Retrieval-Augmented Era (RAG) has turn into the go-to technique for constructing dependable AI functions that rely on exterior information, because it helps overcome LLM limitations, cuts down hallucinations, and delivers expert-level responses grounded in trusted sources. As curiosity in RAG rises, so does the necessity for instruments that make it simpler to discover, check, and refine totally different RAG methods. AutoRAG is likely one of the newer options constructed for this objective, automating a lot of the event workflow so you may experiment with configurations, consider pipelines, and pinpoint what works finest in your use case.
On this information we’ll cowl how AutoRAG works, and learn how to create an end-to-end RAG utility with this know-how.
What’s Retrieval-Augmented Era (RAG)?
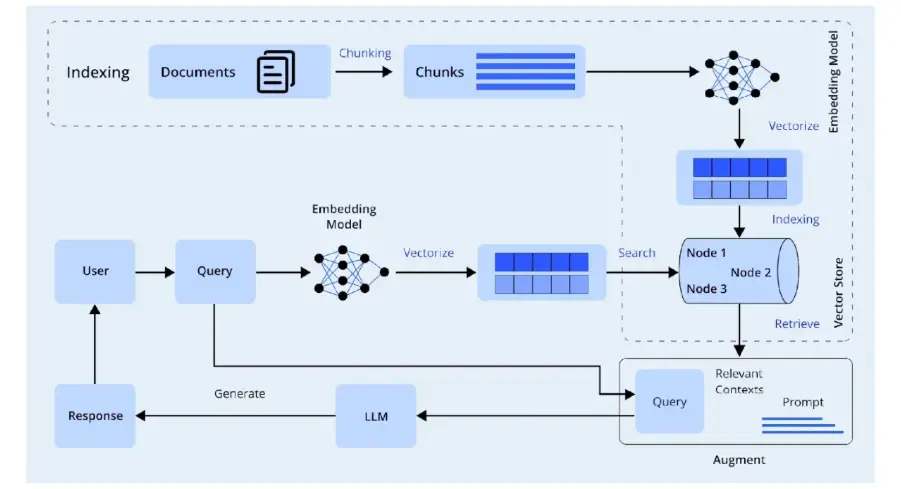
The 2 predominant items of RAG are The Retriever and the Generator. Collectively these items make up the Pipeline of RAG that permits you to get correct solutions to complicated queries. The generator will learn the context that the retriever discovered and generates a response primarily based on that.
RAG is an strategy that mixes searches for exterior information with Generative Fashions to enhance accuracy by offering dependable references for model-generated solutions. Some functions of RAG embrace Chatbots, Data Assistants, Analytics Options and Enterprise Q&A Techniques.
Key Parts of RAG
There are a number of constructing blocks that make RAG profitable and have an effect on the power of RAG to supply correct info. These embrace The Retriever, The Embedding Mannequin and The Generator.
- Retriever: Step one in RAG is to index the paperwork utilizing the retriever, then the retriever will search the index for the related chunks of paperwork. The strategy for looking out the
- Embedding Mannequin: Indexes might be primarily based on the similarity of the chunks of the paperwork by numerous strategies corresponding to Similarity Search, Vector Embedding or Hybrid Retrieval.
- Generator (LLM): The generator should depend on correct context to be able to produce an correct response. Because of this it’s essential to make the most of the absolute best model of the context to be able to generate an correct response.
What’s AutoRAG and When to Use It
AutoRAG is a framework that permits you to create, consider, and optimize a number of RAG pipelines shortly. It helps builders shortly check a number of design selections without having to jot down customized analysis scripts. When groups need to examine totally different retrieval strategies, embedding fashions, chunking methods, or generations, they use AutoRAG.
With AutoRAG, builders can shortly iterate by many alternative RAG configurations as a result of it routinely runs exams and supplies an analysis of retrieval accuracy and finest configuration for producing pipelines. If you want systematic analysis or need to check a lot of pipeline configurations, you need to use AutoRAG.
What Issues AutoRAG Resolve?
AutoRAG addresses most of the challenges that make RAG improvement time-consuming. As RAG initiatives turn into more and more complicated, these challenges turn into much more vital.
- Pipeline Exploration: It allows experimentation throughout a wide range of similarity metrics, chunking sizes, embedding fashions, and retrievers with out guide code.
- Analysis: AutoRAG consists of analysis metrics that embrace retrieval accuracy, quotation correctness, and reply high quality, making it simple to evaluate the effectiveness of RAG pipelines.
- Optimization: AutoRAG identifies the simplest configurations, which allows groups to make the perfect choice doable for the configuration of their information and use case.
Making ready to Construct: Stipulations & Setup
Arrange a improvement setting appropriate for utilizing AutoRAG to develop an utility primarily based on RAG. Meaning you’ll want to ascertain Python, dependencies, information, and discover out what credentials you want out of your LLM or embedding mannequin supplier.
