughout disciplines, mentioned Dr. Ihsanullah. A complete of 89 research revealed primarily after 2015 had been reviewed, masking literature from 2010 to 2025. This method permits a holistic dialogue of rising proof, information gaps, and coverage implications within the context of local weather change, the Sustainable Improvement Objectives (SDGs), and human rights.
The research seeks to handle information gaps within the literature, which, in keeping with the authors, have largely focused on figuring out microplastics and growing cleanup methods. They write, “The extent to which microplastics have an effect on local weather change, ocean well being, and related programs is presently unknown. This may be largely as a result of the problem is novel, intricate, and multifaceted. The numerous ecological results of plastic air pollution within the oceans are properly acknowledged, however its actual connections to those intensive environmental processes are usually not properly understood.”
To bridge the gaps, the researchers discover the multifaceted results of microplastics on ocean well being and local weather change, urging future research to focus on the interior linkages between microplastics and local weather change dynamics. Such dynamics, they argue, might foster a shift in “perspective in analysis and policymaking.”
By contemplating the ecological and financial dimensions of microplastic ocean impression, the research goals to boost an understanding of plastic air pollution and help the event of more practical mitigation methods, significantly in addressing microplastics’ position in exacerbating environmental challenges equivalent to oxygen depletion and ecosystem destabilization.”
Ubiquitous and versatile
Plastics are usually not solely pervasive but in addition remarkably versatile, reasonably priced, and sturdy. They’re integral to trendy life, utilized in all the pieces from meals, drugs, retail packaging, development of pipes, insulation and home windows, airplane components, interiors for gasoline, electronics, shopper items, and healthcare functions
In consequence, the worldwide era of plastics is very large. A 2025 U.N. report estimates that annual plastic manufacturing exceeds 400 million tonnes, half of which is designed for single use, and fewer than 10 p.c of it’s recycled. Projections point out that, with out intervention, annual plastic manufacturing might triple by 2060.
To this point, the world has produced over 8.3 billion tonnes of plastic, with 80 p.c ending up in landfills or the setting. Alarmingly, solely 9 p.c of the large quantity is recycled.
Whereas plastics ship plain advantages to society, the authors warn that “their environmental footprint throughout your entire life cycle has turn out to be a rising concern. These plastics, being extremely persistent, have turn out to be a urgent world environmental problem.
“The growing demand for and extreme consumption of plastic have led to severe challenges for human and ecosystem well being, posing threats to environmental sustainability and meals security.”
Built-in motion is required to handle points
The researchers urge policymakers to not underestimate the long-term impression of microplastics on ecosystems and human life, even when their present results seem minimal. They warning that “whereas their (microplastics) present impacts could appear minor, their rising accumulation suggests future significance. The impression of MPs on ocean well being, significantly regarding potential ocean warming and acidification, stays an space of concern.”
The authors name for an built-in method, stressing that microplastic air pollution and local weather change can’t be addressed in isolation. “On this approach, the consequences of local weather change could possibly be lessened by taking applicable motion to decelerate the manufacturing of microplastics,” they observe.
Amongst different suggestions, the authors urge the United Nations to revisit its Sustainable Improvement Objectives, declaring that “plastics are presently represented by a single indicator, which can not adequately seize the widespread dangers posed by microplastics throughout numerous ecological programs.”
In addition they advocate for quick and coordinated efforts to “develop governance frameworks that sort out each MP air pollution and local weather change, significantly their hyperlinks to ocean acidification and warming.”
To safeguard the oceans and protect their capacity to soak up carbon dioxide, they define key priorities which embody decreasing single-use plastics, enhancing waste administration, selling biodegradable alternate options, and advancing analysis on how microplastics affect ocean temperature and carbon cycles.
Moreover, they advocate leveraging AI-driven monitoring and revolutionary supplies to curb plastic waste.
When requested about future analysis instructions, Dr. Ihsanullah mentioned, “Our subsequent step is to quantify the local weather impression of microplastics and develop built-in options. This isn’t simply an environmental situation; it is a world sustainability problem.”
Reference: “From air pollution to ocean warming: The local weather impacts of marine microplastics” by Asim Nawab, Muhammad Tariq Khan, I. Ihsanullah, Mohammad Nafees and Aamir Mehmood Shah, 18 December 2025, Journal of Hazardous Supplies: Plastics.
DOI: 10.1016/j.hazmp.2025.100032


