In an period outlined by digital transactions, the worldwide stream of fee information has develop into the lifeblood of commerce. Nevertheless, this borderless economic system operates on a basis of distinctly bordered legal guidelines. For companies leveraging the ability of the cloud, this creates a crucial problem: methods to innovate and scale globally whereas adhering to a fancy internet of native rules governing information. That is the realm of information sovereignty and fee compliance, the place the agility of cloud computing meets the calls for of nationwide and regional legal guidelines.
Who’s this text for
This text is supposed for expertise leaders, compliance officers, and enterprise decision-makers in organizations that deal with fee information. Whether or not you’re a fintech startup or a longtime commerce enterprise accepting funds on-line, in-store or through financial institution and ACH transfers, this information will stroll you thru the core ideas of information sovereignty, the worldwide regulatory setting, and actionable methods for architecting a compliant fee processing framework within the cloud.
As companies more and more depend on cloud companies for fee processing, understanding these regulatory necessities shouldn’t be non-obligatory—it’s important for survival and progress.
Understanding the core ideas and the converging challenges
To construct a compliant technique, a agency grasp of the foundational terminology is essential. These ideas, whereas associated, have distinct meanings and implications in your information governance and cloud structure.
What’s information sovereignty
Information sovereignty dictates that information is topic to the legal guidelines of the nation the place it’s generated and picked up, no matter the place it’s bodily saved and processed. Associated to this, information residency is concerning the bodily location of the place information is saved and processed. A substantial variety of rules mandate information residency compliance as a baseline for assembly sovereignty necessities.
Information residency vs. information localization: key distinctions
Though these phrases are typically used interchangeably, they’ve completely different meanings. Information localization is a authorized requirement that mandates information be saved inside a particular nation’s borders. Information residency is a alternative of technique (the geographical location the place a corporation chooses to retailer its information); information localization is a authorized obligation that enforces that alternative.
In case your buyer information is generated in Belgium, France, or the Netherlands and saved in a German information heart, it’s topic to the info safety legal guidelines of every nation, significantly the Common Information Safety Regulation (GDPR). This idea extends past storage to incorporate processing and accessing information, which has vital implications for a way international corporations handle their cloud infrastructure.

What does fee compliance entail
With organizations going through a barrage of assaults—79% of U.S. corporations reported being victims of funds fraud in 2024—sturdy compliance is the primary line of protection in sustaining the integrity of the fee ecosystem.
This crucial space is topic to strict guidelines, just like the outstanding Cost Card Business Information Safety Customary (PCI DSS), a world commonplace outlining technical and operational necessities for securing cardholder information.
PCI DSS is a foundational pillar for funds compliance. Its necessities—together with constructing a safe community, defending saved cardholder information, and implementing robust entry management measures—are non-negotiable for any entity that processes funds.
There are 4 ranges of compliance in PCI, primarily based on the variety of transactions carried out and each firm processing funds ought to pay attention to these.
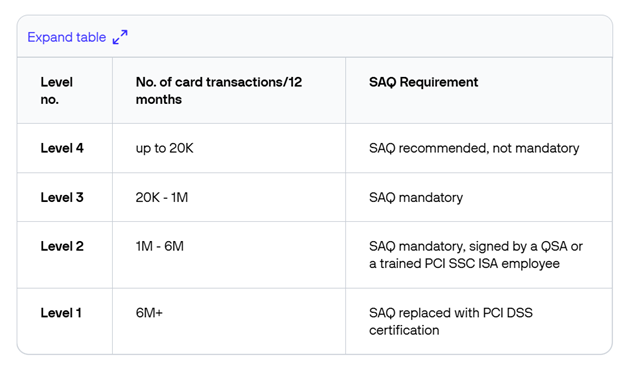
Supply: Verifone Cloud
For the bottom degree of compliance – degree 4 – organizations are primarily confronted with assembly the PCI necessities of their financial institution or funds supplier. Whereas they do have some particular obligations to carry out, the excellent news is that they’ll significantly scale back the complexity of their PCI-DSS compliance.
Streamline your compliance efforts by working with funds supplier 2Checkout. All of our software program and {hardware} options are PCI-compliant. This simplifies your efforts to adjust to monetary and privateness rules in new markets and channels
One other essential commonplace shaping international fee interoperability is ISO 20022, which defines a common information format for monetary messaging. By selling richer, structured information and standardizing communication between banks and fee techniques, ISO 20022 enhances transparency, compliance, and effectivity throughout borders. Retailers can use this structured information for higher analytics and insights into their fee information.
Different regulation examples embrace: EU’s open banking regulation PSD2 (quickly to be PSD3), which regulates digital fee companies and protects delicate monetary info. A crucial element of PSD2 is SCA (Sturdy Buyer Authentication), which goals to bolster the safety of on-line transactions. Equally, 1033 in the US forces banks to permit third-party-provider entry to checking account information.
Cost-specific rules, such because the EU Prompt Cost Regulation, are impacting banks and fee corporations, whereas Know Your Buyer (KYC), Anti-Cash Laundering (AML) and sanction screening rules are in extensively place to forestall monetary crime.
