Retrieval-Augmented Technology, or RAG, has turn into the spine of most critical AI programs in the true world. The reason being easy: massive language fashions are nice at reasoning and writing, however horrible at realizing the target reality. RAG fixes that by giving fashions a stay connection to data.
What follows are interview-ready query that is also used as RAG questions guidelines. Every reply is written to replicate how sturdy RAG engineers truly take into consideration these programs.
Newbie RAG Interview Questions
Q1. What downside does RAG resolve that standalone LLMs can not?
A. LLMs when used alone, reply from patterns in coaching knowledge and the immediate. They’ll’t reliably entry your personal or up to date data and are compelled to guess after they don’t know the solutions. RAG provides an specific data lookup step so solutions might be checked for authenticity utilizing actual paperwork, not reminiscence.
Q2. Stroll by a fundamental RAG pipeline finish to finish.
A. A standard RAG pipelines is as follows:
- Offline (constructing the data base)
Paperwork
→ Clear & normalize
→ Chunk
→ Embed
→ Retailer in vector database - On-line (reply a query)
Person question
→ Embed question
→ Retrieve top-k chunks
→ (Non-compulsory) Re-rank
→ Construct immediate with retrieved context
→ LLM generates reply
→ Closing response (with citations)
Q3. What roles do the retriever and generator play, and the way are they coupled?
A. The retriever and generator work as follows:
- Retriever: fetches candidate context prone to comprise the reply.
- Generator: synthesizes a response utilizing that context plus the query.
- They’re coupled by the immediate: retriever decides what the generator sees. If retrieval is weak, technology can’t prevent. If the technology is weak, good retrieval nonetheless produces a foul last reply.
Q4. How does RAG cut back hallucinations in comparison with pure technology?
A. It offers the mannequin “proof” to cite or summarize. As a substitute of inventing particulars, the mannequin can anchor to retrieved textual content. It doesn’t remove hallucinations, but it surely shifts the default from guessing to citing what’s current.
AI scratch engines like Perplexity are primarily powered by RAG, as they floor/confirm the authenticity of the produced data by offering sources for it.
Q5. What sorts of knowledge sources are generally utilized in RAG programs?
A. Listed below are a number of the generally used knowledge sources in a RAG system:
- Inner paperwork
Wikis, insurance policies, PRDs - Information and manuals
PDFs, product guides, stories - Operational knowledge
Assist tickets, CRM notes, data bases - Engineering content material
Code, READMEs, technical docs - Structured and net knowledge
SQL tables, JSON, APIs, net pages
Q6. What’s a vector embedding, and why is it important for dense retrieval?
A. An embedding is a numeric illustration of textual content the place semantic similarity turns into geometric closeness. Dense retrieval makes use of embeddings to seek out passages that “imply the identical factor” even when they don’t share key phrases.
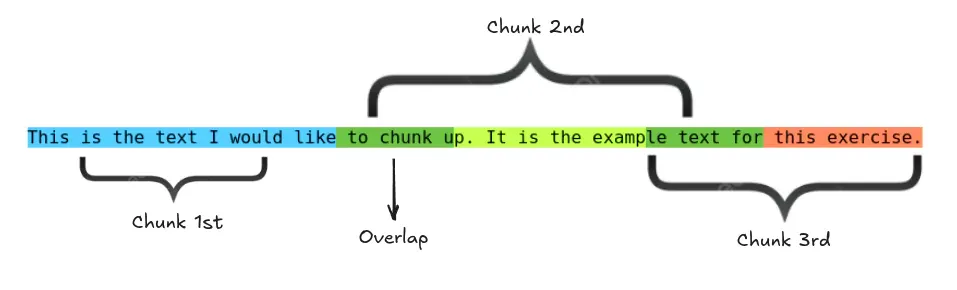
Q7. What’s chunking, and why does chunk measurement matter?
A. Chunking splits paperwork into smaller passages for indexing and retrieval.
- Too massive: retrieval returns bloated context, misses the precise related half, and wastes context window.
- Too small: chunks lose which means, and retrieval could return fragments with out sufficient data to reply.
Q8. What’s the distinction between retrieval and search in RAG contexts?
A. In RAG, search often means key phrase matching like BM25, the place outcomes rely on precise phrases. It’s nice when customers know what to search for. Retrieval is broader. It contains key phrase search, semantic vector search, hybrid strategies, metadata filters, and even multi-step choice.
Search finds paperwork, however retrieval decides which items of knowledge are trusted and handed to the mannequin. In RAG, retrieval is the gatekeeper that controls what the LLM is allowed to cause over.
Q9. What’s a vector database, and what downside does it resolve?
