Pushed by speedy innovation and rising expectations, the electronics business stands on the crossroads of sensible manufacturing, digital transformation, and sustainability. How do these go hand in hand? Delving deep, Prashant Kumkar from Tata Applied sciences broke down this transition on the EFY Expo in Pune.
Electronics and sensible manufacturing: A mutual drive for progress
We all know that electronics not solely allow sensible manufacturing in factories however that sensible manufacturing itself drives progress in electronics part manufacturing. These components complement and reinforce one another relatively than being fully dependent.
World over the business is experiencing sturdy development, with a worldwide compound annual development fee (CAGR) of round 10%. In India, development is even larger, typically surpassing this benchmark. Towards this backdrop, analyzing the broader traits in sensible manufacturing which are reshaping the economic panorama turns into important.
Manufacturing traits and expertise choice
There are numerous manufacturing applied sciences accessible available in the market. Nonetheless, the true problem lies in figuring out and making use of the suitable expertise to handle particular business issues. This course of requires vital time, effort, and an understanding of each the expertise panorama and aligning it with enterprise priorities.
Some digital applied sciences, akin to PLM, ERP, and MES, and their integration, have to be deployed horizontally throughout the manufacturing unit, together with completely different departments and features. Whereas some applied sciences could be deliberate on a point-to-point foundation, for example, automating guide processes, materials motion, and high quality inspection utilizing robots, cobots, AMRs (autonomous cell robots), and AI-computer imaginative and prescient, it’s critical to evaluate which processes could be digitised, specializing in whether or not they add worth in OpEx discount and enhance high quality and security.
Manufacturing facility well being and efficiency
To keep up manufacturing unit efficiency, industries should monitor the efficiency of every machine and piece of kit, significantly these situated at essential stations. Checking key metrics akin to availability, efficiency, and high quality (APQ) is important for attaining general gear effectiveness.
Transferring in direction of sensible manufacturing environments, that is particularly related for the electronics sector, which performs a twin position: it transforms internally and permits transformation in different industries, akin to automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing. This twin position makes it important to judge the electronics business from each views.
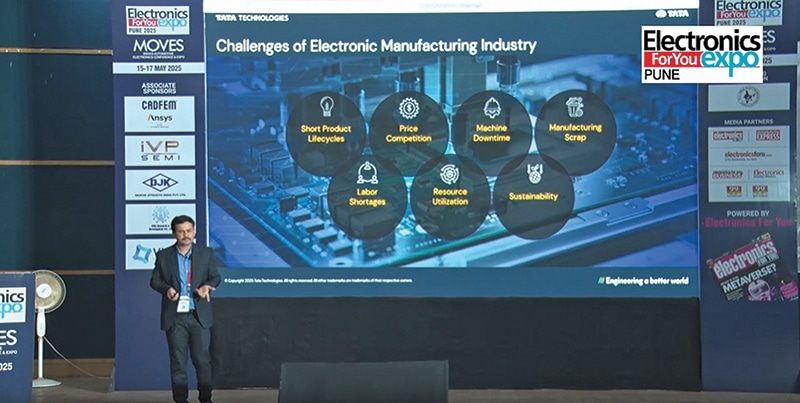
Challenges of the digital manufacturing business
- Product life cycles. These have grow to be considerably shorter. Automotive applications that when lasted 4 to 5 years are actually changed in a single to 2 years. Within the client electronics business, fixed demand for brand new options pressures producers to innovate quickly.
- Pricing pressures. Competitors is intense. Managing prices—not simply the ultimate product worth but in addition CapEx and OpEx—is essential for sustaining profitability.
- Brownfield machines. Factories typically have many current machines which are non-communicating with one another. Changing outdated machines is neither possible nor cost-effective, so retrofitting with IoT gadgets, sensors, or comparable upgrades is important to allow significant analytics.
- Scrap administration. On account of essential operations and precision manufacturing necessities, high quality rejections are very excessive, resulting in heavy course of scrap.
- Expert labour. Shortages of specialists or expert operators affect high quality and on-time supply to prospects.
- Useful resource utilisation. Low utilisation of manufacturing unit sources considerably impacts day-to-day output and OpEx. Efficient use of manpower, machines, supplies, and manufacturing unit house is essential.
- Sustainability. That is now a non-negotiable a part of any industrial technique. Dedication to sustainable practices is crucial from a compliance perspective.
| Good Electronics, Smarter Factories |
| • Electronics gasoline sensible factories; sensible manufacturing, and, in flip, drive electronics innovation • Trade development: 10% globally, even sooner in India • Roadblocks: Shorter product cycles, worth wars, outdated machines, scrap losses, talent gaps, and sustainability calls for • The shift: Join→Combine→AI-power • True success=course of+expertise+individuals working in sync |
The transformation
After we ask what sensible manufacturing really means for the electronics business, the reply begins with recognising the manufacturing unit challenges we face and figuring out cost-effective expertise options to unravel them. From administration’s view, aggressive pressures, operational inefficiencies, financial constraints, and shifting market calls for all push producers towards digital transformation. Applied sciences akin to AI, huge information, and linked methods function foundational enablers.