As international fee techniques evolve, compliance should adapt to an more and more various and fragmented ecosystem. Retailers as we speak function throughout a number of fee rails—from card networks to cell wallets and prompt fee infrastructures—every ruled by its personal safety and information guidelines. On the similar time, native fee strategies proceed to dominate client preferences in lots of markets, requiring retailers to fulfill home compliance requirements alongside international ones. The necessity for sturdy, standardized, and safe compliance practices has by no means been larger—making certain that pace, comfort, and belief advance collectively.
The implications of privateness and information safety legal guidelines
This sort of laws is mandating what information (together with private information) might be collected, the place and the way this information should be saved and processed, in addition to how it may be accessed.
The GDPR within the European Union is the benchmark for complete information safety regulation, nevertheless it’s removed from the one one. International locations worldwide have enacted their very own information safety legal guidelines, such because the CCPA within the US (extra particularly, California), Brazil’s LGPD, India’s DPDP Act, and China’s PIPL. Every has related in addition to distinctive necessities for information dealing with, consent, and cross-border information transfers, forcing corporations to undertake localized compliance methods.
Understanding native cloud rules
Cloud expertise has develop into a cornerstone of contemporary fee operations, giving retailers the scalability, flexibility, and effectivity to innovate quicker and scale back dependence on pricey on-premises infrastructure. It permits speedy deployment of latest companies, simpler integration with third-party instruments, and improved resilience by stronger catastrophe restoration and enterprise continuity capabilities. Retailers can select from varied cloud configurations—non-public, public, or hybrid—to align efficiency, safety, and compliance wants with enterprise targets.
Cloud rules consult with particular legal guidelines enacted by governments or industry-specific rules that target information safety, information privateness and compliance, mandating how information, significantly delicate private or monetary info, is dealt with within the cloud. Examples embrace the important thing rules talked about above, in addition to strict safety requirements that cloud suppliers want to stick to.
Native cloud rules differ by area and by nation, however all give attention to information residency, privateness and safety. Strict information localization necessities are sometimes included in information safety legal guidelines, that are the important thing frameworks right here. As these legal guidelines often require information to be saved on servers bodily positioned inside the nation or area, their necessities straight impression the selection of cloud suppliers and the configuration of cloud companies.
Cloud compliance refers back to the strategy of adhering to all of those regulatory requirements, worldwide legal guidelines and mandates, and {industry} finest practices (frameworks, benchmarks) within the context of cloud computing. The purpose is to make sure that the way in which information is saved, managed and guarded within the cloud meets these common or industry-specific regulatory necessities.
In recent times, attributable to issues over information sovereignty, the idea of the sovereign cloud has gained vital traction—particularly in Europe. A sovereign cloud ensures that information, operations, and help stay solely inside the borders and jurisdiction of a particular nation or area. This strategy supplies a further layer of assurance for organizations managing extremely regulated information, similar to fee or private info, or for these topic to nationwide restrictions on cross-border information transfers. Past compliance, sovereign clouds additionally deal with rising issues about information management, nationwide safety, and geopolitical danger, providing organizations larger transparency and belief of their digital infrastructure.
When assessing suppliers, prioritize these with regional information facilities that meet not solely all of the wanted technical facets, but additionally residency legal guidelines. It is a foundational step in constructing a compliant fee structure. All main cloud suppliers—similar to AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud—enable prospects to specify information areas.
The stakes: Dangers of non-compliance
It’s clear simply by these definitions and ideas that companies as we speak face a several-pronged problem. Mismanaging this convergence isn’t only a technical misstep; it’s a big enterprise danger. Failure to fulfill information sovereignty and fee compliance requirements carries vital dangers:
- Reputational injury: Lack of belief can have long-term penalties that straight impression buyer retention and market place.
As organizations more and more rely upon the cloud for fee processing, compliance is not only a authorized requirement—it’s important for enterprise continuity and progress.

Mastering fee compliance in a cloud setting
Attaining fee compliance inside the constraints of information sovereignty requires a devoted and multi-faceted strategy, beginning with foundational safety requirements.
Map and classify your fee information
Efficient information governance begins with figuring out what information it’s important to cope with. Determine what fee information you course of, the place it resides, and the way delicate it’s. Classify information varieties in line with their regulatory necessities and related danger ranges (e.g., cardholder information, personally identifiable info).
Information mapping clarifies cross-border information flows and helps compliance choices similar to encryption, localization, and entry management—making certain delicate information is protected in line with each PCI DSS and native information safety legal guidelines.
Handle cross-border information transfers
Within the funds and fintech ecosystem, cross-border information transfers are important for fee processing, fraud detection, and analytics—however they’re closely regulated. Below GDPR and the Schrems II ruling, private or monetary information can solely be transferred exterior the EEA if equal protections are assured. This sometimes entails mechanisms similar to:
- Customary Contractual Clauses (SCCs)
- Binding Company Guidelines (BCRs)
For fintechs and retailers utilizing multi-cloud or API-driven infrastructures, this implies performing Switch Impression Assessments (TIAs) and implementing robust technical measures like encryption and pseudonymization. SCCs stay probably the most extensively used mechanism, however they require operational safeguards and authorized due diligence.
