ESET Analysis has found HybridPetya, on the VirusTotal pattern sharing platform. It’s a copycat of the notorious Petya/NotPetya malware, including the aptitude of compromising UEFI-based programs and weaponizing CVE‑2024‑7344 to bypass UEFI Safe Boot on outdated programs.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- New ransomware samples, which we named HybridPetya, resembling the notorious Petya/NotPetya malware, had been uploaded to VirusTotal in February 2025.
- HybridPetya encrypts the Grasp File Desk, which comprises vital metadata about all of the information on NTFS-formatted partitions.
- Not like the unique Petya/NotPetya, HybridPetya can compromise trendy UEFI-based programs by putting in a malicious EFI software onto the EFI System Partition.
- One of many analyzed HybridPetya variants exploits CVE‑2024‑7344 to bypass UEFI Safe Boot on outdated programs, leveraging a specifically crafted cloak.dat file.
- ESET telemetry exhibits no indicators of HybridPetya getting used within the wild but; this malware doesn’t exhibit the aggressive community propagation seen within the unique NotPetya.
Overview
Late in July 2025, we encountered suspicious ransomware samples, uploaded to VirusTotal from Poland, below numerous filenames, together with notpetyanew.exe and different comparable ones, suggesting a reference to the infamously harmful malware that struck Ukraine and lots of different international locations again in 2017. The NotPetya assault is believed to be essentially the most harmful cyberattack in historical past, with greater than $10 billion in whole damages. Regardless of NotPetya’s similarity to the Petya ransomware, first found in March 2016, NotPetya’s function was pure destruction, as encryption key restoration from the sufferer’s private set up key was not attainable. Due to the shared traits of the at the moment found samples with each Petya and NotPetya, we named the brand new discovery HybridPetya.
Whereas ESET telemetry exhibits no lively use of HybridPetya within the wild, one vital element in these samples nonetheless caught our consideration – in contrast to the unique NotPetya (and Petya ransomware as effectively), HybridPetya can be able to compromising trendy UEFI-based programs by putting in a malicious EFI software to the EFI System Partition. The deployed UEFI software is then chargeable for encryption of the NTFS-related Grasp File Desk (MFT) file – an vital metadata file containing details about all of the information on the NTFS-formatted partition.
After a bit extra digging, we found one thing much more fascinating on VirusTotal: an archive containing the entire EFI System Partition contents, together with a really comparable HybridPetya UEFI software, however this time bundled in a specifically formatted cloak.dat file, susceptible to CVE‑2024‑7344 – the UEFI Safe Boot bypass vulnerability – that our staff disclosed in early 2025.
Curiously, regardless of the filenames on VirusTotal and the format of the ransom word within the present samples suggesting that they could be associated to NotPetya, the algorithm used for the technology of the sufferer’s private set up key, in contrast to within the unique NotPetya, permits the malware operator to reconstruct the decryption key from the sufferer’s private set up keys. Thus, HybridPetya can function common ransomware (extra like Petya), moderately than being solely harmful like NotPetya.
Curiously, on September 9th, 2025, @hasherezade printed a submit concerning the existence of a UEFI Petya PoC, with a video demonstrating execution of the malware with UEFI Safe Boot enabled. Regardless that the pattern from the video is clearly completely different from the one introduced on this blogpost (displaying the standard Petya ASCII artwork cranium, which isn’t current within the samples we found), we suspect that there could be some relationship between the 2 instances, and that HybridPetya may also be only a proof of idea developed by a safety researcher or an unknown menace actor.
On this blogpost, we deal with the technical evaluation of HybridPetya.
HybridPetya technical evaluation
On this part, we offer a technical evaluation of HybridPetya’s elements: the bootkit and its installer. We additionally individually dissect a model of HybridPetya that’s able to bypassing UEFI Safe Boot by exploiting CVE-2024-7344. Be aware that HybridPetya helps each legacy and UEFI based mostly programs – on this blogpost, we’ll deal with the UEFI half.
