Git can really feel like a puzzle till you study the important thing strikes. On this information, you’ll discover the highest 20 Git instructions, ordered by how usually they’re used. Every entry begins with a fast “What it does” abstract, adopted by a picture displaying its performance. No partitions of textual content, no unexplained flags, no perusing by means of the documentation. Simply sensible, bite-size entries that you need to use as a cheat sheet. Let’s make Git easy, quick, and enjoyable.
1. git commit
Creates a brand new commit from staged modifications, assigning a snapshot ID and message.
git commit -m []Instance:
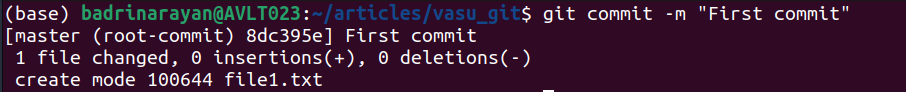
The command data “First commit” and shows its commit hash and abstract.
*You’ll be able to solely commit if you happen to’ve staged first
2. git standing
Experiences untracked, modified, and staged information to point the subsequent steps.
git standing []Instance:
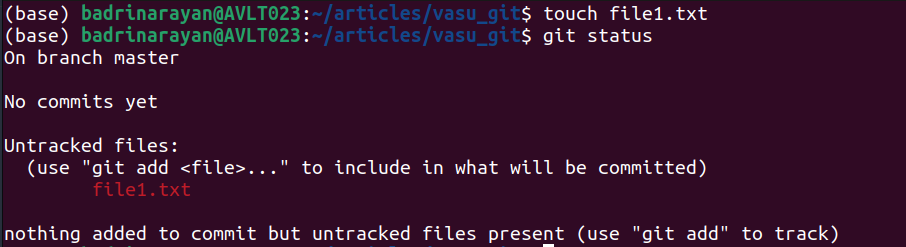
We are able to see that file1.txt is showing crimson, which signifies that git has not began monitoring this file.
3. git add
Levels specified file modifications, shifting them into the index for the subsequent commit.
git add .Instance:
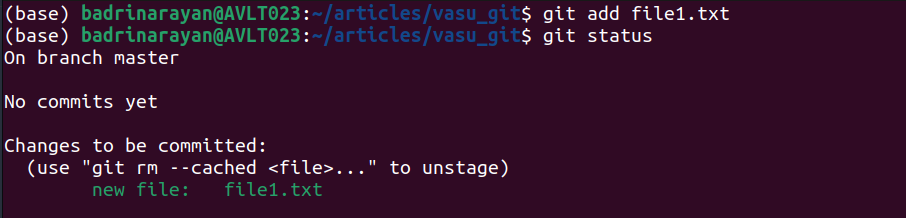
The output (utilizing standing command) confirms that file1.txt has been added to the staging space.
4. git push
Sends your native commits on a department as much as a distant repo.
git pushInstance:
git push origin fundamentalUploads your fundamental department commits to “origin”.
5. git pull
Fetches and merges modifications from a distant department into your present department.
git pull [] []Instance:
git pull origin devWill get origin/dev and merges it into what you’ve checked out.
6. git clone
Creates a neighborhood copy of a distant repository.
git clone []Instance:
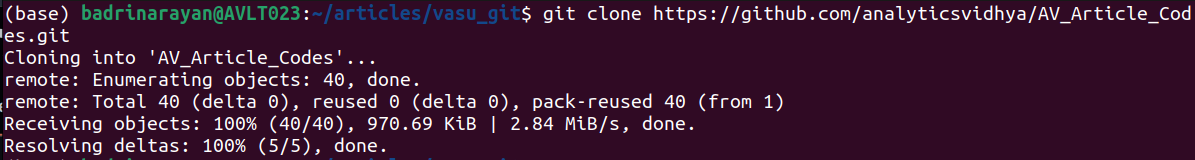
The clone course of fetches objects and deltas, creating an AV_Article_Codes folder.
7. git department
Lists, creates, or deletes branches in your repo.
git department [] []Instance:
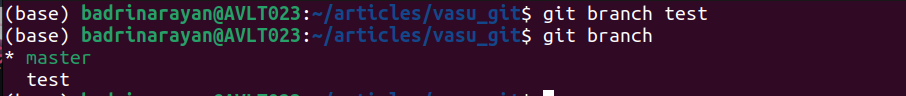
Within the instance, a brand new department check is created alongside grasp.
8. git checkout
Switches to a different department or restores information from a selected commit.
git checkout [--] [] Instance:
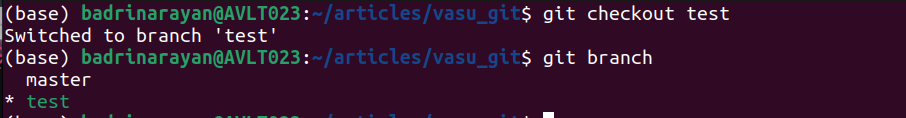
The output signifies a profitable change from grasp to the check department.
