A current evaluate printed in ScienceDirect by researchers from RMIT College, College of Southern Queensland (UniSQ), College of Melbourne, College of Sherbrooke and the Division of Transport and Most important Roads, Queenslandexamines the usage of polymer composites in civil infrastructure by way of additive manufacturing. The authors argue that 3D printing with polymer composites provides options that align with trendy development calls for, highlighting advances, challenges, and analysis alternatives on this subject.
Polymer composites have emerged as a flexible class of supplies in civil engineering because of their excessive strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. The evaluate particulars how these supplies have changed metals in quite a few sectors, together with automotive, aerospace, and development. Combining polymers with reinforcing supplies corresponding to fibers or particulates enhances their mechanical and thermal properties, supporting a variety of commercial purposes.
The evaluate notes that whereas polymers alone have restricted standalone purposes, they’re regularly mixed with different supplies to kind composites appropriate for structural and non-structural makes use of. These composites present advantages corresponding to superior fatigue resistance, put on resistance, and environmental sturdiness. Functions in civil engineering vary from polymer-modified concrete and fiber-reinforced polymer bars to sealing supplies, waterproof membranes, and protecting coatings.


Additive Manufacturing Strategies for Polymer Composites
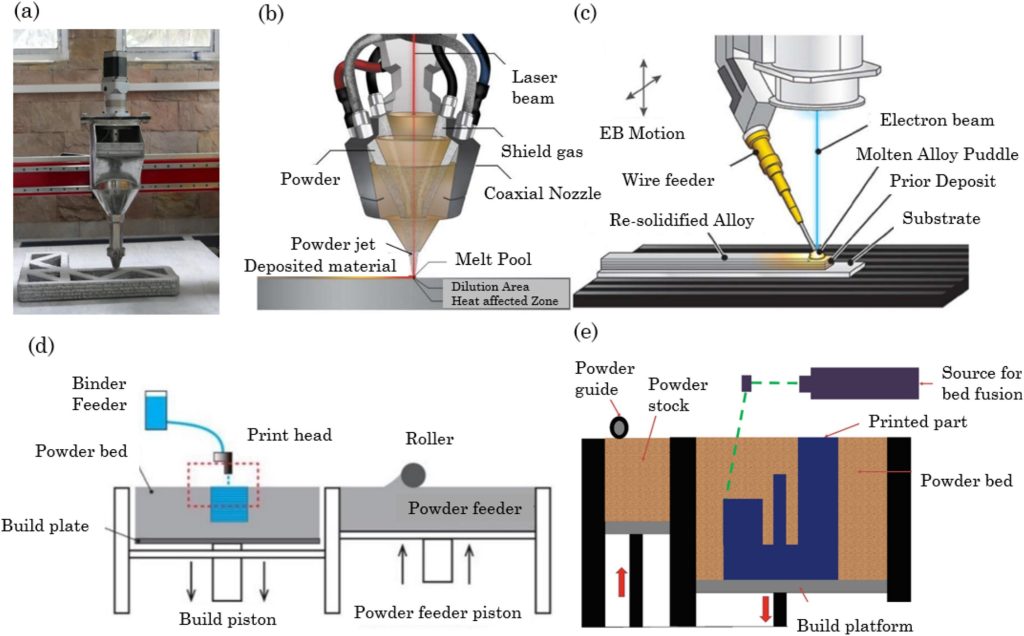
Additive manufacturing (AM), generally referred to as 3D printing, allows layer-by-layer development of objects primarily based on digital fashions, lowering materials waste and permitting for advanced geometries. The evaluate outlines numerous AM methods relevant to polymer composites, together with extrusion-based processes like fused deposition modeling (FDM) and direct ink writing (DIW), powder-bed fusion strategies corresponding to selective laser sintering (SLS), and binder jetting.
Materials extrusion is broadly utilized in civil infrastructure for printing concrete, ceramics, and polymers. Binder jetting applies liquid binders to powder beds to create stable elements, whereas powder-bed fusion makes use of thermal vitality, usually from lasers or electron beams, to selectively soften or sinter powders. Direct vitality deposition methods, which contain feeding supplies in powder or wire kind and melting them throughout deposition, are additionally related for metallic parts in development.
The authors emphasize that extrusion-based 3D printing is especially vital for producing large-scale parts. For thermoplastics, feedstock may be provided in filament or granular kind, with the fabric melted and extruded to construct elements. The evaluate additionally describes the function of printing parameters corresponding to extrusion pace, layer top, and thermal settings in reaching structural integrity and mechanical efficiency.

Gaps in Literature, Mechanical Efficiency and Sturdiness Challenges
Whereas additive manufacturing has gained traction in civil infrastructure—significantly with 3D printed concrete—the mixing of polymer composites by way of AM stays underrepresented in tutorial research. The evaluate highlights that the majority present evaluations concentrate on fiber-reinforced polymers in typical development purposes corresponding to reinforcing bars and retrofitting, typically overlooking their potential in additive manufacturing contexts.
Sustainable alternate options, corresponding to recycled and bio-based polymers, are additionally underexplored, regardless of their rising relevance in efforts to decarbonize the development sector. The evaluate factors out that restricted consideration has been given to how these supplies can be utilized in 3D printing for infrastructure, leaving a vital information hole for researchers and practitioners.
Mechanical efficiency is a key consideration for 3D printed polymer composites in civil infrastructure. The evaluate identifies points corresponding to anisotropic properties ensuing from the layer-by-layer deposition course of, which may result in decreased tensile power and interlayer adhesion. These elements have an effect on the load-bearing capability and long-term reliability of printed parts.