Curiously, the code chargeable for producing the victims’ private set up keys appears to be impressed by the RedPetyaOpenSSL PoC. We’re conscious of at the least one different UEFI-compatible PoC rewrite of NotPetya, dubbed NotPetyaAgain, which is written in Rust; nonetheless, that code is unrelated to HybridPetya.
UEFI bootkit
We obtained two distinct variations of the UEFI bootkit element, each very comparable however with sure variations. When executed, the bootkit first hundreds its configuration from the EFIMicrosoftBootconfig file, and checks the encryption flag indicating the present encryption standing – identical as the unique Petya/NotPetya samples, the encryption flag can have one of many following values:
- 0 – prepared for encryption,
- 1 – already encrypted, or
- 2 – ransom paid, disk decrypted.
It continues with execution based mostly on the encryption standing flag, as proven in Determine 1.
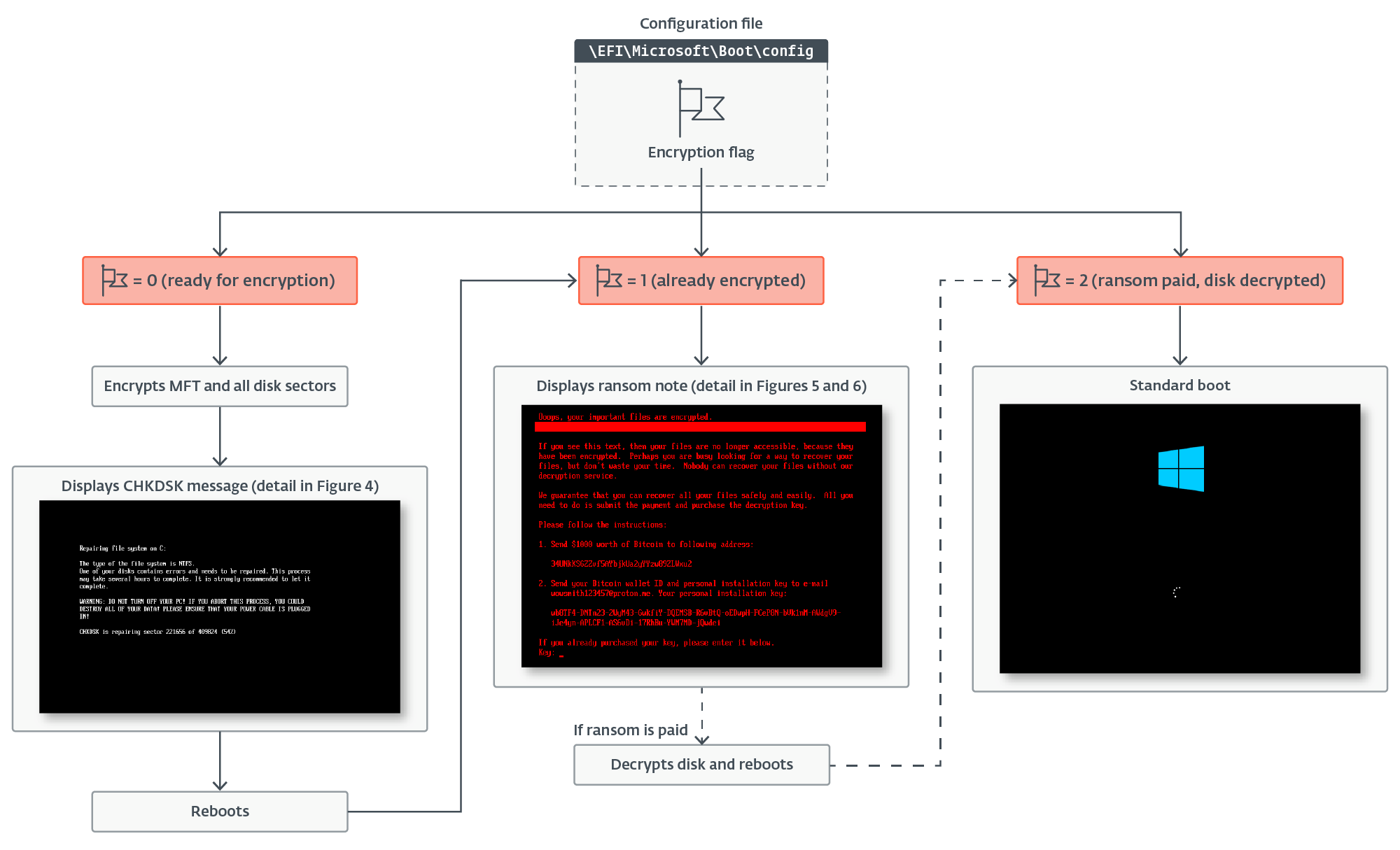
Disk encryption
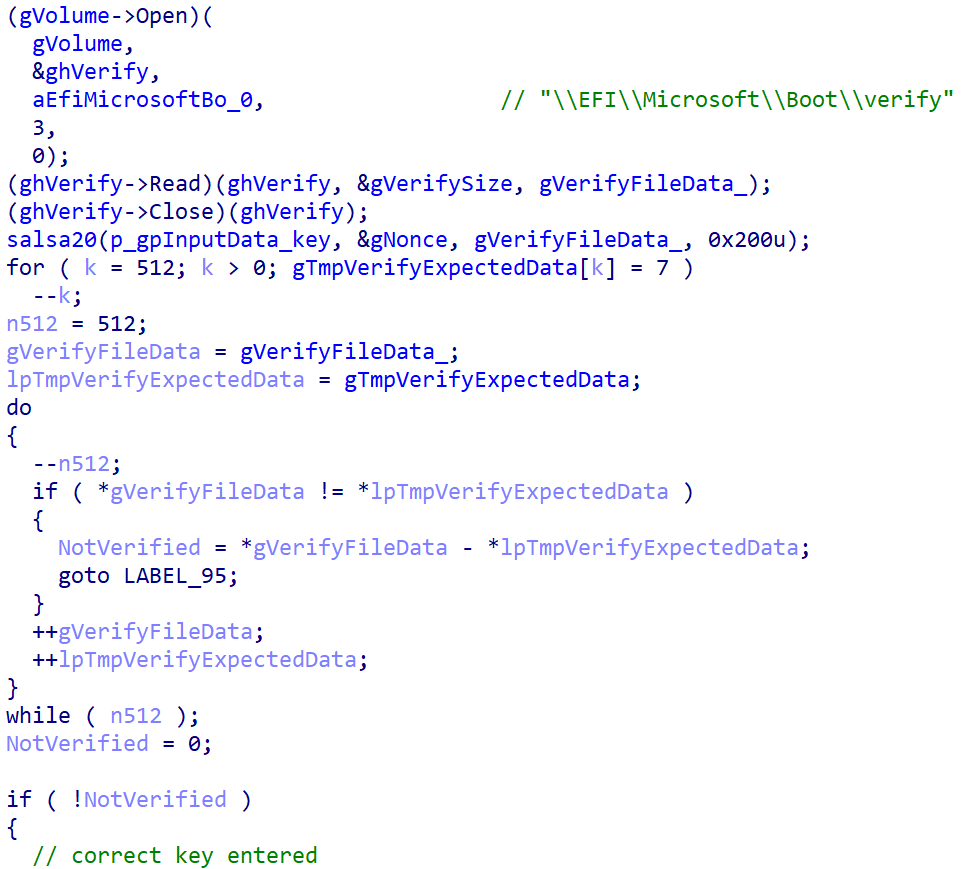
If the worth of the encryption flag is 0, the bootkit extracts the 32-byte-long Salsa20 encryption key and 8-byte-long nonce from the configuration knowledge, and subsequently rewrites the configuration file, now with the encryption key zeroed and the encryption flag set to 1. It continues with encryption of the EFIMicrosoftBootverify file with the Salsa20 encryption algorithm utilizing the important thing and nonce from the configuration. Then, earlier than continuing to its essential performance – disk encryption – it creates the file EFIMicrosoftBootcounter on the EFI System Partition; the aim of this file is defined later.