A. A vector DB (brief for vector database) shops embeddings and helps quick nearest-neighbor lookup to retrieve comparable chunks at scale. With out it, similarity search turns into sluggish and painful as knowledge grows, and also you lose indexing and filtering capabilities.
Q10. Why is immediate design nonetheless vital even when retrieval is concerned?
A. As a result of the mannequin nonetheless decides find out how to use the retrieved textual content. The immediate should: set guidelines (use solely supplied sources), outline output format, deal with conflicts, request citations, and stop the mannequin from treating context as non-compulsory.
This supplies a construction during which the response needs to be positioned. It’s vital as a result of regardless that the retrieved data is the crux, the way in which it’s represented issues simply as a lot. Copy-pasting the retrieved data could be plagiarism, and typically a verbatim copy isn’t required. Due to this fact, this data is represented in a immediate template, to guarantee appropriate data illustration.
Q11. What are widespread real-world use instances for RAG in the present day?
A. AI powered serps, codebase assistants, buyer assist copilots, troubleshooting assistants, authorized/coverage lookup, gross sales enablement, report drafting grounded in firm knowledge, and “ask my data base” instruments are a number of the real-world functions of RAG.
Q12. In easy phrases, why is RAG most popular over frequent mannequin retraining?
A. Updating paperwork is cheaper and quicker than retraining a mannequin. Plug in a brand new data supply and also you’re executed. Extremely scalable. RAG enables you to refresh data by updating the index, not the weights. It additionally reduces threat: you possibly can audit sources and roll again unhealthy docs. Retraining requires plenty of effort.
Q13. Examine sparse, dense, and hybrid retrieval strategies.
A.
| Retrieval Sort | What it matches | The place it really works finest |
| Sparse (BM25) | Precise phrases and tokens | Uncommon key phrases, IDs, error codes, half numbers |
| Dense | Which means and semantic similarity | Paraphrased queries, conceptual search |
| Hybrid | Each key phrases and which means | Actual-world corpora with combined language and terminology |
Q14. When would BM25 outperform dense retrieval in a RAG system?
A. BM25 works finest when the person’s question comprises precise tokens that should be matched. Issues like half numbers, file paths, operate names, error codes, or authorized clause IDs don’t have “semantic which means” in the way in which pure language does. They both match or they don’t.
Dense embeddings usually blur or distort these tokens, particularly in technical or authorized corpora with heavy jargon. In these instances, key phrase search is extra dependable as a result of it preserves precise string matching, which is what truly issues for correctness.
Q15. How do you resolve optimum chunk measurement and overlap for a given corpus?
A. Listed below are a number of the tips that could resolve the optimum chunk measurement:
- Begin with: The pure construction of your knowledge. Use medium chunks for insurance policies and manuals so guidelines and exceptions keep collectively, smaller chunks for FAQs, and logical blocks for code.
- Finish with: Retrieval-driven tuning. If solutions miss key situations, improve chunk measurement or overlap. If the mannequin will get distracted by an excessive amount of context, cut back chunk measurement and tighten top-k.
Q16. What retrieval metrics would you employ to measure relevance high quality?
A.
| Metric | What it measures | What it actually tells you | Why it issues for retrieval |
| Recall@okay | Whether or not a minimum of one related doc seems within the prime okay outcomes | Did we handle to retrieve one thing that truly comprises the reply? | If recall is low, the mannequin by no means even sees the appropriate data, so technology will fail irrespective of how good the LLM is |
| Precision@okay | Fraction of the highest okay outcomes which can be related | How a lot of what we retrieved is definitely helpful | Excessive precision means much less noise and fewer distractions for the LLM |
| MRR (Imply Reciprocal Rank) | Inverse rank of the primary related end result | How excessive the primary helpful doc seems | If the very best result’s ranked larger, the mannequin is extra seemingly to make use of it |
| nDCG (Normalized Discounted Cumulative Acquire) | Relevance of all retrieved paperwork weighted by their rank | How good the whole rating is, not simply the primary hit | Rewards placing extremely related paperwork earlier and mildly related ones later |
Q17. How do you consider the ultimate reply high quality of a RAG system?
A. You begin with a labeled analysis set: questions paired with gold solutions and, when doable, gold reference passages. Then you definitely rating the mannequin throughout a number of dimensions, not simply whether or not it sounds proper.
Listed below are the principle analysis metrics:
- Correctness: Does the reply match the bottom reality? This may be a precise match, F1, or LLM primarily based grading in opposition to reference solutions.
- Completeness: Did the reply cowl all required components of the query, or did it give a partial response?
- Faithfulness (groundedness): Is each declare supported by the retrieved paperwork? That is vital in RAG. The mannequin mustn’t invent info that don’t seem within the context.