9. git merge
Integrates one other department’s commits into your present department.
git merge [--no-ff]Instance:
git merge --no-ff function/apiMerges function/api and at all times creates a merge commit.
10. git log
Shows the mission’s commit historical past in reverse chronological order.
git log []Instance:
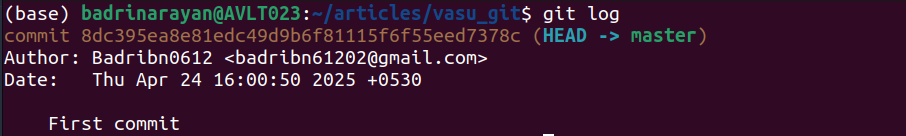
The log lists the commits – “First commit” together with its timestamps and authors.
11. git diff
Exhibits line-by-line variations between commits, branches, or index vs. working tree.
git diff [--staged] […]Instance:
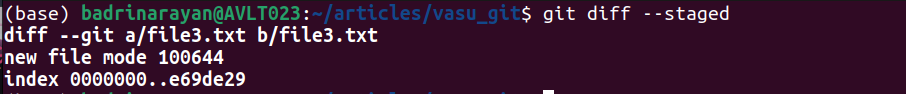
Utilizing --staged shows the diff of a newly added file3.txt prepared for commit.
12. git stash
Quickly saves uncommitted modifications, cleansing the working listing.
git stash [save ]Instance:
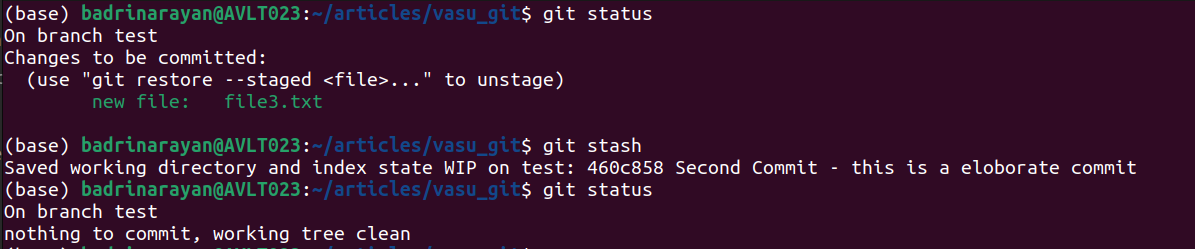
Stashing data the present state on department check and returns a clear working tree.
13. git init
Initializes a brand new Git repository by making a .git listing and displaying branch-naming hints.
git init []Instance:
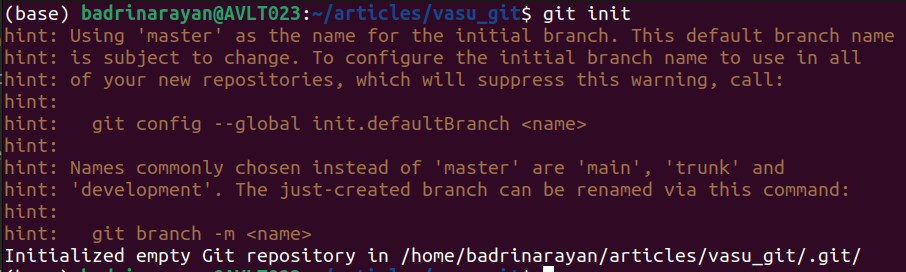
The instance reveals repository initialization with steerage on renaming the default department.
14. git fetch
Downloads commits and refs from a distant with out merging them.
git fetch [] []Instance:
git fetch --allPulls updates from each configured distant.
15. git reset
Strikes your HEAD and optionally updates the index or working tree.
git reset [] []Instance:
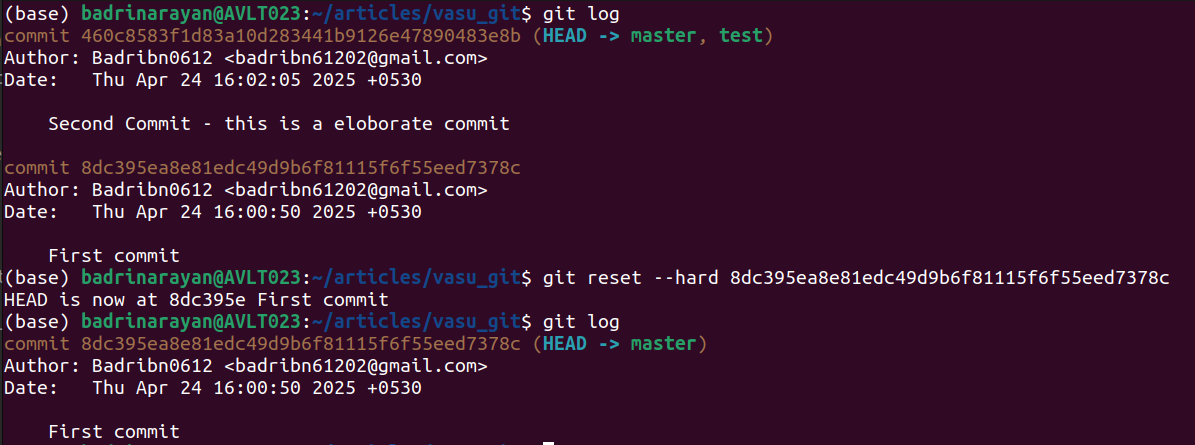
A tough reset to the primary commit discards later modifications and resets HEAD accordingly.