The disk encryption course of begins with identification of all NTFS-formatted partitions. As proven in Determine 2, the pattern does so by getting the record of handles for related storage gadgets, figuring out the person partitions by checking that EFI_BLOCK_IO_MEDIA->LogicalPartition is TRUE, and at last verifying whether or not the partition is NTFS formatted by evaluating the primary 4 bytes of the information current within the first partition’s sector with the NTFS signature NTFS.

As soon as the NTFS partitions have been recognized, the bootkit continues with encryption of the Grasp File Desk (MFT) file, the important metadata file containing details about different information and the situation of their knowledge on the NTFS-formatted partition. As proven in Determine 3, through the encryption, the bootkit rewrites the contents of the EFIMicrosoftBootcounter file with the variety of already encrypted disk clusters, and updates the pretend CHKDSK message displayed on the sufferer’s display (proven in Determine 4), with the details about the present encryption standing (although, based mostly on the message, the sufferer could imagine that the disk is being checked for errors, not being encrypted).

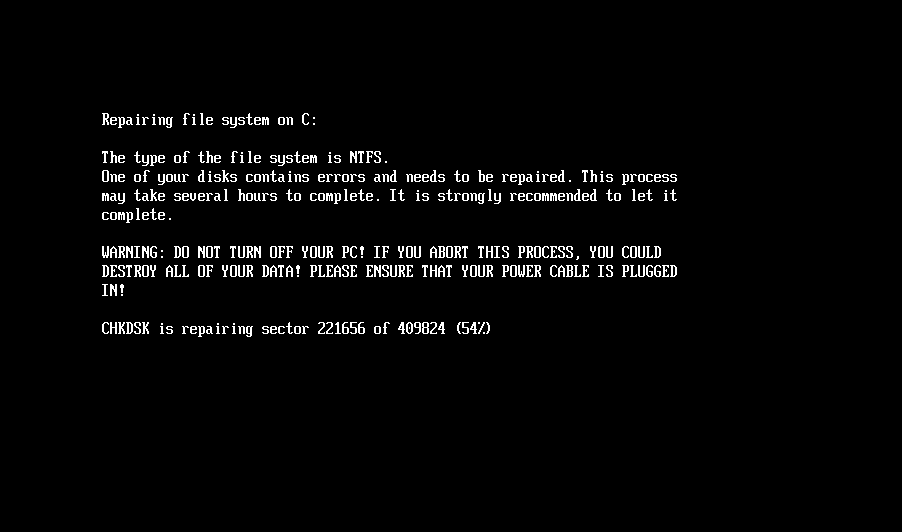
When carried out with the encryption, the bootkit reboots the machine.
Disk decryption
If the bootkit detects that the disk is already encrypted, which means that the worth of the encryption flag from the configuration file is 1, it exhibits the ransom word proven in Determine 5 or Determine 6 (relying on the bootkit model), and asks the sufferer to enter the decryption key. Be aware that whereas the HybridPetya ransom word has the identical format as that of the unique NotPetya (proven in Determine 7), the ransom quantity, bitcoin deal with, and the operator’s e-mail deal with are completely different. Additionally, the model deployed with the UEFI Safe Boot bypass makes use of a special contact e-mail deal with (wowsmith999999@proton[.]me) than the model deployed by the obtained installers (wowsmith1234567@proton[.]me). It’s value mentioning that the bitcoin deal with is similar in each variations.
