AI brokers are LLM-powered methods that act autonomously to unravel complicated duties. Not like easy chatbots, brokers plan steps, name exterior instruments, and use reminiscence to maintain context. For instance, an agent can analyse information sources and generate a multi-step plan, whereas a fundamental LLM app can solely reply a single immediate.
Subsequently, builders now want to know not solely how brokers work but additionally the layers that make them dependable at scale. Frameworks, runtimes, and harnesses every play a special position, and selecting the incorrect one typically results in complexity, inefficiency, or issues in a while. On this article, we’ll undergo the variations between agent frameworks, agent runtimes, and agent harnesses. And by the top you’ll find out how they work, when to make use of every, and the way they match collectively in a contemporary agent stack.
Background: What’s an “Agent” in AI Programs
An AI agent is an autonomous system that makes use of an LLM and exterior instruments to carry out duties and autonomously takes actions towards a objective. Fashionable generative brokers use massive language fashions as a “mind” however increase them with additional capabilities. This makes them much more highly effective than standalone LLMs. Conventional LLM apps reply prompts immediately, however brokers iteratively plan, make the most of instruments, and bear in mind info.
Brokers vs Conventional LLM Apps
Standard LLM purposes generate a response in a single shot, with out long-term context. In distinction, an AI agent can break a fancy process into subproblems, name exterior APIs or databases, and loop till the objective is met.
For instance, A standard chatbot may translate textual content, however an agent might retrieve dwell information, summarize it, after which generate an motion plan.
Why instruments, reminiscence, and planning matter
Instruments permit brokers to entry real-world information by means of APIs or code execution. Reminiscence shops context past a single dialog. Planning lets brokers break massive issues into steps. With out these elements, an LLM can solely produce one-off responses. With them, it operates extra like a software program employee able to finishing complicated duties.
Core Parts of an AI Agent
Efficient brokers are constructed on three pillars: planning, software utilization, and reminiscence. Planning is the LLM’s reasoning course of. Software utilization provides the agent fingers and senses.
For Instance, net search, calculators, or code execution environments. Reminiscence permits the agent to retailer previous interactions to take care of context over a dialog. Collectively, these elements let an agent map an issue to a sequence of actions that obtain the objective. Subsequently, each useful agent contains the next:
- Reasoning engine (LLM or multimodal mannequin)
- Tooling system for executing exterior actions
- Reminiscence administration
- Planner for multi-step execution
- Runtime to handle execution, retries, and state
- Interface or harness that wraps the agent for deployment
What are Agent Frameworks?
Agent frameworks are libraries or SDKs that enable you construct agentic purposes. They supply abstractions and commonplace patterns for composing language fashions with instruments, reminiscence, and management logic. In essence, a framework is your blueprint for the agent: it defines prompts, software calls, and the general agent loop in a structured means so that you don’t must code every part from scratch.
Or just, an agent framework is a set of libraries that helps builders construct an agent’s reasoning course of, software definitions, prompts, and reminiscence buildings. Frameworks outline what an agent is and the way it ought to behave, however they don’t assure sturdy execution.
Learn extra: Prime 7 Agent Frameworks to Construct AI Brokers
Key Capabilities
Agent frameworks normally embody modules for orchestration, reminiscence, and gear setups. They provide flexibility for builders who need full management over how brokers assume and act.
- Software Orchestration: Frameworks assist outline instruments that an agent can use. They handle how instruments are uncovered to the mannequin, how parameters are validated, and the way responses movement again into the agent’s reasoning loop.
- Reminiscence Integration: Frameworks combine short-term and long-term reminiscence methods. They supply vector retailer interfaces, summarizers, and retrieval instruments so brokers can retailer and recall info reliably.
When to Use an Agent Framework
Use a framework everytime you’re constructing or prototyping an LLM agent. Frameworks are perfect for improvement and early-stage tasks the place ease-of-use issues. There are among the benefits of utilizing an Agent framework:
- Extremely customizable agent behaviour
- Nice-grained management over reminiscence, instruments, or planning
- Fast prototyping with out worrying about long-running execution
- Analysis and experimentation the place flexibility issues
For instance, for an information evaluation agent that makes use of a search API and reminiscence, a framework like LangChain enables you to assemble these items shortly with out writing all of the boilerplate.
What are Agent Runtimes?
Agent runtime is execution engines designed for working brokers in manufacturing. They deal with how the agent runs over time, specializing in reliability and state administration.
In different phrases, a runtime is just like the backend service that powers the agent as soon as it’s deployed. It makes positive the agent’s workflow can pause, resume, and get well from failures, and infrequently supplies extra options like streaming and human-in-the-loop help.