- Quotation high quality: When the system supplies citations, do they really assist the statements they’re hooked up to? Are the important thing claims backed by the appropriate sources?
- Helpfulness: Even whether it is appropriate, is the reply clear, properly structured, and immediately helpful to a person?
Q18. What’s re-ranking, and the place does it match within the RAG pipeline?
A. Re-ranking is a second-stage mannequin (usually cross-encoder) that takes the question + candidate passages and reorders them by relevance. It sits after preliminary retrieval, earlier than immediate meeting, to enhance precision within the last context.
Learn extra: Complete Information for Re-ranking in RAG
Q19. When is Agentic RAG the fallacious answer?
A. While you want low latency, strict predictability, or the questions are easy and answerable with single-pass retrieval. Additionally when governance is tight and you may’t tolerate a system that may discover broader paperwork or take variable paths, even when entry controls exist.
Q20. How do embeddings affect recall and precision?
A. Embedding quality control the geometry of the similarity area. Good embeddings pull paraphrases and semantically associated content material nearer, which will increase recall as a result of the system is extra prone to retrieve one thing that comprises the reply. On the similar time, they push unrelated passages farther away, bettering precision by protecting noisy or off matter outcomes out of the highest okay.
Q21. How do you deal with multi-turn conversations in RAG programs?
A. You want question rewriting and reminiscence management. Typical strategy: summarize dialog state, rewrite the person’s newest message right into a standalone question, retrieve utilizing that, and solely maintain the minimal related chat historical past within the immediate. Additionally retailer dialog metadata (person, product, timeframe) as filters.
Q22. What are the latency bottlenecks in RAG, and the way can they be lowered?
A. Bottlenecks: embedding the question, vector search, re-ranking, and LLM technology. Fixes: caching embeddings and retrieval outcomes, approximate nearest neighbor indexes, smaller/quicker embedding fashions, restrict candidate rely earlier than re-rank, parallelize retrieval + different calls, compress context, and use streaming technology.
Q23. How do you deal with ambiguous or underspecified person queries?
A. Do one in all two issues:
- Ask a clarifying query when the area of solutions is massive or dangerous.
- Or retrieve broadly, detect ambiguity, and current choices: “If you happen to imply X, right here’s Y; should you imply A, right here’s B,” with citations. In enterprise settings, ambiguity detection plus clarification is often safer.
Clarifying questions are the important thing to dealing with ambiguity.
Q24. When may key phrase search be enough as a substitute of vector search?
A. Use it when the question is literal and the person already is aware of the precise phrases, like a coverage title, ticket ID, operate title, error code, or a quoted phrase. It additionally is sensible once you want predictable, traceable conduct as a substitute of fuzzy semantic matching.
Q25. How do you stop irrelevant context from polluting the immediate?
A. The following advice might be adopted to stop immediate air pollution:
- Use a small top-k so solely probably the most related chunks are retrieved
- Apply metadata filters to slender the search area
- Re-rank outcomes after retrieval to push the very best proof to the highest
- Set a minimal similarity threshold and drop weak matches
- Deduplicate near-identical chunks so the identical thought doesn’t repeat
- Add a context high quality gate that refuses to reply when proof is skinny
- Construction prompts so the mannequin should quote or cite supporting strains, not simply free-generate
Q26. What occurs when retrieved paperwork contradict one another?
A. A well-designed system surfaces the battle as a substitute of averaging it away. It ought to: determine disagreement, prioritize newer or authoritative sources (utilizing metadata), clarify the discrepancy, and both ask for person desire or current each prospects with citations and timestamps.
Q27. How would you model and replace a data base safely?
A. Deal with the RAG stack like software program. Model your paperwork, put exams on the ingestion pipeline, use staged rollouts from dev to canary to prod, tag embeddings and indexes with variations, maintain chunk IDs backward suitable, and assist rollbacks. Log precisely which variations powered every reply so each response is auditable.
Q28. What indicators would point out retrieval failure vs technology failure?
A. Retrieval failure: top-k passages are off-topic, low similarity scores, lacking key entities, or no passage comprises the reply regardless that the KB ought to.
Technology failure: retrieved passages comprise the reply however the mannequin ignores it, misinterprets it, or provides unsupported claims. You detect this by checking reply faithfulness in opposition to retrieved textual content.
Superior RAG Interview Questions
Q29. Examine RAG vs fine-tuning throughout accuracy, value, and maintainability.