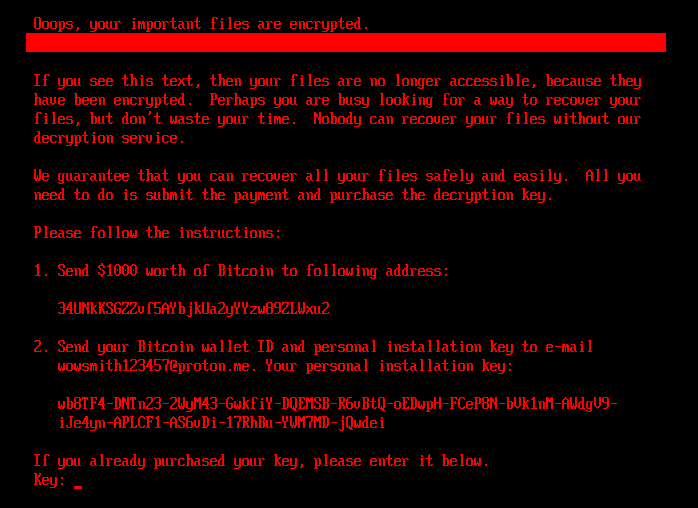
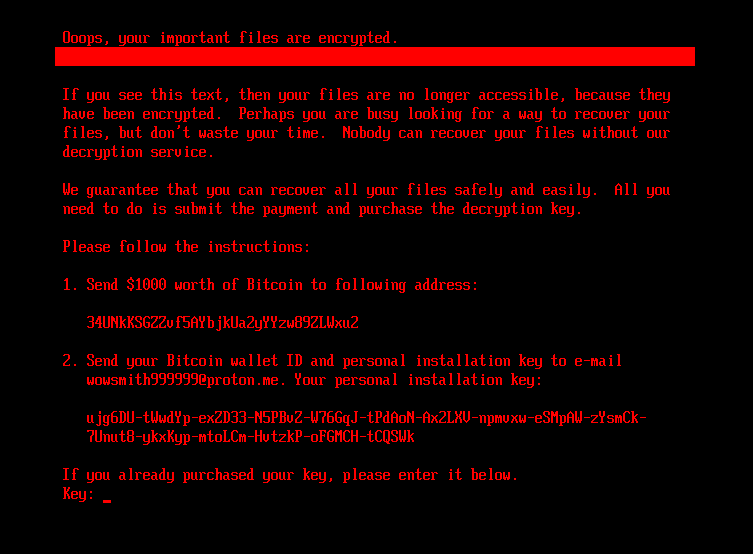
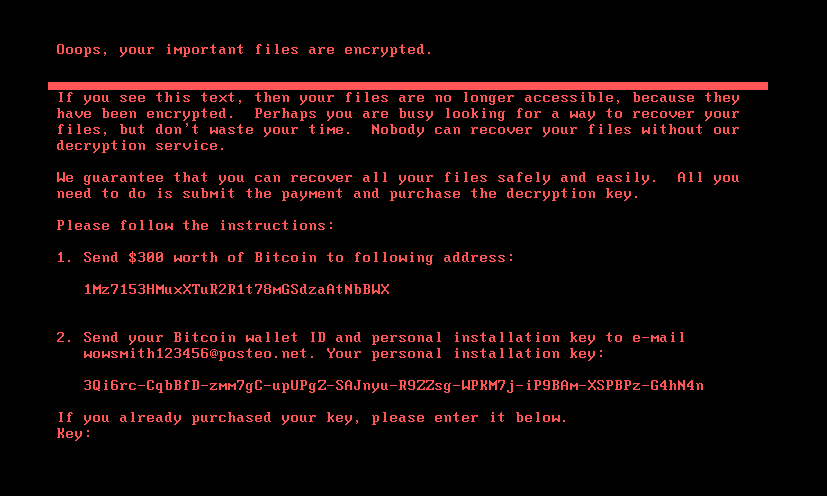
When a key with the right size – 32 characters – is entered and confirmed by the sufferer urgent Enter, the bootkit proceeds to verification of the important thing. As depicted in Determine 8, key validity is established by making an attempt to decrypt the aforementioned EFIMicrosoftBootverify file with the equipped key, and checking whether or not the plaintext comprises solely bytes with worth 0x07. Be aware that the bootkit variant deployed through the UEFI Safe Boot bypass hashes the equipped key with an algorithm most likely based mostly on SPONGENT-256/256/16, utilizing that hash worth because the decryption key, whereas the bootkit deployed by the obtained installers takes the person’s enter as is.
If the right key’s entered, the bootkit updates the configuration file with the encryption flag worth set to 2 and likewise fills within the decryption key. Then it reads the contents of the EFIMicrosoftBootcounter file (containing the variety of disk clusters beforehand encrypted) and proceeds with disk decryption. For the decryption, the bootkit proceeds with a really comparable course of to that of NTFS partition discovery and MFT decryption (the Salsa20 encryption and decryption course of is similar) as described within the Disk encryption part. The decryption stops when the variety of decrypted clusters is the same as the worth from the counter file. In the course of the technique of MFT decryption, the bootkit exhibits the present decryption course of standing, depicted in Determine 9, on the sufferer’s display.