For instance, LangChain’s LangGraph is a runtime that saves every step’s state to a database, so the agent can resume precisely the place it left off even after a crash.
Key Options
- Sturdy Execution: Sturdy execution ensures that if an agent crashes mid-task, the runtime restores the final identified state and resumes the workflow. This prevents lack of progress throughout multi-step operations.
- Error Dealing with & Retries: Runtimes implement structured failure dealing with. They retry failed steps, restore damaged states, and stop runaway loops. Good runtimes scale back human intervention by dealing with predictable failures routinely.
When to Select a Runtime
Select a devoted runtime whenever you transfer into manufacturing or want strong execution. In case your agent must run throughout hours or days, deal with many parallel periods, or survive infrastructure hiccups, a runtime is critical:
- You deploy brokers to manufacturing
- Duties require long-running execution
- You want state restoration after failures
- You run multi-step workflows that should stay steady
- You need predictable error boundaries
What are Agent Harnesses?
Agent harnesses are higher-level methods that wrap agent frameworks and supply opinionated defaults or testing suites. Consider a harness as a “mannequin wrapper” that comes with batteries included. Harnesses arrange built-in instruments, prompts, and workflows so you’ll be able to spin up an agent shortly. In addition they typically double as analysis frameworks, permitting you to check the agent’s behaviour underneath managed situations.
Key Capabilities
The key key functionality of harness contains:
- Prebuilt instruments and workflows: Harnesses include ready-to-use utilities and patterns. For instance, DeepAgents supplies file operations similar to ls, read_file, and write_file, together with computerized subagent creation. This makes it simple to interrupt a big process into smaller elements with out additional coding.
- Opinionated defaults: Harnesses select wise defaults so workflows run instantly with little configuration. For instance, a harness could preselect a mannequin, set a default system immediate, and resolve which instruments needs to be used first. One other instance is a harness that routinely prioritizes search earlier than code execution to make sure dependable outcomes.
When to Use a Harness
Use a harness whenever you need a fast, ready-made agent that works with minimal setup. It’s preferrred when you’re prototyping or want an end-to-end answer that already follows finest practices. In these conditions, a harness saves important effort and time. It’s best to select a harness when:
- You need to launch an agent shortly
- The use case matches a standard or commonplace sample
- You don’t want customized planning or software orchestration
- You like managed defaults as a substitute of handbook configuration
How These Layers Match Collectively: The Tri-Layer Structure
Conceptually, you’ll be able to consider it as Framework → Runtime → Harness. First, you utilize a framework to configure the agent. Lastly, a harness wraps across the course of for analysis: it would routinely run check situations or provide higher-level providers. Every layer builds on the one earlier than, and collectively they cowl the complete lifecycle of an agentic system.
The Tri-Layer Structure
Framework → Runtime → Harness
For instance: you may write a LangChain agent (framework) to outline a buyer help workflow. Then you definitely deploy it with LangGraph (runtime) so it will probably deal with actual person periods and interruptions.
Lastly, you utilize DeepAgents or a check harness to run that agent in opposition to 1000’s of pattern queries to catch hallucinations or bugs. In apply, the runtime and harness are powering or testing what you designed with the framework. The runtime “operationalizes” the framework’s logic, and the harness “validates” it, reinforcing a suggestions loop for enchancment.
How They Interoperate
An agent created in a framework can run inside any appropriate runtime. A harness wraps each and provides workflows, guardrails, and deployment integrations. This stack mirrors conventional software program structure however optimizes for LLM-driven autonomy.
For Instance: A workflow outlined in a single framework might run on LangGraph or one other scheduler with out adjustments. Equally, harnesses depend on the definitions from the framework and the traces from the runtime. Logs, metrics, and state snapshots from the runtime feed into the harness (for scoring or monitoring), and outcomes from the harness can lead you to tweak the framework’s design.
When to Use What: Resolution Matrix
Which layer you prioritize is dependent upon your stage and wishes:
Framework vs Runtime vs Harness: Fast Comparability
- Framework: Defines the agent logic. It’s a static blueprint specifying which LLM, prompts, and instruments to make use of. Use it whenever you’re constructing or customizing an agent.
- Runtime: Manages the execution. It runs the agent loop with persistence, concurrency, and fault tolerance. Use it whenever you want stateful, production-grade efficiency.
- Harness: Gives testing and defaults. It executes the agent underneath managed situations or with opinionated settings. Use it whenever you need to validate behaviour or jump-start with ready-made workflows.
