Researchers on the College of Freiburg have launched a course of for volumetric 3D printing that allows advanced multi-material components and microscale inner channels to be produced in a single curing step. The tactic, known as Embedded Extrusion-Volumetric Printing (EmVP), was detailed in a peer-reviewed research revealed in Nature Communications and integrates embedded 3D printing (EMB3D) with tomographic volumetric additive manufacturing (TVAM), eliminating the necessity for vat exchanges or post-print alignment.
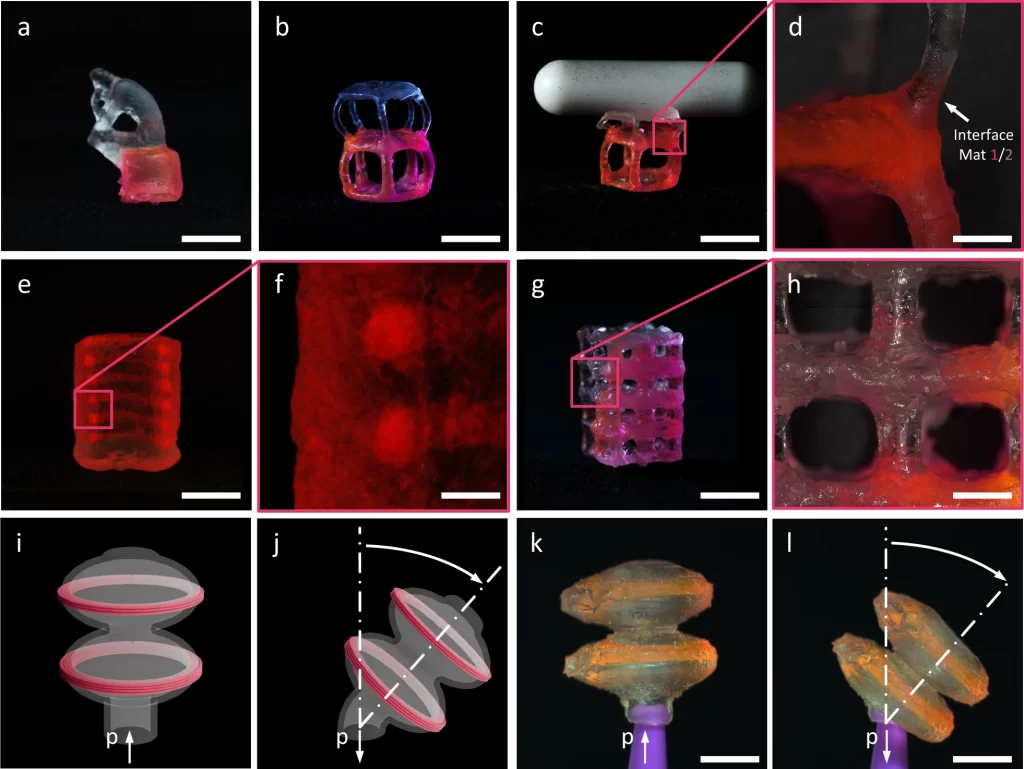
The method embeds one materials into one other earlier than projection, utilizing EMB3D to deposit an ink right into a photopolymerizable assist tub. Each supplies are then polymerized concurrently utilizing TVAM. To attain synchronization, the Freiburg staff engineered the gelation instances of the supplies to converge: 59.8 seconds for the embedded high-modulus ink (Mat 1) and 64.7 seconds for the low-modulus assist tub (Mat 2). Every resin was modified with Aerosil R805 to create a thixotropic matrix appropriate for each extrusion and volumetric curing. Refractive index variations had been minimized to scale back mild scattering throughout publicity.


Mat 1, primarily based on hexanediol diacrylate (HDDA), exhibited a Shore D hardness of 27.4 and an elastic modulus of 122 MPa. Mat 2, primarily based on Genomer 1122TF, confirmed a Shore D hardness of 4.9 and an elastic modulus of 1.28 MPa. To stop sedimentation throughout printing, each resins had been thickened past 2000 mPa·s. Restoration instances had been measured at 4.7 seconds for Mat 1 and 1.7 seconds for Mat 2 following shear removing, enabling exact ink deposition and stabilization. UV-Vis spectroscopy confirmed that each supplies maintained enough transmittance on the 450 nm projection wavelength used within the TVAM setup.
Multi-material components fabricated through EmVP included stacked dual-hardness spheres, filaments embedded in partitions of versatile cylinders, and actuators composed of soppy shells bolstered with stiff embedded rings. The embedded filament diameter achieved with EMB3D was 175 µm. One construction featured Rodin’s Thinker sitting atop a inflexible platform embedded inside a tender resin physique, with deformation exams confirming selective mechanical response. The common Hausdorff distance between printed and modeled geometries was 0.23 ± 0.28 mm, as decided through microCT, demonstrating spatial constancy in volumetric materials transitions.

Along with optimistic materials integration, the researchers used sacrificial inks to kind embedded voids. Often known as adverse EmVP, this course of permits direct fabrication of hole microchannels by flushing out a non-photopolymerizable ink after volumetric curing. Utilizing Pluronic PE3100 because the sacrificial section, the staff printed Y-junction chips and coiled cylindrical designs with inner diameters as small as 119 µm. This decision surpasses the five hundred µm decrease restrict of the standalone TVAM system, the place overcuring and diffusion results usually constrain adverse characteristic constancy. Channel diameters had been verified by microCT scans utilizing 15 µm voxel decision.
In comparison with sequential multi-material volumetric printing (SMVP), which requires curing one materials at a time adopted by vat alternative and alignment, EmVP avoids the necessity for extra assist buildings, advanced mechanical positioning, or dual-wavelength projection methods. In SMVP, any misalignment may end up in geometric error or print failure. Freiburg’s EmVP method, against this, performs all curing in a single volumetric step, with the embedded materials held in place by the rheological properties of the encompassing tub.


Earlier implementations of EmVP had been restricted to overprinting, the place one materials was totally encased in one other. The current research extends that by enabling uncovered, spatially distinct areas composed of various supplies. By depositing solely the minimal essential ink quantity, the researchers minimized oozing artifacts and diminished EMB3D print period. This selective deposition was coupled with projection optimization utilizing Object Area Mannequin Optimization (OSMO) refined through Proportional-Integral Histogram Equalization. Projections had been computed by voxelizing the 3D mannequin, forward-projecting to simulate mild paths, and iteratively adjusting dose distributions to match goal geometry.
To scale the method with out optical redesign, the staff prioritized embedding the higher-absorbing materials because the minority section, permitting projections to remedy the whole construction with out extreme vitality absorption. This setup maintains decision with out lowering pixel measurement or rising system complexity. For microchannel manufacturing, EmVP decouples channel decision from pixel density by permitting management through needle diameter throughout EMB3D, enabling finer inner options than what TVAM alone can ship.


EmVP expands the vary of printable architectures in volumetric methods, supporting each heterogeneous mechanical properties and embedded microfluidic geometries. Functions embrace tender robotics, practical half prototyping, and lab-on-a-chip gadgets. The method operates on standard LCD-based TVAM {hardware} with out requiring wavelength-selective resins or {hardware} augmentation. Its twin functionality to supply optimistic and adverse options inside a single volumetric print step provides a path ahead for scalable, multi-material additive manufacturing.
Prepared to find who received the 2024 3D Printing Business Awards?
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Business e-newsletter to remain up to date with the newest information and insights.
Featured picture reveals collection of components printed with the optimistic EmVP course of. Picture through Nature Communications.