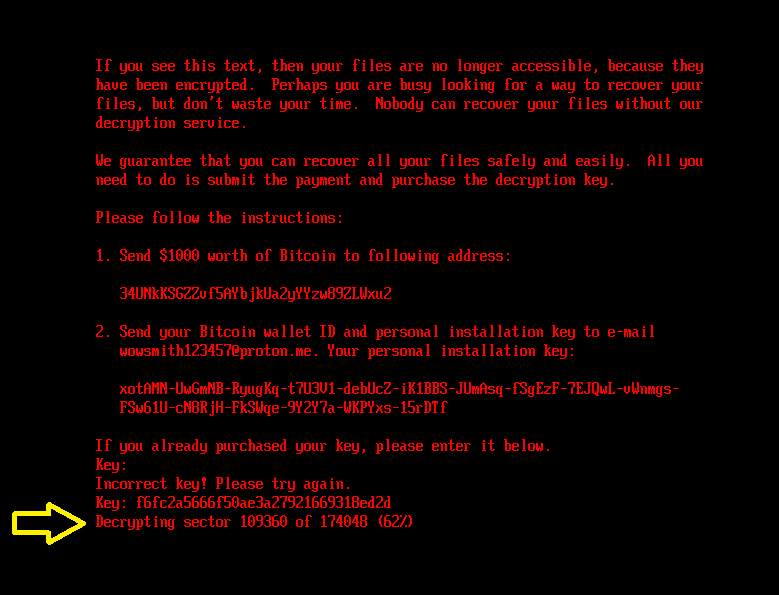
Subsequent, the bootkit proceeds with recovering the professional bootloaders EFIMicrosoftBootbootmgfw.efi and EFIBootbootx64.efi from the backup file beforehand created through the set up course of: EFIMicrosoftBootbootmgfw.efi.previous.
Lastly, after the decryption course of is completed and the professional bootloaders recovered, the bootkit prompts the sufferer to reboot the gadget (Determine 10). If every thing went effectively, the gadget ought to begin the working system efficiently after the reboot.

Deploying the UEFI bootkit element
On this part, we deal with the bootkit-installation performance of the found HybridPetya installers. Be aware that the installers we had been capable of get hold of don’t take UEFI Safe Boot under consideration. Nevertheless, as defined within the CVE-2024-7344 exploitation part, there’s possible a variant with such an enchancment.
To resolve whether or not the system is UEFI based mostly, the installer retrieves the disk info (IOCTL_DISK_GET_DRIVE_LAYOUT_EX), checks whether or not the GPT partitioning scheme is used (PARTITION_STYLE_GPT), and walks by way of the partitions till it discovers the one with PARTITION_INFORMATION_GPT.PartitionType set to PARTITION_SYSTEM_GUID, which is the identifier of the EFI System Partition. After discovering the EFI System Partition, it continues:
- Eradicating the fallback UEFI bootloader, saved in EFIBootBootx64.efi.
- Dropping a disk-encryption-related configuration together with the encryption flag, to the EFIMicrosoftBootconfig file on the EFI System Partition; the encryption configuration comprises the Salsa20 encryption key, 8-byte nonce, and sufferer’s private set up key (base58-encoded knowledge).
- Dropping an encryption-verification array consisting of 0x200 bytes with worth 0x07 to the EFIMicrosoftBootverify file on the EFI System Partition; this array is later encrypted by the bootkit element utilizing the identical Salsa20 key as used for disk encryption. The aim of this array is to confirm whether or not the sufferer entered a sound decryption key (by decrypting the array with the entered key, and verifying that the plaintext comprises an array of bytes with worth 0x07).
- Making a backup of EFIMicrosoftBootbootmgfw.efi, the default bootloader for Home windows-based programs, by copying it into EFIMicrosoftBootbootmgfw.efi.previous.