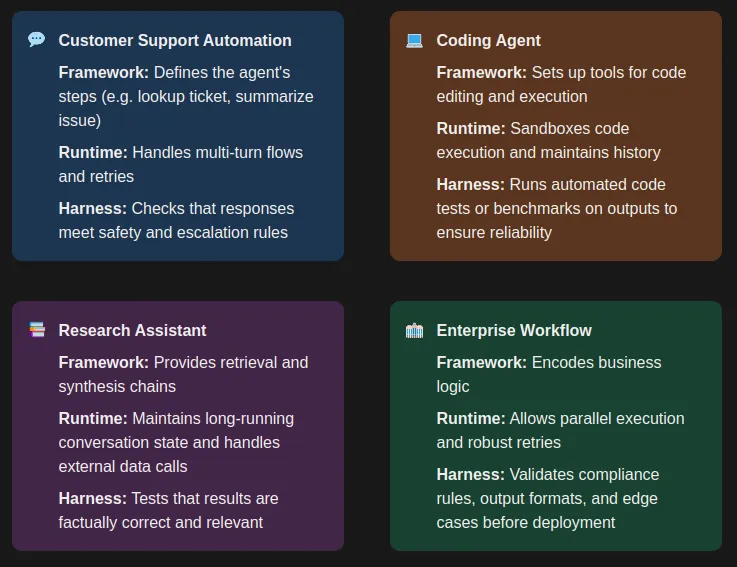
Use-Case Primarily based Suggestions
- Buyer Assist Automation: A framework defines the agent’s steps (e.g. lookup ticket, summarize situation). A runtime handles multi-turn flows and retries. A harness can then verify that responses meet security and escalation guidelines.
- Analysis Assistant: The framework supplies retrieval and synthesis chains. The runtime maintains long-running dialog state and handles exterior information calls. The harness exams that outcomes are factually appropriate and related.
- Coding Agent: The framework units up instruments for code modifying and execution. The runtime sandboxes code execution and maintains historical past. The harness runs automated code exams or benchmarks on outputs to make sure reliability.
- Enterprise Workflow: The framework encodes enterprise logic. The runtime permits parallel execution and strong retries. The harness validates compliance guidelines, output codecs, and edge instances earlier than deployment.
A number of instruments fall into every class. Figuring out the ecosystem helps you choose the appropriate stack.
Frameworks
- LangChain: A number one open-source agent framework, providing wealthy abstractions for LLMs and instruments.
- LlamaIndex: Helps construct retrieval-augmented brokers by managing indexes and information sources.
- Microsoft Semantic Kernel: Gives elements (plugins, reminiscence, chains) for constructing agentic apps.
- OpenAI Brokers SDK: An official SDK for constructing brokers with OpenAI fashions.
- Vercel AI SDK, CrewAI, and so on.: Different libraries that summary widespread agent patterns
Runtimes
- LangGraph: LangChain’s production-ready runtime for sturdy agent execution.
- Temporal: A general-purpose workflow engine typically used for AI brokers, providing sturdy fault tolerance.
- Inngest: A serverless orchestration platform that may schedule agent duties.
- Airflow/Argo: DAG schedulers typically tailored for AI pipelines.
These runtimes deal with stateful, long-running operations like working distributed brokers.
Harnesses
- DeepAgents: LangChain’s opinionated agent harness. It comes with planning instruments, filesystem entry, and built-in workflows.
- Claude Agent SDK: Anthropic’s toolkit for constructing brokers (impressed by their Claude Code system).
- Amp Code: A specialised harness for coding brokers, with built-in defaults tuned for software program improvement.
- Customized Take a look at Harnesses: For instance, utilizing OpenAI Evals or customized scripts to benchmark agent outputs. These function analysis harnesses to make sure agent high quality.
Conclusion
Agent frameworks, runtimes, and harnesses every serve a singular objective. Frameworks outline how brokers behave, runtimes guarantee steady execution, and harnesses present ready-made options for fast deployment. Understanding these layers helps builders select the appropriate instruments, keep away from pitfalls, and construct dependable AI methods.
Collectively, they create a contemporary stack for scalable agent improvement. So, from this detailed information our ultimate take is begin easy with a harness, transfer to a framework when customization is required, and use a runtime when reliability turns into important. This method ensures your brokers keep versatile, steady, and future proof.
Continuously Requested Questions
A. An AI agent is a system powered by an LLM that autonomously plans, makes use of instruments, and maintains reminiscence to finish complicated duties past single-shot responses.
A. Conventional LLM apps generate one-off responses. Brokers can plan, use APIs or instruments, bear in mind context, and iterate till a process is full.
A. Each agent features a reasoning engine, instruments, reminiscence, a planner, a runtime for execution, and an interface or harness for deployment.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.


