With the potential to dramatically enhance coloration accuracy, decision, and even allow hyperspectral imaging, this breakthrough may reshape every little thing from smartphone cameras to medical diagnostics.
Each smartphone and digital digital camera as we speak makes use of picture sensors—gadgets that detect mild very like the human eye. Simply as cone cells in our retina acknowledge purple, inexperienced, and blue (RGB), pixels in picture sensors take up these mild wavelengths and convert them into electrical alerts. Most picture sensors are constructed from silicon, a cloth that naturally captures the complete seen spectrum. To isolate particular person colours, filters are utilized to every pixel. Sadly, this design wastes two-thirds of the incoming mild, as every pixel solely captures one coloration.
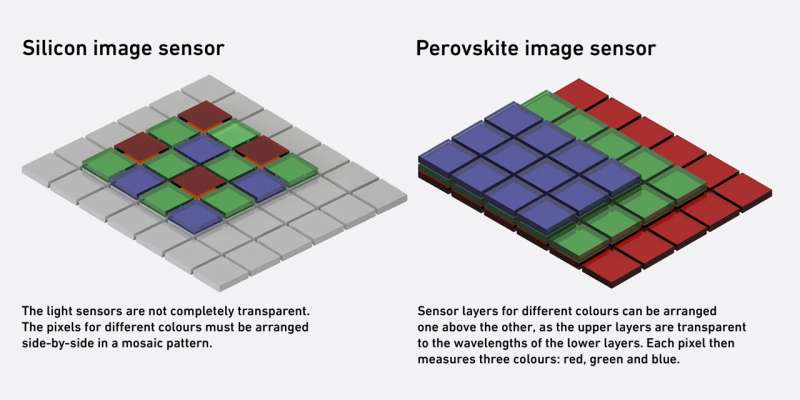
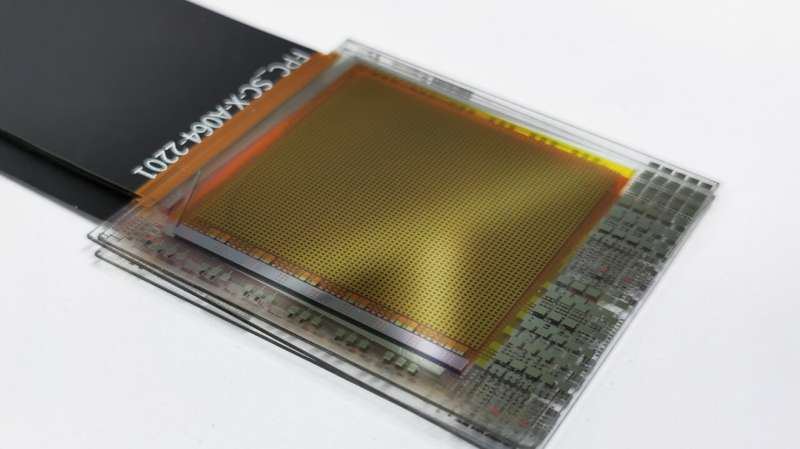
Researchers led by Maksym Kovalenko at ETH Zurich and Empa have developed a groundbreaking different: perovskite-based picture sensors. Their analysis outlines how this new method may triple the effectivity and backbone of conventional sensors. The important thing lies in a cloth known as lead halide perovskite, a semiconductor that may be chemically adjusted to soak up particular colours. By barely altering its composition—including iodine for purple, bromine for inexperienced, or chlorine for blue—researchers created layers that every seize a unique coloration of sunshine, with out the necessity for filters. These layers are stacked vertically, in contrast to the horizontal format of silicon pixels.
This stacking technique permits all the sunshine for use, considerably boosting picture high quality and coloration accuracy. Two thin-film prototypes have already been constructed, proving the tech will be scaled down from lab-sized crystals to sensible gadgets.Past pictures, these sensors may energy hyperspectral imaging, the place a number of mild wavelengths (past RGB) are analyzed.
That is essential in fields like medical diagnostics, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. Perovskite sensors provide fine-tuned wavelength management with out the cumbersome filters and heavy processing silicon methods require.Whereas nonetheless in early improvement, the researchers goal to shrink pixel sizes from the present 0.5–1 mm to the micrometer scale, typical in business gadgets. It will require rethinking readout electronics designed for silicon.