Environmental sturdiness is one other concern. Publicity to ultraviolet radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations can degrade the efficiency of polymer composites, limiting their applicability in outside or high-stress environments. Strategies corresponding to steady fiber reinforcement, post-processing strategies, and hybrid manufacturing approaches are being explored to deal with these challenges and enhance interlayer bonding and total mechanical properties.
The absence of standardized design codes and certification pathways additional complicates the adoption of 3D printed polymer composites in civil infrastructure. In contrast to conventional supplies like metal and concrete, which have established testing protocols, polymer-based 3D-printed parts lack unified efficiency benchmarks, creating uncertainty for engineers and regulators.
Analysis Instructions and Future Alternatives
The authors, together with Dr. Sachini Wickramasinghe (RMIT College and UniSQ), Professor Allan Manalo (UniSQ), Affiliate Professor Omar Alajarmeh (UniSQ), Charles Dean Sorbello (Division of Transport and Most important Roads, Queensland), Senarath Weerakoon (UniSQ), Professor Tuan D. Ngo (College of Melbourne), and Professor Brahim Benmokrane (College of Sherbrooke), determine a number of analysis priorities. These embrace optimizing printing parameters to scale back porosity and improve interlayer adhesion, exploring sustainable supplies like recycled and bio-based polymers, and investigating sensible supplies with properties corresponding to self-healing and embedded sensors.
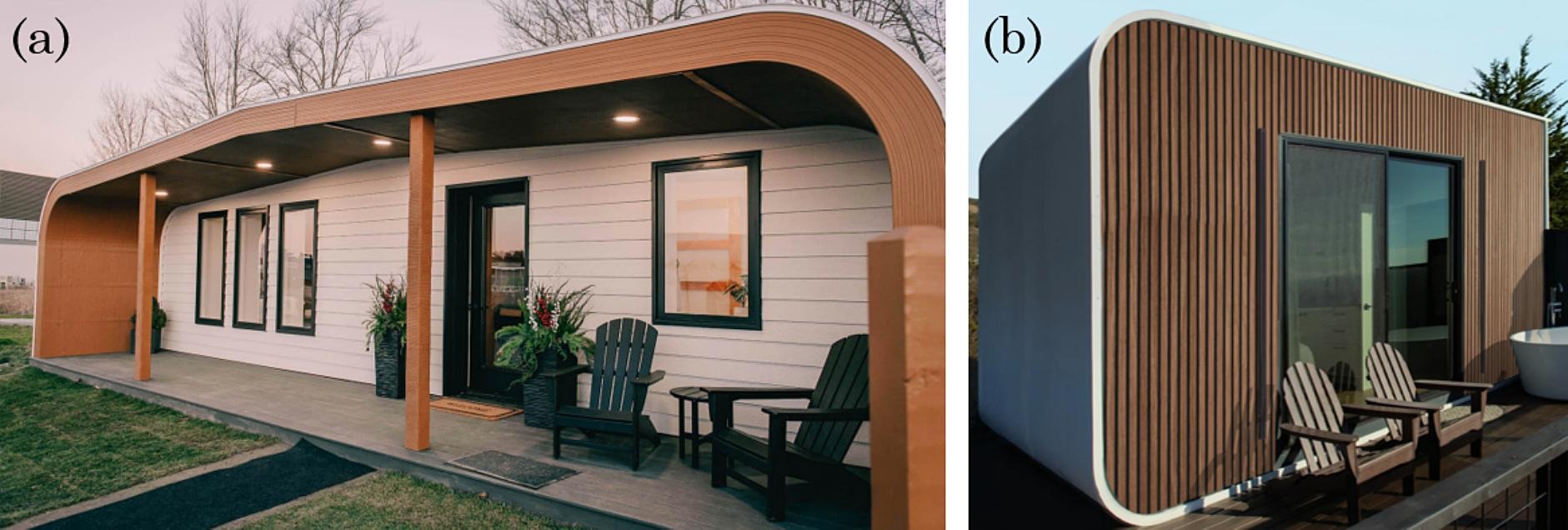


Giant-format additive manufacturing can also be highlighted as a chance to supply sturdy, high-performance parts for infrastructure. Strategies corresponding to robotic large-format additive manufacturing allow the creation of advanced geometries and steady fiber reinforcements, supporting purposes that demand each power and design flexibility.
The evaluate concludes that interdisciplinary collaboration amongst materials scientists, engineers, and regulatory our bodies is important to advance the adoption of 3D printed polymer composites in civil infrastructure. Analysis efforts ought to concentrate on growing sturdy testing protocols, understanding the long-term efficiency of those supplies beneath environmental stressors, and integrating them into sustainable development practices.
Take the 3DPI Reader Survey — form the way forward for AM reporting in beneath 5 minutes.
Prepared to find who received the 2024 3D Printing Business Awards?
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Business publication to remain up to date with the most recent information and insights.
Featured picture exhibits extrusion-based 3D printing setup. Picture through ScienceDirect.