When carried out, it triggers a system crash (Blue Display Of Demise, BSOD) by utilizing the identical technique that Petya did – invoking the NtRaiseHardError API with the ErrorStatus parameter set to 0xC0000350 (STATUS_HOST_DOWN) and the ResponseOption set to worth 6 (OptionShutdownSystem), leading to a system shutdown.
The abovementioned modifications make sure that on programs with Home windows set as the first OS, the bootkit binary will likely be executed as soon as the gadget is powered on once more.
CVE-2024-7344 exploitation
On this part, we look at an archive that we found on VirusTotal that comprises a variant of the UEFI bootkit described within the UEFI bootkit part, however this time bundled in a specifically formatted cloak.dat file associated to CVE-2024-7344 – the UEFI Safe Boot bypass vulnerability that our staff publicly disclosed in early 2025.
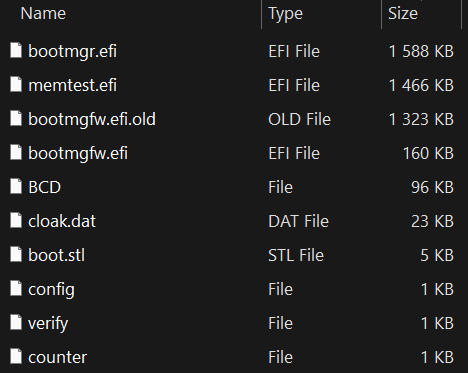
A listing of the information current within the archive together with their contents means that this EFI System Partition was copied from a system already encrypted by this Petya/NotPetya copycat variant. Be aware that we haven’t obtained the installer chargeable for deploying this model with the UEFI Safe Boot bypass, however based mostly on the archive’s contents, that are proven in Determine 11, it could be fairly just like the method described within the earlier part. Particularly, the archive comprises:
- EFIMicrosoftBootcounter, a file already containing a non-zero worth representing the variety of disk clusters beforehand encrypted by the bootkit,
- EFIMicrosoftBootconfig, a file with the encryption flag worth set to 1, which means that the disk needs to be already encrypted and the bootkit ought to proceed with displaying the ransom word,
- EFIMicrosoftBootbootmgfw.efi.previous, a file with the primary 0x400 bytes XORed with the worth 0x07,
- EFIMicrosoftBootbootmgfw.efi, a professional, however susceptible (CVE‑2024‑7344) UEFI software signed by Microsoft (revoked in Microsoft’s dbx since January 2025); on this part we’ll confer with this file with its unique title reloader.efi, and
- EFIMicrosoftBootcloak.dat, a specifically crafted file loadable by way of reloader.efi and containing the XORed bootkit binary.
As described in our report from January 2025, the exploit mechanism is kind of easy. The cloak.dat file comprises specifically formatted knowledge that comprises a UEFI software. When the reloader.efi binary (deployed as bootmgfw.efi) is executed throughout boot, it searches for the presence of the cloak.dat file on the EFI System Partition, and hundreds the embedded UEFI software from the file in a really unsafe approach, fully ignoring any integrity checks, thus bypassing UEFI Safe Boot.
Be aware that our blogpost from January 2025 didn’t clarify the exploitation in high-quality element; thus, the malware writer most likely reconstructed the right cloak.dat file format based mostly on reverse engineering the susceptible software on their very own.
The vulnerability can’t be exploited on programs with Microsoft’s January 2025 dbx replace utilized. For steerage on defend and confirm whether or not your system is uncovered to this vulnerability, test the Safety and Detection part of our January 2025 blogpost.
Conclusion
HybridPetya is now at the least the fourth publicly recognized instance of an actual or proof-of-concept UEFI bootkit with UEFI Safe Boot bypass performance, becoming a member of BlackLotus (exploiting CVE‑2022‑21894), BootKitty (exploiting LogoFail), and the Hyper-V Backdoor PoC (exploiting CVE‑2020‑26200). This exhibits that Safe Boot bypasses will not be simply attainable – they’re turning into extra widespread and engaging to each researchers and attackers.