You will need to have a well-defined Python setting in addition to a number of further dependencies to have the ability to efficiently run AutoRAG. You probably have an unclean or improperly outlined setting, you could expertise conflicts inside your dependencies, and your experiments with RAG won’t run easily.
- Python Setup
python3 -m venv autorag-venv
supply autorag-venv/bin/activate
python -m pip set up --upgrade pip- Python 3.10 or larger
- A digital setting utilizing venv or conda
- pip for package deal set up
- Core Dependencies
Set up the next packages as required by AutoRAG:
pip set up AutoRAG pandas langchain sentence-transformers faiss-cpu - autorag
- pandas
- sentence-transformers
- faiss-cpu or one other vector retailer backend
- langchain or langchain-community for LLM integrations
- Export LLM / embedding keys
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-..." If you’re utilizing someother suppliers, set their env vars equally.
Constructing a RAG Utility with AutoRAG
To create an utility primarily based on RAG utilizing AutoRAG and a data base, proceed by the next predominant steps.
- Indexing and Embedding: Every chunk of knowledge might be transformed into an embedding and saved in a vector database.
- Retrieval and Pipeline Experimenting: Create a QA analysis set if crucial, then run AutoRAG to experiment with totally different RAG pipelines to find out which produces the perfect outcomes.
- Deployment: Use the ensuing RAG pipeline to reply to consumer enquiries.
Information Ingestion and Preprocessing
Firstly, we’ll load the uncooked paperwork:
import json
import os
from pathlib import Path
import PyPDF2
def parse_pdf(pdf_path="information/raw_docs/consideration.pdf", out_path="information/parsed.jsonl"):
os.makedirs("information", exist_ok=True)
with open(pdf_path, "rb") as f, open(out_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
reader = PyPDF2.PdfReader(f)
for i, web page in enumerate(reader.pages):
textual content = web page.extract_text() or ""
fout.write(json.dumps({
"doc_id": "consideration.pdf",
"web page": i + 1,
"content material": textual content,
"supply": "consideration.pdf",
"title": "Consideration Is All You Want"
}) + "n")
print("Parsed PDF → information/parsed.jsonl")
parse_pdf()The next technique would babe used for splitting and chunking paperwork:
import json
def chunk_text(textual content, chunk_size=600, overlap=60):
phrases = textual content.break up()
i = 0
chunks = []
whereas i = len(phrases):
break
i += chunk_size - overlap
return chunks
def create_corpus(parsed="information/parsed.jsonl", out="information/corpus.jsonl"):
with open(parsed, "r") as fin, open(out, "w") as fout:
for line in fin:
row = json.hundreds(line)
chs = chunk_text(row["content"])
for idx, c in enumerate(chs):
fout.write(json.dumps({
"id": f"{row['doc_id']}_p{row['page']}_c{idx}",
"doc_id": row["doc_id"],
"web page": row["page"],
"chunk_id": idx,
"content material": c,
"supply": row["source"],
"title": row["title"]
}) + "n")
print("Created corpus → information/corpus.jsonl")
create_corpus()The next code normalises metadata:
import json
def normalize_metadata(path="information/corpus.jsonl"):
rows = []
with open(path) as fin:
for line in fin:
obj = json.hundreds(line)
obj.setdefault("supply", "consideration.pdf")
obj.setdefault("title", "Consideration Is All You Want")
rows.append(obj)
with open(path, "w") as fout:
for r in rows:
fout.write(json.dumps(r) + "n")
print("Metadata normalized.")