A.
| Dimension | RAG | Advantageous-tuning |
| What it modifications | Provides exterior data at question time | Adjustments the mannequin’s inside weights |
| Greatest for | Contemporary, personal, or often altering data | Tone, format, fashion, and area conduct |
| Updating data | Quick and low cost: re-index paperwork | Sluggish and costly: retrain the mannequin |
| Accuracy on info | Excessive if retrieval is sweet | Restricted to what was in coaching knowledge |
| Auditability | Can present sources and citations | Data is hidden inside weights |
Q30. What are widespread failure modes of RAG programs in manufacturing?
A. Stale indexes, unhealthy chunking, lacking metadata filters, embedding drift after mannequin updates, overly massive top-k inflicting immediate air pollution, re-ranker latency spikes, immediate injection through paperwork, and “quotation laundering” the place citations exist however don’t assist claims.
Q31. How do you steadiness recall vs precision at scale?
A. Begin high-recall in stage 1 (broad retrieval), then improve precision with stage 2 re-ranking and stricter context choice. Use thresholds and adaptive top-k (smaller when assured). Section indexes by area and use metadata filters to cut back search area.
Q32. Describe a multi-stage retrieval technique and its advantages.
A. Following is a multi-stage retrieval technique:
1st Stage: low cost broad retrieval (BM25 + vector) to get candidates.
2nd Stage: re-rank with a cross-encoder.
third Stage: choose numerous passages (MMR) and compress/summarize context.|
Advantages of this course of technique are higher relevance, much less immediate bloat, larger reply faithfulness, and decrease hallucination price.
Q33. How do you design RAG programs for real-time or often altering knowledge?
A. Use connectors and incremental indexing (solely modified docs), brief TTL caches, event-driven updates, and metadata timestamps. For actually real-time info, choose tool-based retrieval (querying a stay DB/API) over embedding the whole lot.
Q34. What privateness or safety dangers exist in enterprise RAG programs?
A. Delicate knowledge leakage through retrieval (fallacious person will get fallacious docs), immediate injection from untrusted content material, knowledge exfiltration by mannequin outputs, logging of personal prompts/context, and embedding inversion dangers. Mitigate with entry management filtering at retrieval time, content material sanitization, sandboxing, redaction, and strict logging insurance policies.
Q35. How do you deal with lengthy paperwork that exceed mannequin context limits?
A. Don’t shove the entire thing in. Use hierarchical retrieval (part → passage), doc outlining, chunk-level retrieval with good overlap, “map-reduce” summarization, and context compression (extract solely related spans). Additionally retailer structural metadata (headers, part IDs) to retrieve coherent slices.
Q36. How do you monitor and debug RAG programs post-deployment?
A. Log: question, rewritten question, retrieved chunk IDs + scores, last immediate measurement, citations, latency by stage, and person suggestions. Construct dashboards for retrieval high quality proxies (similarity distributions, click on/quotation utilization), and run periodic evals on a set benchmark set plus real-query samples.
Q37. What strategies enhance grounding and quotation reliability in RAG?
A. Span highlighting (extract precise supporting sentences), forced-citation codecs (every declare should cite), reply verification (LLM checks if every sentence is supported), contradiction detection, and citation-to-text alignment checks. Additionally: choose chunk IDs and offsets over “document-level” citations.
Q38. How does multilingual knowledge change retrieval and embedding technique?
A. You want multilingual embeddings or per-language indexes. Question language detection issues. Typically translate queries into the corpus language (or translate retrieved passages into the person’s language) however watch out: translation can change which means and weaken citations. Metadata like language tags turns into important.
Q39. How does Agentic RAG differ architecturally from classical single-pass RAG?
A.
| Facet | Classical RAG | Agentic RAG |
|---|---|---|
| Management move | Fastened pipeline: retrieve then generate | Iterative loop that plans, retrieves, and revises |
| Retrievals | One and executed | A number of, as wanted |
| Question dealing with | Makes use of the unique question | Rewrites and breaks down queries dynamically |
| Mannequin’s position | Reply author | Planner, researcher, and reply author |
| Reliability | Relies upon fully on first retrieval | Improves by filling gaps with extra proof |
Q40. What new trade-offs does Agentic RAG introduce in value, latency, and management?
A. Extra instrument calls and iterations improve value and latency. Conduct turns into much less predictable. You want guardrails: max steps, instrument budgets, stricter stopping standards, and higher monitoring. In return, it could actually resolve more durable queries that want decomposition or a number of sources.
Conclusion
RAG isn’t just a trick to bolt paperwork onto a language mannequin. It’s a full system with retrieval high quality, knowledge hygiene, analysis, safety, and latency trade-offs. Robust RAG engineers don’t simply ask if the mannequin is wise. They ask if the appropriate data reached it on the proper time.
If you happen to perceive these 40 questions and solutions, you aren’t simply prepared for a RAG interview. You might be able to design programs that truly work in the true world.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.


