Utilizing AI, researchers recognized one tiny molecular interplay that viruses must infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus earlier than an infection may start.
Washington State College scientists have uncovered a technique to intervene with a key viral protein, stopping viruses from getting inside cells the place they will trigger illness. The invention factors towards a doable new technique for creating antiviral therapies sooner or later.
The work, printed within the journal Nanoscale, concerned researchers from the College of Mechanical and Supplies Engineering and the Division of Veterinary Microbiology and Pathology. Collectively, they recognized and disrupted a particular molecular interplay that herpes viruses depend upon to enter cells.
“Viruses are very sensible,” mentioned Jin Liu, corresponding writer of the examine and a professor within the College of Mechanical and Supplies Engineering. “The entire strategy of invading cells could be very complicated, and there are loads of interactions. Not all the interactions are equally essential — most of them may be background noise, however there are some essential interactions.”
Concentrating on the Protein Viruses Use to Break In
The researchers targeted on a viral “fusion” protein, which herpes viruses use to connect to cells and merge with them, triggering an infection and illness. Scientists nonetheless lack a transparent understanding of how this massive and complex protein adjustments form to permit viruses inside cells. This restricted information is one cause vaccines for a lot of frequent herpes viruses have remained elusive.
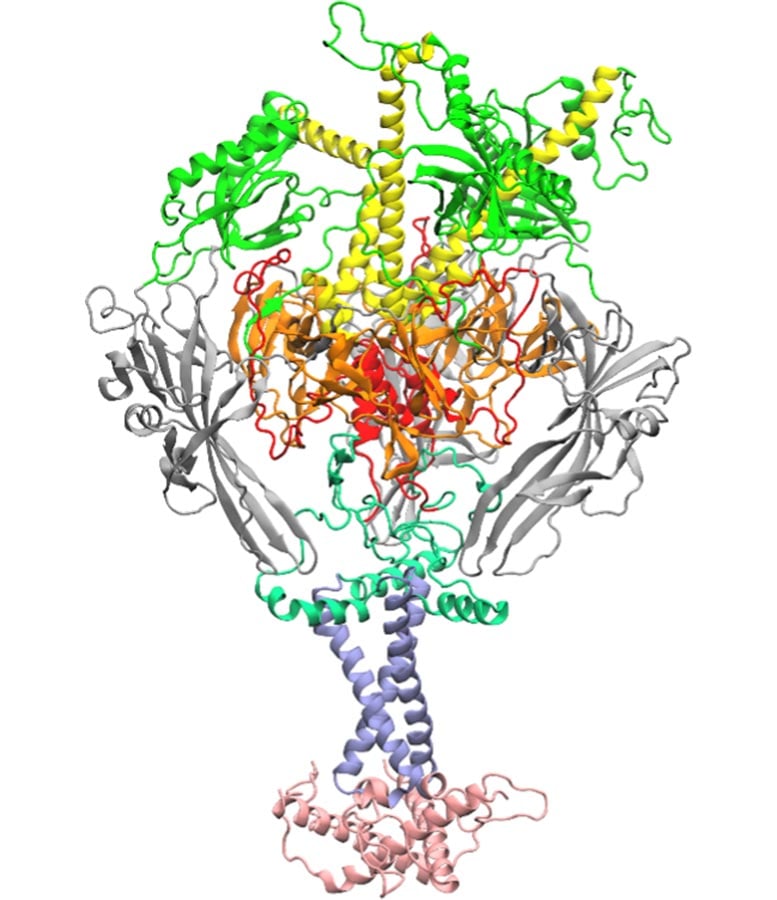
How AI Narrowed Down Hundreds of Potentialities
To sort out this problem, the crew turned to synthetic intelligence and molecular scale simulations. Professors Prashanta Dutta and Jin Liu analyzed hundreds of doable interactions throughout the fusion protein to discover a single amino acid that performs a central function in viral entry. They designed an algorithm to look at interactions amongst amino acids, the essential constructing blocks of proteins, after which utilized machine studying to type by means of the information and establish which interactions mattered most.
A Single Mutation That Blocks An infection
As soon as the important thing amino acid was recognized, laboratory experiments led by Anthony Nicola from the Division of Veterinary Microbiology and Pathology put the findings to the take a look at. By altering that one amino acid, the researchers discovered that the virus may now not efficiently fuse with cells. Because of this, the herpes virus was successfully prevented from coming into the cells.
In line with Liu, the computational work was important as a result of testing even one interplay within the lab can take months. Narrowing the main target forward of time made the experimental section much more environment friendly.
“It was only a single interplay from hundreds of interactions. If we do not do the simulation and as an alternative did this work by trial and error, it may have taken years to seek out,” mentioned Liu. “The mix of theoretical computational work with the experiments is so environment friendly and may speed up the invention of those essential organic interactions.”
What Scientists Nonetheless Must Perceive
Though the crew confirmed the significance of this particular interplay, many questions stay about how altering one amino acid impacts the construction of all the fusion protein. The researchers plan to proceed utilizing simulations and machine studying to raised perceive how small molecular adjustments affect the protein at bigger scales.
“There’s a hole between what the experimentalists see and what we are able to see within the simulation,” mentioned Liu. “The subsequent step is how this small interplay impacts the structural change at bigger scales. That can be very difficult for us.”
Reference: “Modulation of particular interactions inside a viral fusion protein predicted from machine studying blocks membrane fusion” by Ryan E. Odstrcil, Albina O. Makio, McKenna A. Hull, Prashanta Dutta, Anthony V. Nicola and Jin Liu, 4 November 2025, Nanoscale.
DOI: 10.1039/D5NR03235K
Along with Liu, Dutta and Nicola, the undertaking was performed by PhD college students Ryan Odstrcil, Albina Makio, and McKenna Hull. The work was funded by the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.