16. git revert
Creates a brand new commit that undoes modifications from a previous commit.
git revertInstance:
git revert a1b2c3dProvides a commit that reverses a1b2c3d with out rewriting historical past.
17. git rebase
Strikes your commits onto a brand new base, preserving historical past linear.
git rebase [-i]Instance:
git rebase -i fundamentalAllows you to reorder, squash, or edit commits interactively.
18. git present
Shows metadata and patch particulars for a given commit or object.
git present []Instance:
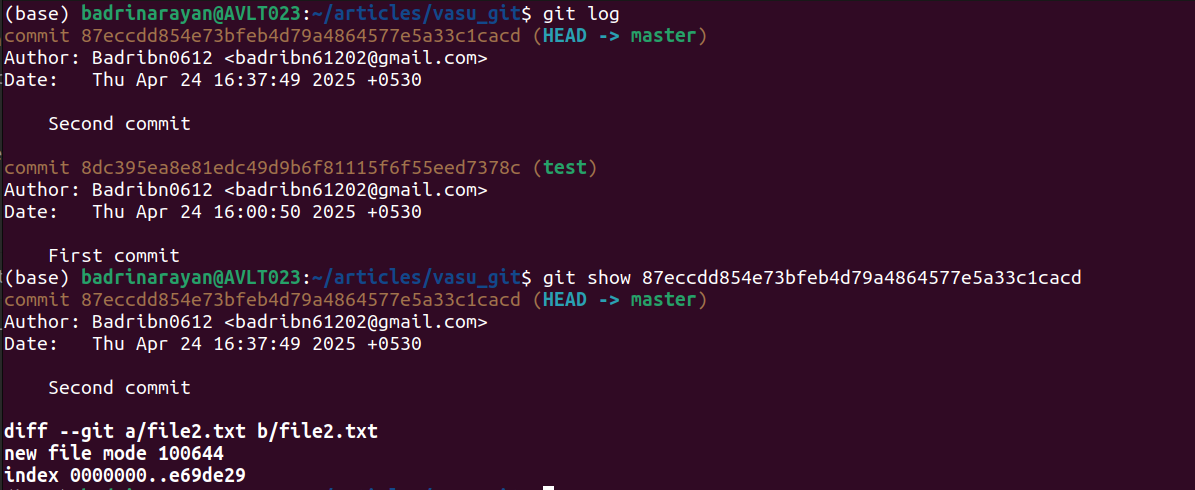
Exhibiting a selected hash prints its creator, date, commit message, and the diff of file2.txt.
19. git cherry-pick
Applies one particular commit from one other department onto your present HEAD.
git cherry-pickInstance:
git cherry-pick f4e5d6cPulls that single become your department
20. git bisect
Automates a binary search to search out which commit launched a bug.
git bisect [good/bad/start]Example:
git bisect begin; git bisect unhealthy; git bisect good v1.0Slim down the unhealthy commit in just a few steps.
Finest Practices
Listed here are among the go-tos on the subject of git instructions:
- Hold commits small: Focus every commit on one change and write clear messages.
- Use branches: Do function work by itself department, then merge by way of pull requests.
- Stash earlier than switching: Keep away from half-done commits by stashing WIP modifications first.
- Rebase domestically: Clear up your department historical past earlier than sharing, however by no means rebase shared branches.
- Evaluate with diff/log: All the time look at git diff and git log earlier than pushing.

Conclusion
You now have the highest 20 Git instructions, every with a fast “what it does,” and a one-line instance. Begin by practising the primary 5 till they’re second nature, then add branching, merging, rebasing, and stashing to your muscle reminiscence. Hold this checklist helpful in Google Docs or your sticky notes. You’ll be able to go to this information if you’re new to Git or GitHub to get a head begin. With these instructions underneath your belt, you’ll spend much less time wrestling with model management and extra time writing code. Go forward, open your terminal and degree up your Git recreation!
Steadily Requested Questions
Use git checkout —
Run git rebase -i
Stash your modifications with git stash and reapply them whenever you’re prepared utilizing git stash pop.
Git fetch downloads updates from the distant with out touching your information, whereas git pull fetches and merges in a single step. The 2 git instructions might sound related of their performance, however their purposes are vastly totally different.
Use git bisect to do a binary search by means of your historical past and pinpoint the precise unhealthy commit.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.