Though HybridPetya shouldn’t be actively spreading, its technical capabilities – particularly MFT encryption, UEFI system compatibility, and Safe Boot bypass – make it noteworthy for future menace monitoring.
For any inquiries about our analysis printed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at [email protected].ESET Analysis affords personal APT intelligence stories and knowledge feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Risk Intelligence web page.
IoCs
A complete record of indicators of compromise (IoCs) and samples will be present in our GitHub repository.
Recordsdata
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| BD35908D5A5E9F7E41A6 |
bootmgfw.efi | EFI/Diskcoder.A | HybridPetya – UEFI bootkit element. |
| 9DF922D00171AA3C31B7 |
N/A | EFI/Diskcoder.A | HybridPetya – UEFI bootkit element, extracted from cloak.dat. |
| 9B0EE05FFFDA0B16CF9D |
N/A | Win32/Injector.AJBK | HybridPetya installer. |
| CDC8CB3D211589202B49 |
core.dll | Win32/Filecoder.OSK | HybridPetya installer. |
| D31F86BA572904192D74 |
f20000.mbam |
Win32/Filecoder.OSK | HybridPetya installer. |
| A6EBFA062270A3212414 |
improved_not |
Win32/Kryptik.BFRR | HybridPetya installer. |
| C8E3F1BF0B67C83D2A6D |
notpetya |
Win32/Kryptik.BFRR | HybridPetya installer. |
| C7C270F9D3AE80EC5E89 |
notpetyanew.exe | Win32/Kryptik.BFRR | HybridPetya installer. |
| 3393A8C258239D680255 |
notpetyanew_imp |
Win32/Kryptik.BFRR | HybridPetya installer. |
| 98C3E659A903E74D2EE3 |
bootmgfw.efi | N/A | UEFI software susceptible to CVE-2024-7433. |
| D0BD283133A80B471375 |
cloak.dat | EFI/Diskcoder.A | Specifically formatted cloak.dat associated to CVE-2024-7433, comprises XORed HybridPetya UEFI bootkit element. |
MITRE ATT&CK strategies
This desk was constructed utilizing model 17 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Title | Description |
| Useful resource Improvement | T1587.001 | Develop Capabilities: Malware | HybridPetya is new ransomware with UEFI compatibility and a UEFI bootkit element developed by unknown authors. |
| T1587.004 | Develop Capabilities: Exploits | HybridPetya’s authors developed an exploit for the CVE‑2024‑7344 UEFI Safe Boot bypass vulnerability. | |
| Execution | T1203 | Exploitation for Consumer Execution | HybridPetya exploits CVE‑2024‑7344 to execute an unsigned UEFI bootkit on outdated programs with UEFI Safe Boot enabled. |
| T1106 | Native API | HybridPetya installers use undocumented native API NtRaiseHardError to trigger a system crash after the bootkit’s set up. | |
| Persistence | T1542.003 | Pre-OS Boot: Bootkit | HybridPetya persists utilizing the bootkit element. It helps each legacy and UEFI programs. |
| T1574 | Hijack Execution Circulation | HybridPetya installers hijack the common system boot course of by changing the professional Home windows bootloader with a malicious one. | |
| Privilege Escalation | T1068 | Exploitation for Privilege Escalation | HybridPetya exploits CVE‑2024‑7344 to bypass UEFI Safe Boot and execute the malicious UEFI bootkit with excessive privileges throughout bootup. |
| Protection Evasion | T1211 | Exploitation for Protection Evasion | HybridPetya exploits CVE‑2024‑7344 to bypass UEFI Safe Boot. |
| T1620 | Reflective Code Loading | HybridPetya installers use the reflective DLL loading method. | |
| T1036 | Masquerading | The HybridPetya bootkit shows pretend CHKDSK messages on the display throughout disk encryption to masks its malicious exercise. | |
| Influence | T1486 | Information Encrypted for Influence | The HybridPetya installer encrypts information with specified extensions and the bootkit element encrypts MFT file on every NTFS-formatted partition. |
| T1529 | System Shutdown/Reboot | HybridPetya reboots the gadget after MFT encryption. |