normalize_metadata()Indexing / Embedding + Storage Setup
Now, we’d be utilizing the embedding mannequin:
import json
import numpy as np
import faiss
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
import os
def build_faiss_index(corpus="information/corpus.jsonl", index_dir="information/faiss_index"):
os.makedirs(index_dir, exist_ok=True)
texts, ids = [], []
with open(corpus) as f:
for line in f:
row = json.hundreds(line)
texts.append(row["content"])
ids.append(row["id"])
mannequin = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
embeddings = mannequin.encode(texts, convert_to_numpy=True)
faiss.normalize_L2(embeddings)
index = faiss.IndexFlatIP(embeddings.form[1])
index.add(embeddings)
faiss.write_index(index, f"{index_dir}/index.faiss")
json.dump(ids, open(f"{index_dir}/ids.json", "w"))
print("Saved FAISS index at", index_dir)
build_faiss_index()Vector retailer or database setup:
vectordb: faiss_local
index_dir: information/faiss_index
embedding_module: sentence_transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2Retrieval and RAG Pipeline Experimentation with AutoRAG
Firstly, we’ll be creating an QA Analysis Dataset:
import pandas as pd
from autorag.information.qa.schema import Uncooked, Corpus
from autorag.information.qa.pattern import random_single_hop
from autorag.information.qa.question.llama_gen_query import factoid_query_gen
from autorag.information.qa.generation_gt.llama_index_gen_gt import make_basic_gen_gt
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
def create_qa():
raw_df = pd.read_parquet("information/parsed.parquet")
corpus_df = pd.read_parquet("information/corpus.parquet")
raw_inst = Uncooked(raw_df)
corpus_inst = Corpus(corpus_df, raw_inst)
llm = OpenAI()
sampled = corpus_inst.pattern(random_single_hop, n=140)
sampled = sampled.make_retrieval_gt_contents()
sampled = sampled.batch_apply(factoid_query_gen, llm=llm)
sampled = sampled.batch_apply(make_basic_gen_gt, llm=llm)
sampled.to_parquet("information/qa.parquet", index=False)
print("Created information/qa.parquet")
create_qa()Working AutoRAG analysis:
configs/default_rag_config.yaml
node_lines:
- node_line_name: retrieve_node_line
nodes:
- node_type: semantic_retrieval
top_k: 3
modules:
- module_type: vectordb
vectordb: faiss_local
index_dir: information/faiss_index
embedding_module: sentence_transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2
- node_line_name: post_retrieve_node_line
nodes:
- node_type: prompt_maker
modules:
- module_type: fstring
immediate: |
Use the passages to reply the query.
Query: {question}
Passages: {retrieved_contents}
Reply:
- node_type: generator
modules:
- module_type: openai_llm
llm: gpt-4o-mini
batch: 8Use the next code for operating the evaluator:
from autorag.evaluator import Evaluator
evaluator = Evaluator(
qa_data_path="information/qa.parquet",
corpus_data_path="information/corpus.parquet"
)
evaluator.start_trial("configs/default_rag_config.yaml")Working the RAG:
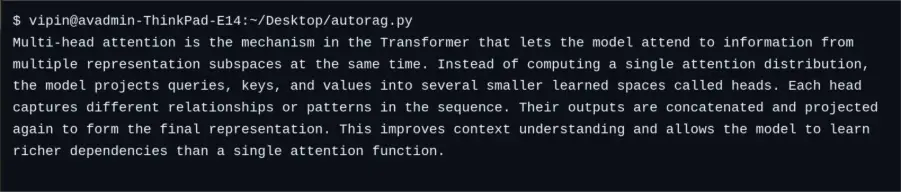
Person Question: “What’s multi-head consideration within the Transformer mannequin?”
Greatest Practices & Suggestions
Constructing a strong RAG utility includes cautious planning. Listed below are some finest practices:
- Hold authentic textual content with embeddings: It is best to at all times hold the inode content material of any chunk or reference to the inode content material together with the embeddings for that content material chunk – don’t rely solely upon the embeddings.
- Chunk sensibly: Chunking is completed in method that preserves which means on the boundaries of chunks when being processed; due to this fact, you need to use the identical tokenization and the identical measurement for all chunks of content material (e.g., 300 to 512 tokens) and keep overlap of chunks (e.g., 50 overlapping tokens).
- Cache embeddings: Cache equivalent embeddings for all content material when sending a repeated question or when processing giant quantities of content material.
- Monitor high quality: Monitor retrieval and era efficiency utilizing customary metrics; for instance: AutoRAG supplies customary metrics for assessing retrieval F1, recall, and proper answering; you should utilize these metrics to establish any issues with the efficiency of your RAG system.
- Safe your keys: Defend your API keys or mannequin tokens; don’t hard-code your keys into your utility; as an alternative, make use of setting variables or safe vaults.
By following the above pointers, improvement groups will be capable to construct sturdy and dependable RAG functions that reap the benefits of AutoRAG’s automation and yield high-quality outcomes.
Conclusion
The design of a RAG utility consists of a number of parts between information processing and retrieval strategies. AutoRAG allows builders to automate the experimental part and analysis processes to make the creation of RAG functions easier. With AutoRAG, builders can shortly experiment with numerous pipeline designs and launch a superior RAG utility primarily based on conclusive information.
By following the directions offered inside this doc, customers will be capable to produce a reliable, correct, and ready-to-use utility with the implementation of optimum strategies. Using AutoRAG’s optimization capabilities and incorporating established finest practices, groups have a larger alternative to create probably the most useful AI expertise whereas decreasing the necessity for time-consuming guide configuration.
Regularly Requested Questions
A. AutoRAG automates RAG pipeline exploration, analysis, and optimization. It helps builders establish the perfect configuration for retrieval and era duties.
A. No, AutoRAG works with small and huge datasets. Nevertheless, extra information improves analysis accuracy and retrieval efficiency.
A. The selection is determined by your use case. Light-weight fashions like MiniLM supply pace, whereas fashions like BGE or Jina present larger semantic accuracy.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.