- Connecting AI with sensible merchandise drives predictive capabilities
- Linking AI with huge information permits superior analytics
- Integrating huge information with connectivity ends in real-time information seize and monitoring
But, transformation shouldn’t be restricted to machines and expertise. Operators on the store flooring play a pivotal position. With out correct coaching and mindset change, even essentially the most superior applied sciences can not ship anticipated outcomes. Thus, sensible manufacturing rests on three pillars: course of, expertise, and other people.
The transformation journey begins with consulting and extends throughout the sensible manufacturing cloud. This journey could be visualised in three progressive levels:
- Digital manufacturing. Focuses on linked machines and factories. Related machines require a communication structure. Non-communicable and legacy machines want retrofitting with sensors and PLCs to grow to be communicable.
- Digital manufacturing unit. Focus shifts to system Integration, utilizing MES (manufacturing execution methods), ERP (enterprise useful resource planning), and PLM (product lifecycle administration). Seamless interplay amongst these layers permits a very linked surroundings.
- AI-driven manufacturing. Captured information is leveraged for data-driven decision-making, supporting high quality management and strategic enterprise planning. Instruments like machine imaginative and prescient and AI-powered predictive upkeep improve manufacturing, guarantee high quality, and enhance operational reliability.
From a data-driven perspective, these three phases are also called Join, Acquire, and Eat.
Steps to make the transformation actual
To start, a manufacturing unit’s present state have to be assessed throughout procurement, stock, manufacturing, provide chain, upkeep, and high quality. Capturing information, analysing it to seek out efficiency gaps, and figuring out enchancment alternatives is essential. Selections have to be justified with a transparent return on funding (ROI).
As soon as the groundwork is laid, the main focus shifts to process-level transformation. Each course of, from manufacturing and meeting to high quality inspection and materials dealing with, have to be simulated and analysed. Simulation instruments, starting from Degree 0 to Degree 5, guarantee layouts and flows are optimised. Each static and dynamic simulations play roles relying on applicability. This consists of simulating human-dependent actions to make sure anticipated output.
Whether or not greenfield or brownfield, manufacturing unit setups have to be just about validated. Bodily and digital validation ensures design, house, gear, and processes align with manufacturing objectives. A communication community, akin to 5G, Wi-Fi, or wired web, have to be chosen to make sure seamless machine-to-machine interplay.
The aim is to create a complete, built-in ecosystem that connects manufacturing methods, manufacturing unit operations, and decision-making capabilities.
Operator coaching is equally very important. Skilled staff could know the method, however new operators should rapidly study to keep away from high quality errors and obtain required efficiency. Instruments akin to digital work directions, AR/VR, and interactive platforms allow just-in-time coaching, even with out formal lecture rooms.
On the execution facet, MES platforms are central. They handle manufacturing orders, monitor workflows and OEE (general gear effectiveness), deal with high quality and upkeep, and monitor power utilization. Actual-time dashboards present visibility into manufacturing unit operations.
For older machines, particularly in brownfield settings, retrofitting is crucial. Sensors can convert even 60- or 70-year-old machines into data-generating models. Newer machines with built-in communication have to be built-in utilizing appropriate protocols akin to MQTT, Modbus, ProfiBus, ProfiNet, and OPC-UA. As soon as linked, this information is then fed into AI-powered methods for predictive upkeep and high quality management.
This brings us to the newest method—6D Good Manufacturing Transformation, which incorporates six pillars:
- Manufacturing facility scanning. Validating that bodily building aligns with digital designs
- Change alerts. Flagging early deviations for well timed corrective actions
- Price anchoring. Monitoring how prices accumulate throughout bodily and digital implementation
- Environmental monitoring. Leveraging information for environmental accountability and compliance
- Sustainability. Aligning with India’s nationwide agenda for sustainable manufacturing
- AI integration. Utilizing AI to handle complexity, drive insights, and assist steady enchancment
Industries are shifting ahead of their manufacturing transformation journey. This evolution extends past digitisation, aiming to create clever, agile, and sustainable ecosystems that handle the altering wants of automotive, aerospace, and electronics sectors.
Primarily based on a session titled ‘Manufacturing Transformation Vs Digital Trade’ delivered by Prashant Kumkar, Observe Head Good Manufacturing, Tata Applied sciences Ltd, on the EFY Expo held on the Auto Cluster Exhibition Middle, Pune, on 16 Might 2025. Transcribed and curated by Shubha Mitra, Assistant Editor at EFY.



