If you happen to’re studying LangGraph or exploring extra about it then it’s good to know concerning the pre-built node-level caching in LangGraph. Caching not solely eliminates pointless computation but additionally fastens the latency. We’ll be wanting on the implementation of the identical within the article. It’s assumed that you’ve got an concept about brokers and nodes in LangGraph as we gained’t be specializing in that facet of the story, so with none additional ado let’s stroll into the ideas and implementation.
What’s Caching?
Caching shops information in non permanent storage so the system can retrieve it shortly. Within the context of LLMs and AI Brokers, it saves earlier requests and reuses them when the identical prompts are despatched to the mannequin or agent. As a result of it’s not a brand new request, the system doesn’t cost for it, and the response arrives quicker because of the non permanent reminiscence. When a part of a immediate stays the identical, the system reuses the earlier response and generates a brand new one just for the extra half, which considerably reduces prices even for brand new requests.
Caching parameters and reminiscence
It’s vital to know concerning the ttl (time to stay) parameter which is used to outline the period of time (in seconds) the cache will stay within the reminiscence. If we set ttl=None or depart it as it’s then the cache won’t ever depart the reminiscence.
We have to specify a cache when compiling a graph. We’ll use InMemoryCache to retailer the node’s inputs and outputs that can be utilized later to retrieve the node’s earlier response on this article. Alternatively, you possibly can implement SqliteCache, redisCache or customized cache as properly relying on the wants.
Caching in Motion
Let’s implement Node-level-caching for a perform that helps convert celsius to fahrenheit.
Installations
!pip set up langgraph Defining the Graph
We’ll first outline the graph construction and a easy perform that simulates a gradual computation utilizing time.sleep() to make the caching impact seen.
import time
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.cache.reminiscence import InMemoryCache
from langgraph.sorts import CachePolicy
class State(TypedDict):
celsius: float
fahrenheit: float
builder = StateGraph(State)
def convert_temperature(state: State) -> dict[str, float]:
time.sleep(2)
fahrenheit = (state['celsius'] * 9/5) + 32
return {"fahrenheit": fahrenheit}
builder.add_node("convert_temperature", convert_temperature, cache_policy=CachePolicy(ttl=None))
builder.set_entry_point("convert_temperature")
builder.set_finish_point("convert_temperature")
cache=InMemoryCache()
graph = builder.compile(cache=cache)Invoking the graph
Now, let’s invoke the graph a number of occasions and observe how the cache behaves.
print(graph.invoke({"celsius": 25}))
print(graph.invoke({"celsius": 25}, stream_mode="updates")) # Cached
print(graph.invoke({"celsius": 36}, stream_mode="updates"))
time.sleep(10)
print(graph.invoke({"celsius": 36}, stream_mode="updates"))
cache.clear() # clears all the cacheOutput:
{'celsius': 25, 'fahrenheit': 77.0} [{'convert_temperature': {'fahrenheit': 77.0}, '__metadata__': {'cached': True}}]
[{'convert_temperature': {'fahrenheit': 96.8}}]
[{'convert_temperature': {'fahrenheit': 96.8}}]
The system fetches the response from the cache on the primary repeated request and the TTL is ready to five seconds. It treats the following repeated request as a brand new one when the hole exceeds the TTL. We used cache.clear() to clear all the cache, that is helpful once we set ttl=None.
Now, let’s implement the caching for node with an agent.
Stipulations
We’ll want a Gemini API key to make use of Gemini fashions within the agent, go to Google AI Studio to get your API key: https://aistudio.google.com/api-keys
Installations
The langchain_google_genai module will assist us combine the Gemini fashions within the node.
!pip set up langgraph langchain_google_genai Agent definition
Let’s outline a basic math agent that has entry to the calculator software and we’ll set the ttl=None for now.
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
def solve_math_problem(expression: str) -> str:
"""Remedy a math drawback."""
attempt:
# Consider the mathematical expression
outcome = eval(expression, {"__builtins__": {}})
return f"The reply is {outcome}."
besides Exception:
return "I could not clear up that expression."
# Initialize the Gemini mannequin with API key
mannequin = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(
mannequin="gemini-2.5-flash",
google_api_key=GOOGLE_API_KEY
)
# Create the agent
agent = create_react_agent(
mannequin=mannequin,
instruments=[solve_math_problem],
immediate=(
"You're a Math Tutor AI. "
"When a consumer asks a math query, cause by way of the steps clearly "
"and use the software `solve_math_problem` for numeric calculations. "
"All the time clarify your reasoning earlier than giving the ultimate reply."
),
)Defining the node
Subsequent, we’ll wrap the agent inside a LangGraph node and fix caching to it.
import time
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.cache.reminiscence import InMemoryCache
from langgraph.sorts import CachePolicy
class AgentState(TypedDict):
immediate: str
response: str
builder = StateGraph(AgentState)
def run_agent(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
print("Operating agent...") # this line helps present caching conduct
response = agent.invoke({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": state["prompt"]}]})
return {"response": response}
builder.add_node("run_agent", run_agent, cache_policy=CachePolicy(ttl=None))
builder.set_entry_point("run_agent")
builder.set_finish_point("run_agent")
graph = builder.compile(cache=InMemoryCache())Invoking the agent
Lastly, let’s name the agent twice to see caching in motion.
# Invoke graph twice to see caching
print("First name")
result1 = graph.invoke({"immediate": "What's (12 + 8) * 3?"},stream_mode="updates")
print(result1)
print("Second name (ought to be cached)")
result2 = graph.invoke({"immediate": "What's (12 + 8) * 3?"},stream_mode="updates")
print(result2)Output:
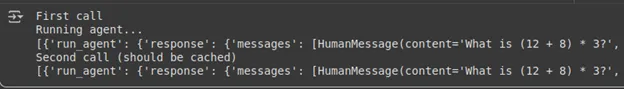
Discover how the second name doesn’t have ‘Operating agent..’ which is a print assertion within the node. So we managed to get the response from the agent with out operating the agent utilizing the cache reminiscence.
Conclusion
LangGraph’s built-in node-level caching gives a easy but highly effective technique to scale back latency and computation by reusing earlier outcomes. With parameters like ttl to handle cache lifetime and choices comparable to InMemoryCache, SqliteCache, or RedisCache, it gives flexibility primarily based on use instances. By way of examples like temperature conversion to agent-based nodes! We noticed how caching avoids redundant execution and saves value. Total, caching in LangGraph significantly improves effectivity, making workflows quicker and extra optimized.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
A. The key_func parameter defines how LangGraph generates a novel cache key for every node’s enter. By default, it makes use of the node’s enter values to create this key. You’ll be able to override it to customise caching conduct. For instance, to disregard particular fields or normalize inputs earlier than comparability.
A. You’ll be able to manually clear the cache anytime utilizing cache.clear(). This removes all saved node responses, forcing LangGraph to re-execute the nodes on the following name. It’s helpful throughout debugging, when working with dynamic inputs, or when the cached information turns into outdated.
A. Sure, every node can have its personal CachePolicy with a customized ttl worth. This lets you cache heavy or gradual computations longer whereas holding incessantly altering nodes contemporary. High quality-tuning TTL values helps stability efficiency, accuracy, and reminiscence effectivity in giant graphs.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.