As well as, legal guidelines just like the US CLOUD Act (Clarifying Lawful Abroad Use of Information Act) add one other layer of complexity. This act permits U.S. federal regulation enforcement to compel U.S.-based expertise corporations to supply requested information, no matter the place that information is saved globally. This creates a possible battle with information privateness legal guidelines just like the GDPR, making the selection of cloud supplier and their company nationality a crucial think about information sovereignty planning. This concern is a significant driver behind the sovereign cloud motion, with 84% of European organizations now utilizing or planning to make use of sovereign cloud options.
The final word purpose is to construct privacy-resilient architectures—the place compliance, transparency, and belief are embedded into each layer of information processing.
Key safety and compliance requirements to examine for
When selecting a cloud supplier, search for certifications that display a critical dedication to safety and compliance:
- ISO 27001/ ISO 27000: A world commonplace for info safety administration techniques, offering a framework for managing dangers and defending information.
- SOC 2 (System and Group Controls): An auditing commonplace that ensures service suppliers securely handle information to guard organizational and consumer pursuits.
- NIST (Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise): The U.S. Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise supplies cybersecurity danger administration frameworks. Integrating the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) with the MITRE ATT&CK mannequin improves a corporation’s capability to foretell, establish, and react to threats.
- CIS (Vital Safety Controls): A set of prioritized, actionable finest practices to protect towards the most typical cyber-attack vectors.
Some areas additionally impose particular cloud safety frameworks. For instance, the U.S. FedRAMP standardizes safety assessments and authorizations for federal cloud companies.
Attaining cloud compliance means implementing robust safety controls, performing common audits, and constantly monitoring for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
One other essential issue is supplier accountability, necessitating the execution of information processing agreements (DPAs). These agreements make sure that the supplier’s compliance is a binding contractual obligation.
Creating a strategic framework for fee information sovereignty
To navigate the intersection of information sovereignty, fee compliance, and cloud operations, organizations ought to undertake an built-in framework constructed on governance, safe structure, and sturdy controls—mapping information flows, designing compliant infrastructure, implementing encryption and entry insurance policies, and sustaining a examined incident response plan to make sure resilience and belief.
Constructing on this basis, cloud-native architectures can additional strengthen compliance and scalability, permitting organizations to design techniques which can be inherently adaptable, resilient, and aligned with evolving regulatory calls for. As a result of fee and information safety compliance is about extra than simply avoiding danger. It’s additionally about enabling safe, scalable progress and staying aggressive in an more and more advanced funds panorama.

FAQs
1. What’s really useful — hybrid, on-premise, or multi-cloud — for managing fee compliance and information sovereignty?
A hybrid or multi-cloud technique is usually finest. It permits delicate or regulated information to stay in-country — whether or not in an on-premise, non-public, or sovereign cloud setting — whereas leveraging international cloud capabilities for scalability and innovation. This steadiness helps each efficiency and compliance, offered you clearly outline the place information is processed and implement robust encryption and entry controls.
2. Are there potential conflicting legal guidelines associated to information safety?
Sure. Conflicts typically come up between regional privateness legal guidelines (just like the EU’s GDPR) and extraterritorial acts (just like the U.S. CLOUD Act). For instance, a U.S.-based supplier may very well be compelled at hand over information saved within the EU, creating stress with European privateness guidelines. The answer is to make use of contractual, authorized, and technical safeguards—similar to Customary Contractual Clauses (SCCs) and encryption with EU-based key administration.
3. If we outsource fee compliance to a supplier and there’s a breach, who’s accountable?
Duty is shared. The supplier is accountable for sustaining PCI DSS compliance and infrastructure-level safety, however your group stays accountable for making certain that supplier compliance is verified and that information is used lawfully. This ought to be clearly outlined in your Information Processing Settlement (DPA) and incident response plan.
4. What suggestions do it’s important to mitigate information fragmentation throughout techniques?
Begin with information mapping and classification—figuring out the place every information set lives, what legal guidelines apply, and who can entry it. Implement centralized information governance insurance policies and use interoperability frameworks. Contemplate instruments for unified monitoring and implement information minimization ideas to cut back pointless replication.
5. How can we future-proof our compliance structure as rules evolve?
Undertake compliance by design ideas—embedding information safety and sovereignty necessities into your structure from the beginning. Keep steady monitoring, automated audit logs, and adaptable insurance policies that may align with new frameworks (e.g., PSD3 or evolving AI-related privateness guidelines). Periodic third-party audits are additionally key to sustaining readiness.
6. How typically ought to compliance and information governance frameworks be reviewed?
At the least yearly, or everytime you develop to a brand new market, undertake a brand new cloud supplier, or endure main system adjustments. Rules evolve shortly—reviewing your danger assessments, information maps, and supplier agreements ensures ongoing alignment with present legal guidelines and requirements.


